Packet forwarding method and device
A message forwarding and message technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as the inability to realize the combination of segment routing network and MTR function
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
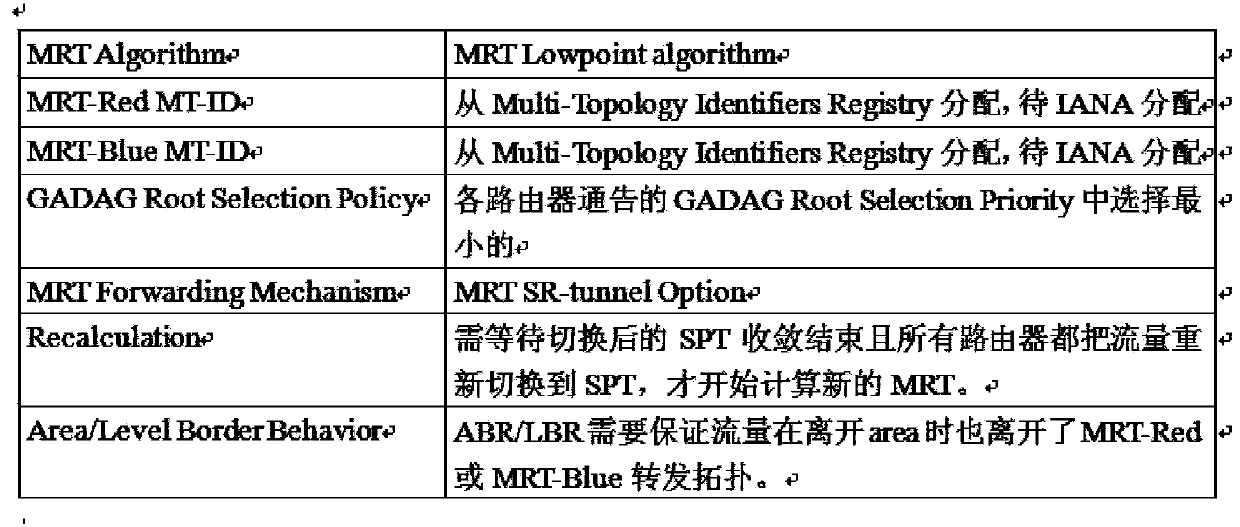
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
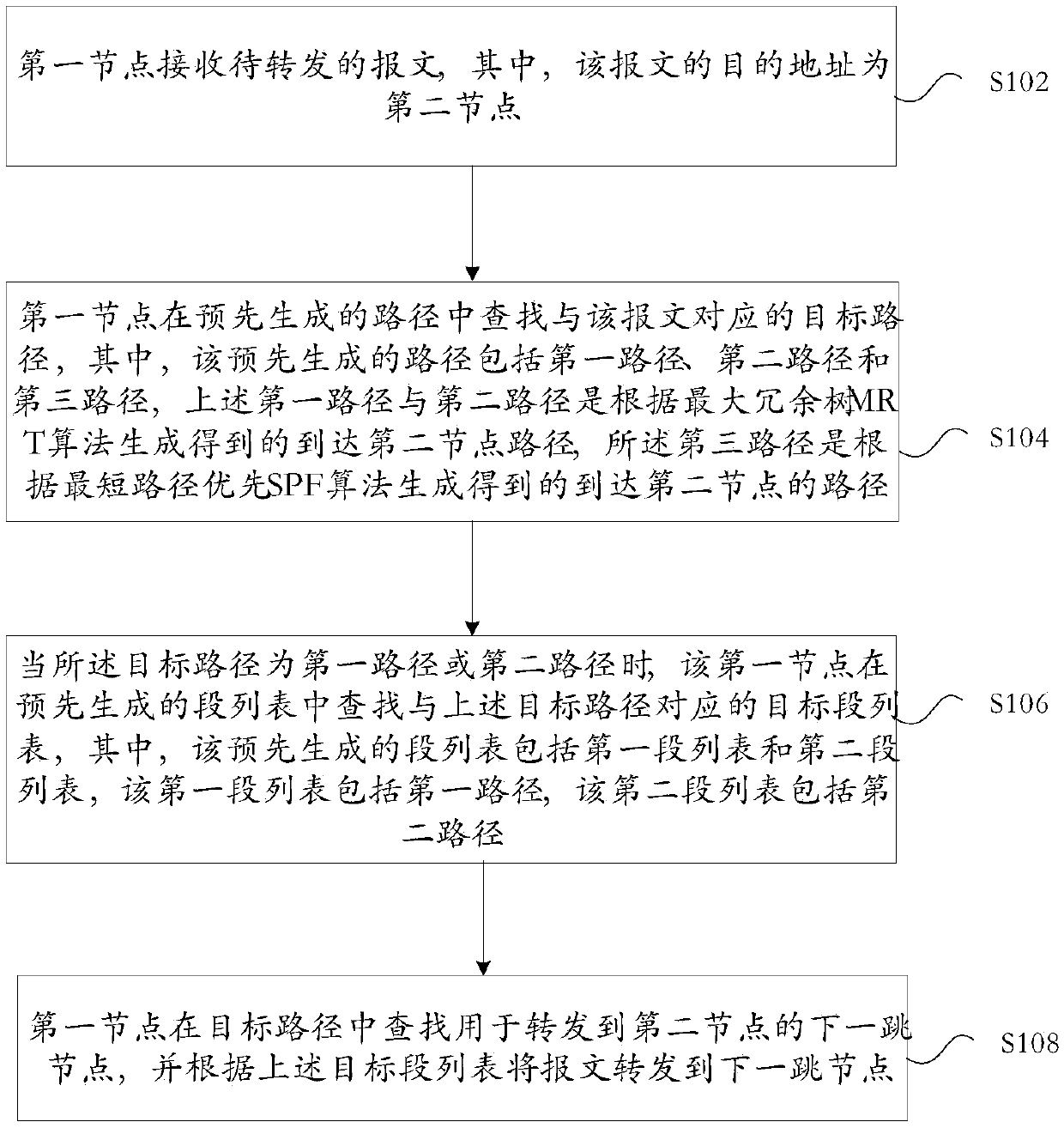
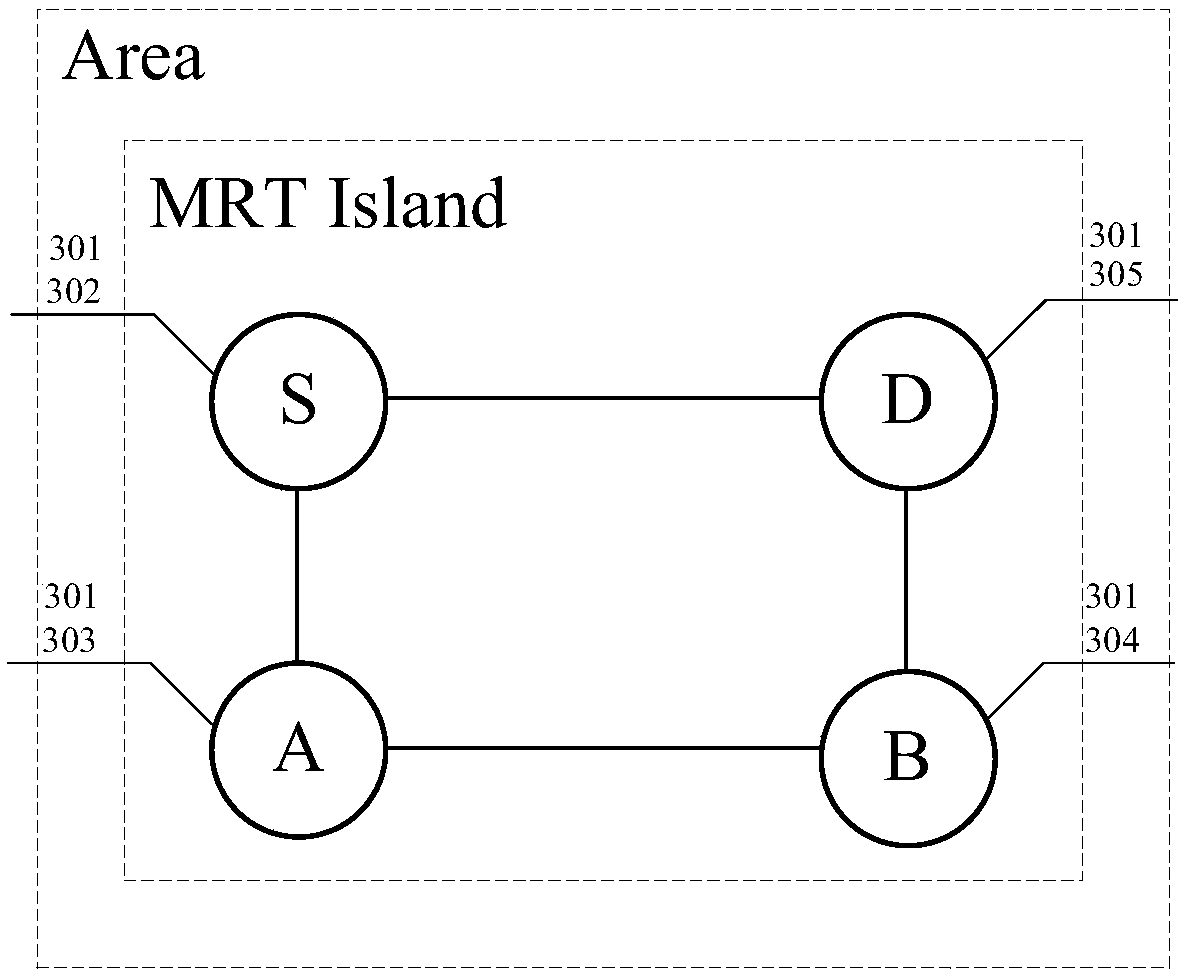
[0069] This embodiment will describe the forwarding process of the MRT path whose destination prefix is within the MRT Island. image 3 is a network topology diagram according to the first embodiment of the present invention, such as image 3 As shown, Openshortest Path First (OSPF for short) is running in the network, all nodes are in the same area, and the segment routing function and the MRT defined in this patent are enabled under the corresponding OSPF instance Profile. S acts as the source node to establish an MRT path to the prefix of the destination node D (such as a loopback route of D), and then protects the SPF main path based on this MRT path. Including the following steps:
[0070] In step S301, the OSPF instance on each node S, A, B, and D enables SR and the MRT Profile defined in the embodiment of the present invention, and then they form an MRT Island in the area.
[0071] Each node will obtain the MT-default topology in the area based on the SPF algorithm...
specific Embodiment 2
[0095] This embodiment will describe the forwarding process of the MRT path whose destination prefix is outside the MRT Island. Figure 4 is the network topology diagram according to the second embodiment of the present invention, such as Figure 4 As shown, OSPF is running in the network, including two areas, and all nodes enable the segment routing function under the corresponding OSPF instance, wherein S, A, B, and C in area1 enable the defined in the embodiment of the present invention MRT Profile. S acts as the source node to establish an MRT path to the prefix of the destination node D (such as a loopback route of D), and then protects the SPF main path based on this MRT path. Including the following steps:
[0096] In step S401, SR is enabled under the OSPF instances of all nodes in area1 and area2. Each node allocates SRGB.
[0097] In step S402, MRTProfile defined in this patent is enabled under the OSPF instance on nodes S, A, B, and C in area1, and they form a...
specific Embodiment 3
[0117] This embodiment will describe the forwarding process of the MRT path whose destination prefix is outside the MRT Island, especially how to implement the rainbow cross-domain forwarding rule defined by RFC7812 based on SR-tunnel. Figure 5 is the network topology diagram according to the third embodiment of the present invention, such as Figure 5 As shown, OSPF is running in the network, including two areas, and all nodes enable the segment routing function under the corresponding OSPF instance, wherein S, A, B, and C in area1 enable the defined in the embodiment of the present invention MRT Profile, B, E, D, and F in area2 also enable the MRT Profile defined in this patent. S acts as the source node to establish an MRT path to the prefix of the destination node D (such as a loopback route of D), and then protects the SPF main path based on this MRT path. Including the following steps:
[0118] In step S501, SR is enabled under the OSPF instances of all nodes in are...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com