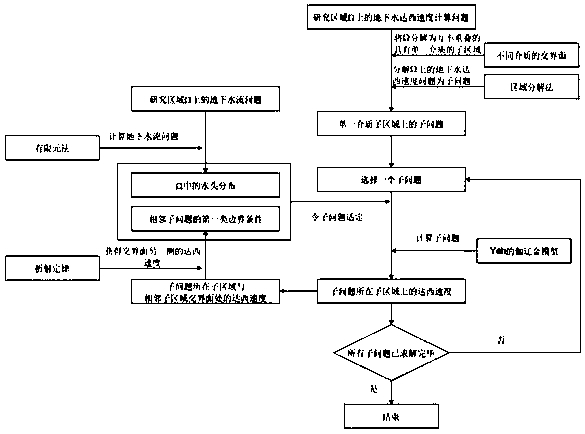
Domain decomposition finite element method for simulating Darcy velocity at interface of groundwater medium
A technology of domain decomposition and finite element method, applied in the field of hydraulics, it can solve the problems of insufficient Darcy speed and low efficiency, and achieve the effect of reducing calculation time and improving calculation efficiency.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
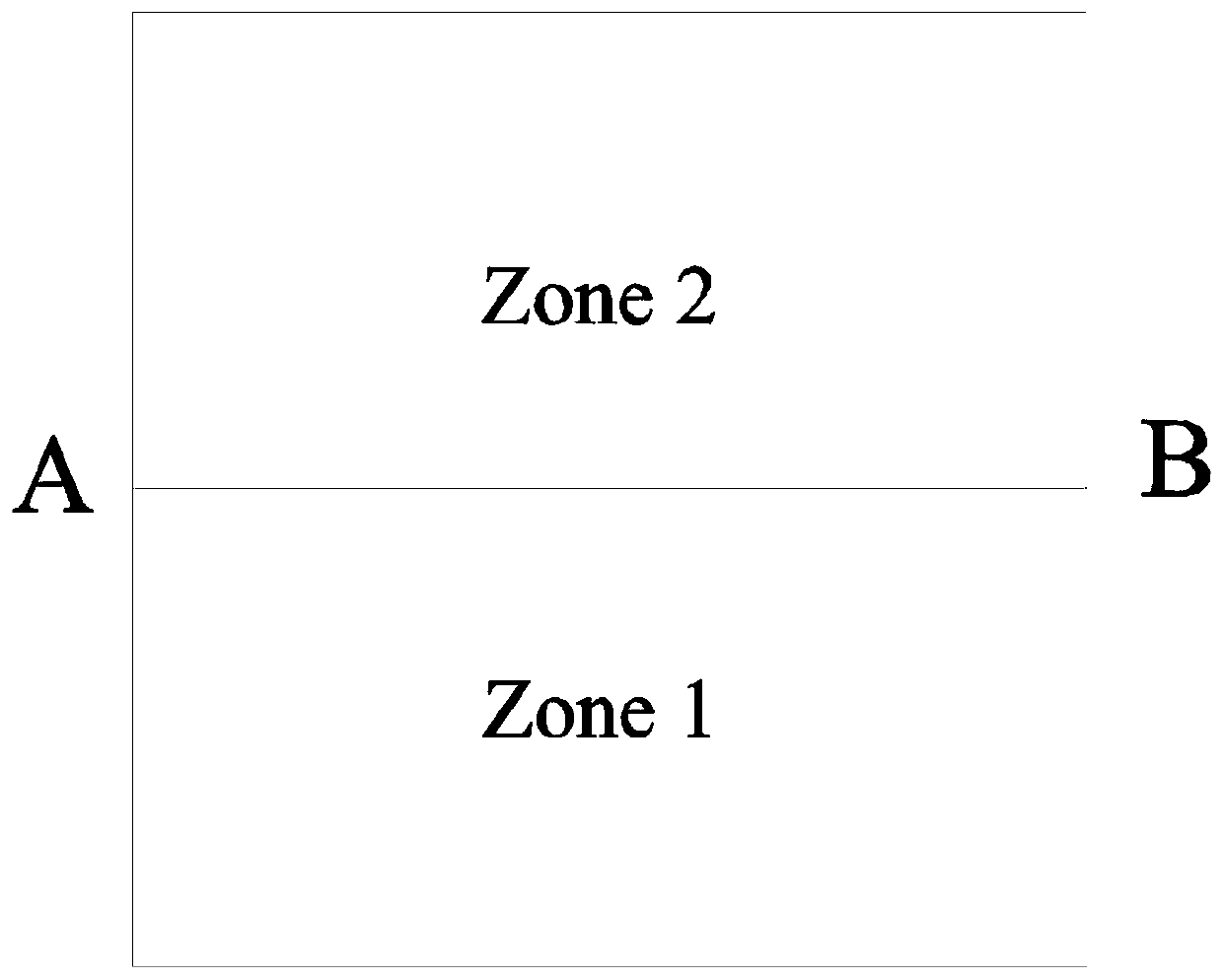
[0102] Example 1: 2D Steady Flow Model with Interfaces Parallel to Coordinate Axes
[0103] Research area such as figure 2 As shown, the equations of groundwater flow and Darcy velocity are (6) and (7) respectively. The research area Ω=[0,1]×[0,1]. The study area contains two different media, which can be divided into two sub-areas by the interface AB (y=0.5). The permeability coefficients of the two sub-areas are: zone 1:K 1x =(1+x)(1+y), K 1y = 10(1+x)(1+y), zone 2:K 2x =10(1+x)(1+y),K 2y =100(1+x)(1+y). This example has an analytical solution:
[0104] Head:
[0105] V x:
[0106] In this example, the source-sink term W and the first type of boundary conditions are given based on the analytical solution of the water head.
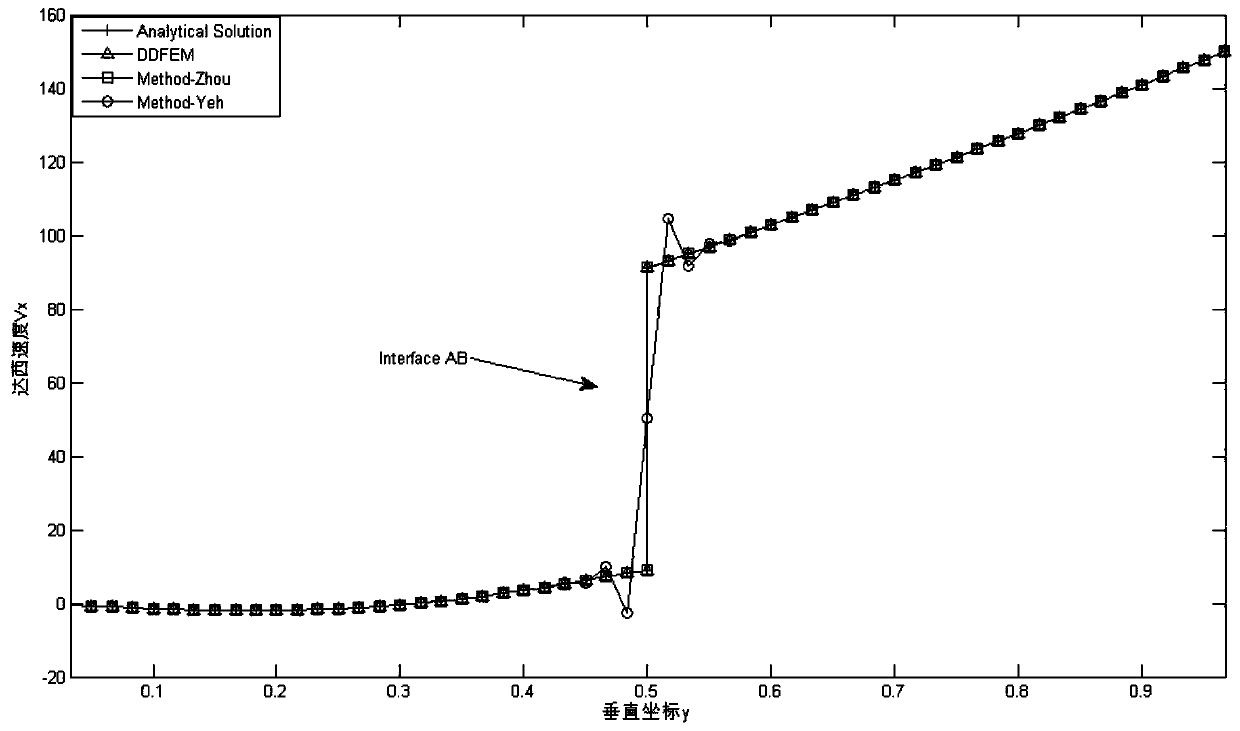
[0107] The study area is divided into 7200 units by a triangular grid, the water head is solved by FEM, and the velocity is solved by DDFEM, Method-Zhou and Method-Yeh.
[0108] The Darcy velocity V of each method at the section x=0.5 of ...
Embodiment 2
[0111] Example 2: 2D Steady Flow Model with Interfaces Not Parallel to Coordinate Axes
[0112] Research areas such as Figure 5 As shown, the equations of groundwater flow and Darcy velocity are (6) and (7) respectively. The research area Ω=[0,120m]×[0,120m] is divided into three sub-areas by the medium interface AB (y=20m) and CD (x+y=160m), and the source-sink term W is 0. The left and right boundaries of the study area are constant water head boundaries, 0m and 1m, respectively, and the upper and lower boundaries are water-isolated boundaries. The study area in this example is an isotropic medium, that is, the permeability coefficients in the x and y directions are equal. The permeability coefficients of the three sub-regions zone 1-zone3 are: 100m / d, 10m / d, 100m / d. Since there is no analytical solution for this example, the solution of Method-Zhou-F will be used as a standard control.
[0113] Method-Zhou-F divided the study area into 18432 triangular units, and appli...
Embodiment 3
[0116] Example 3: 2D Steady Flow Model with Intersecting Interfaces
[0117] Research area such as Figure 11 As shown, the equations of groundwater flow and Darcy velocity are (6) and (7) respectively. Research area Ω=[0,1]×[0,1]. The interface AB (y=0.5) and CD (x=0.5) intersect at point o, which divides the study area into 4 sub-areas, and the permeability coefficients of zone1-zone 4 are 1, 10, 10, and 100, respectively. This example has analytical solutions, where the analytical solutions of zone 1 and zone 3 are the analytical solutions of zone 1 and zone 2 in embodiment 1, respectively. And the analytical solution head of zone 2 and zone 4 is:
[0118]
[0119]
[0120] In this example, the source-sink term, Darcy velocity, and the expressions of the first-type boundary conditions can all be given based on the hydraulic coefficient and the analytical solution head.
[0121] In this example, DDFEM, DDFEM-AS, Method-Yeh, and Method-Yeh-AS are used to solve the p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com