Molecular markers closely linked with multiple-effect major quantitative trait loci (QTL) of grain weight or silique length of rape, and application thereof
A molecular marker, pleiotropic technology, applied in the direction of recombinant DNA technology, DNA/RNA fragment, microbial determination/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of difficult rapeseed breeding application, poor repeatability, long linkage marker distance, etc. The detection method is convenient and fast, the selection efficiency is improved, and the effect of accurate and rapid screening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
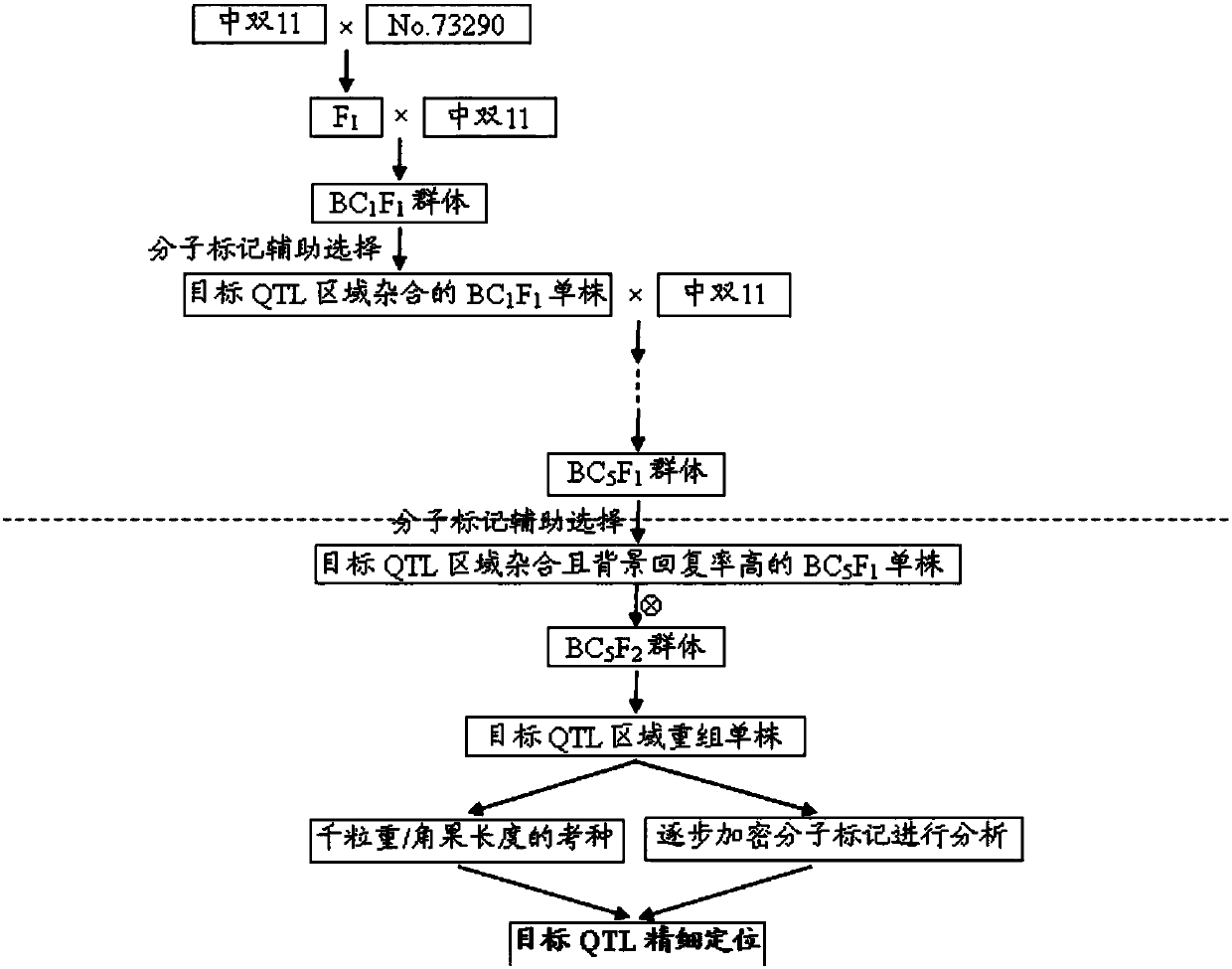
[0028] Construction of target main effect QTL-NIL
[0029] According to the strategy of fine positioning ( figure 1 ), NIL was constructed for the target main effect QTL site. In this experiment, the parents Zhongshuang 11 and No.73290 were used to cross hybrid F1, and then Zhongshuang 11 was used as the recurrent parent, and the BC5F1 generation QTL-NIL was obtained by continuous backcrossing for 5 generations, and the heterozygous individual plants were selected for further backcrossing . Finally, 80 molecular markers (Yang et al., 2016) other than the target main effect QTL were used for genetic background screening, and the BC5F1 single plants that were heterozygous for the target fragment and had a high background recovery rate were self-crossed to obtain the BC5F2 generation QTL-NIL segregation population. The population was planted in the field as experimental material for fine positioning.
Embodiment 2
[0031] Development of Molecular Markers:
[0032] First, use self-designed primers to compare with the genome sequence of Chinese cabbage or Brassica napus to determine the genomic region corresponding to the target QTL. This genomic region was searched for SSRs using MISA software. Use BWA software to locate the resequencing sequence of 73290 to the reference genome sequence of Zhongshuang11, and use samtools software to find the InDel site of the target QTL interval. Then, use Primer3.0 software to design SSR / InDel primers.
[0033] The genomic DNA of Shuang11, No.73290 and QTL-NIL leaves in the parents was extracted by the magnetic bead method, and the parental DNA was amplified by PCR using self-developed SSR / InDel primers, and the products were electrophoresed in a denaturing polyacrylamide gel , after staining and developing, the size of the bands was discriminated, and polymorphic primers were screened.
[0034] PCR reaction system:
[0035]
[0036] PCR reaction...
Embodiment 3
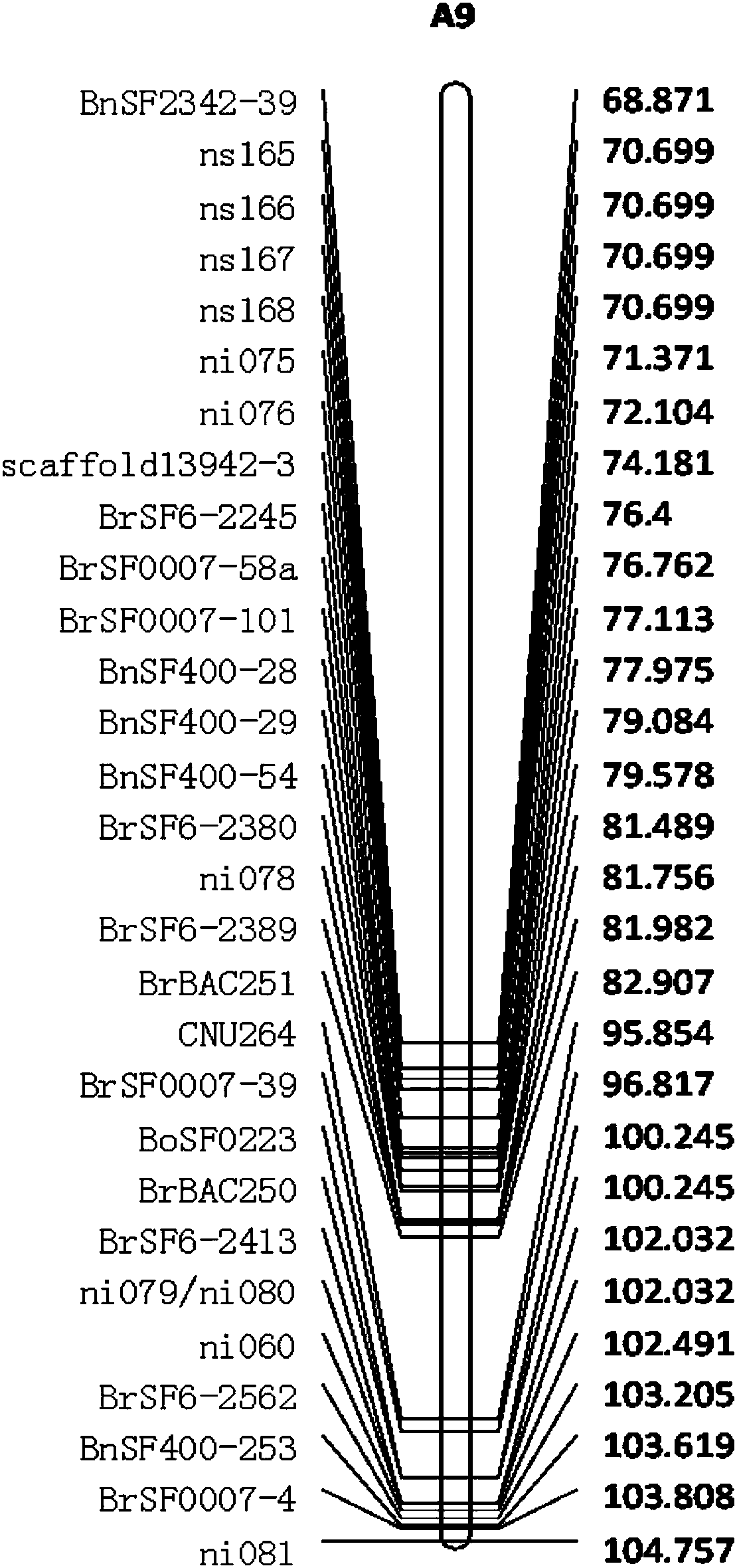
[0041] Genetic Mapping of Newly Developed Molecular Markers
[0042] Using newly developed markers to screen parental polymorphisms, the present invention has developed five specific co-dominant molecular markers (Ni76, BrSF7-101, BrSF6-2389, BrSF6-2562). To further verify whether these 5 newly developed molecular markers are located in the target major QTL interval, we re-mapped them genetically using the BnaZNF2 population (Shi et al., 2015).
[0043] The genotype is read according to the following principles (such as figure 2 shown), the band type of Shuang11 in the parent is marked as 0 (or A in other embodiments of the present invention), the band type of parent 73290 is marked as 1 (or B in other embodiments of the present invention), and the group The same band type as Zhongshuang 11 is marked as 0 (or A in other embodiments of the present invention), the same band type as 73290 in the population is marked as 1 (or B in other embodiments of the present invention), het...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com