Method and material for preparing polylactic acid-natural rubber porous material by micropore injection molding foaming
A natural rubber, injection foaming technology, applied in the direction of coating, etc., can solve the problems of poor toughness of polylactic acid, and achieve the effect of increasing compatibility, cell size and distribution, and good toughness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
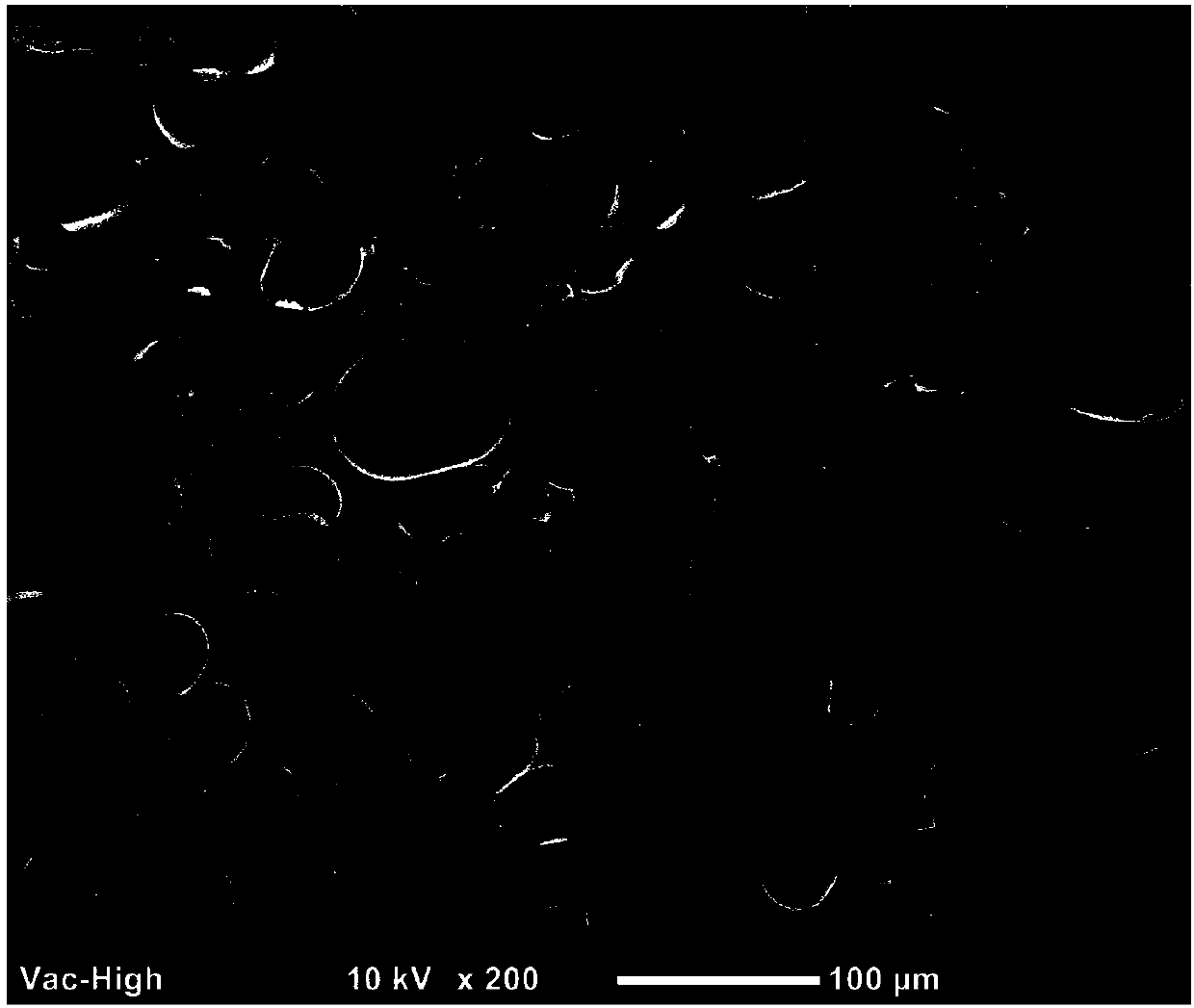
Image
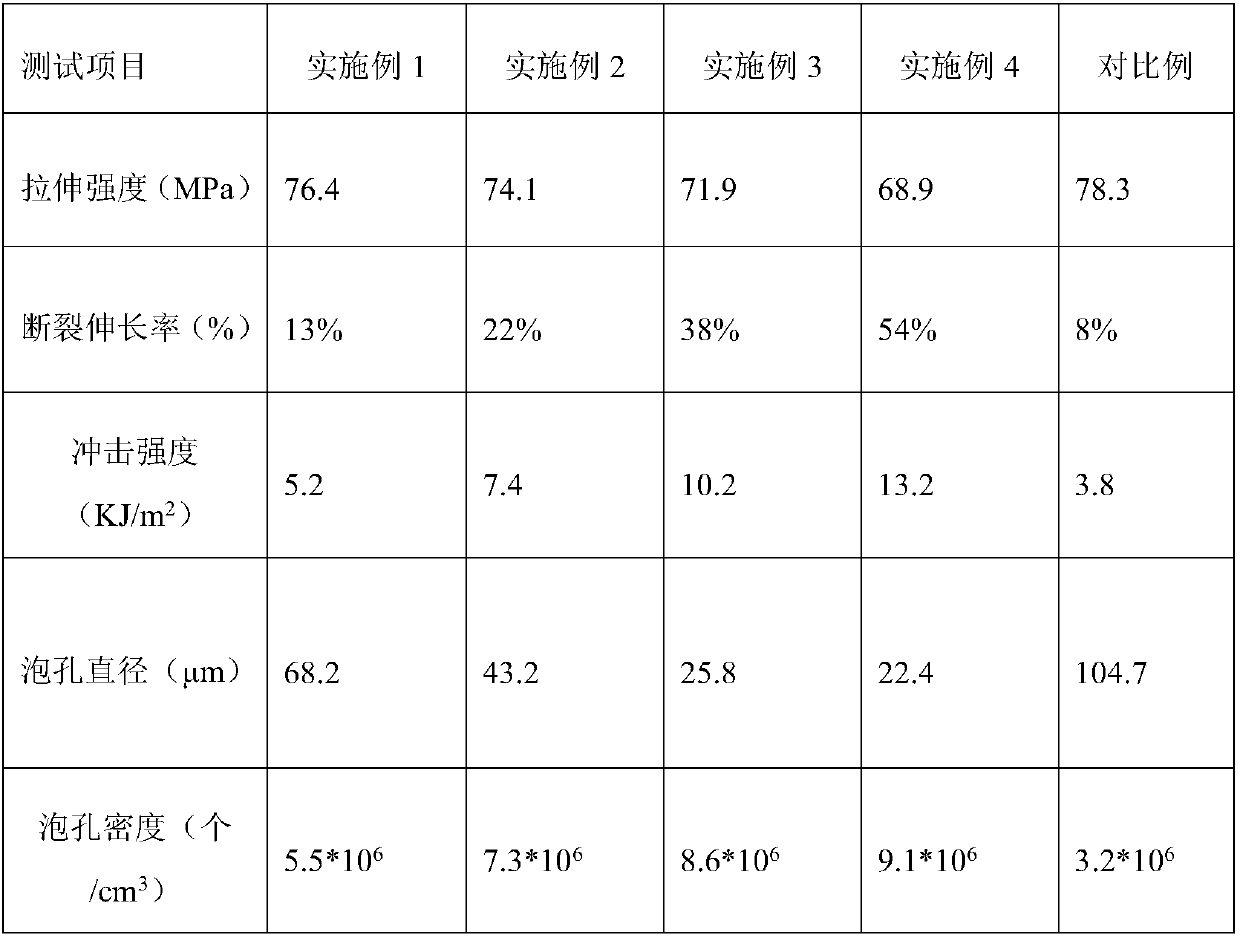
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0015] The dry polylactic acid pellets were mixed with the glycidyl methacrylate-natural rubber graft at a weight ratio of 95 / 5, and extruded and granulated by a twin-screw extruder. The extrusion temperature is 190° C., and the screw speed is 100 revolutions / min.
[0016] The blend pellets were subjected to microcellular injection foaming with supercritical CO 2 The fluid is a blowing agent. Injection temperature 200°C, mold temperature 50°C, injection speed 30cm 3 / s, supercritical CO 2 The fluid accounts for 1% of the mass of the polymer, and the polylactic acid / natural rubber porous material is obtained by injection molding.
Embodiment 2
[0018] The dry polylactic acid pellets and the glycidyl methacrylate-natural rubber graft were mixed in a weight ratio of 90 / 10, and extruded and granulated by a twin-screw extruder. The extrusion temperature is 180° C., and the screw speed is 90 revolutions / min.
[0019] The blend pellets were subjected to microcellular injection foaming with supercritical CO 2 The fluid is a blowing agent. Injection temperature 190°C, mold temperature 40°C, injection speed 30cm 3 / s, supercritical CO 2 The fluid accounts for 1% of the mass of the polymer, and the polylactic acid / natural rubber porous material is obtained by injection molding.
Embodiment 3
[0021] The dry polylactic acid pellets and the glycidyl methacrylate-natural rubber graft were mixed in a weight ratio of 85 / 15, and extruded and granulated by a twin-screw extruder. The extrusion temperature was 170° C., and the screw speed was 80 revolutions / min.
[0022] The blend pellets were subjected to microcellular injection foaming with supercritical CO 2 The fluid is a blowing agent. Injection temperature 180°C, mold temperature 20°C, injection speed 40cm 3 / s, supercritical CO 2 The fluid accounts for 0.5% of the mass of the polymer, and the polylactic acid / natural rubber porous material is obtained by injection molding.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com