Mixed feature-based fine imaginary action online brain-computer interface method
A hybrid feature, machine interface technology, used in electrotherapy, computer parts, mechanical mode conversion, etc., can solve the problems of expensive surgery, not widely used, high infection risk, etc., to improve the recognition accuracy, improve The classification accuracy rate and the effect of preventing muscle atrophy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
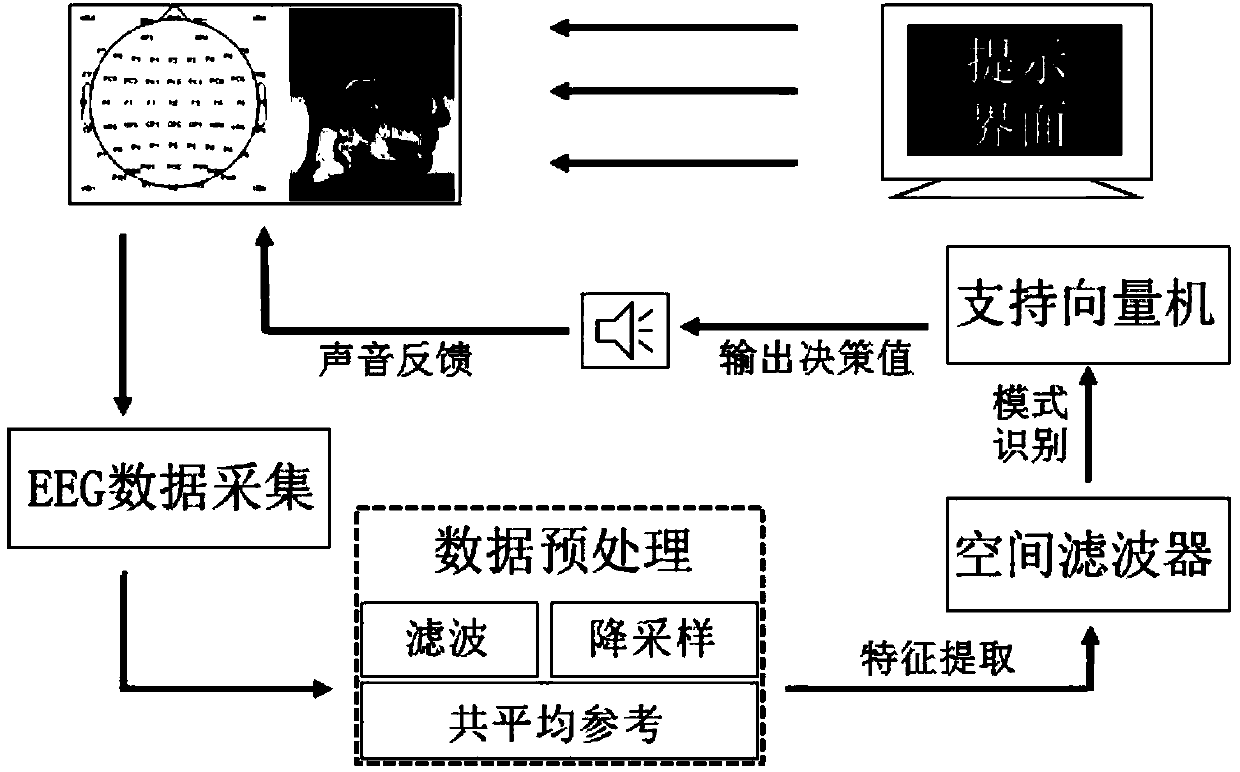
[0038] An Online Brain-Computer Interface Method for Fine Imaging Actions Based on Hybrid Features, see figure 1 , the method includes the following steps:
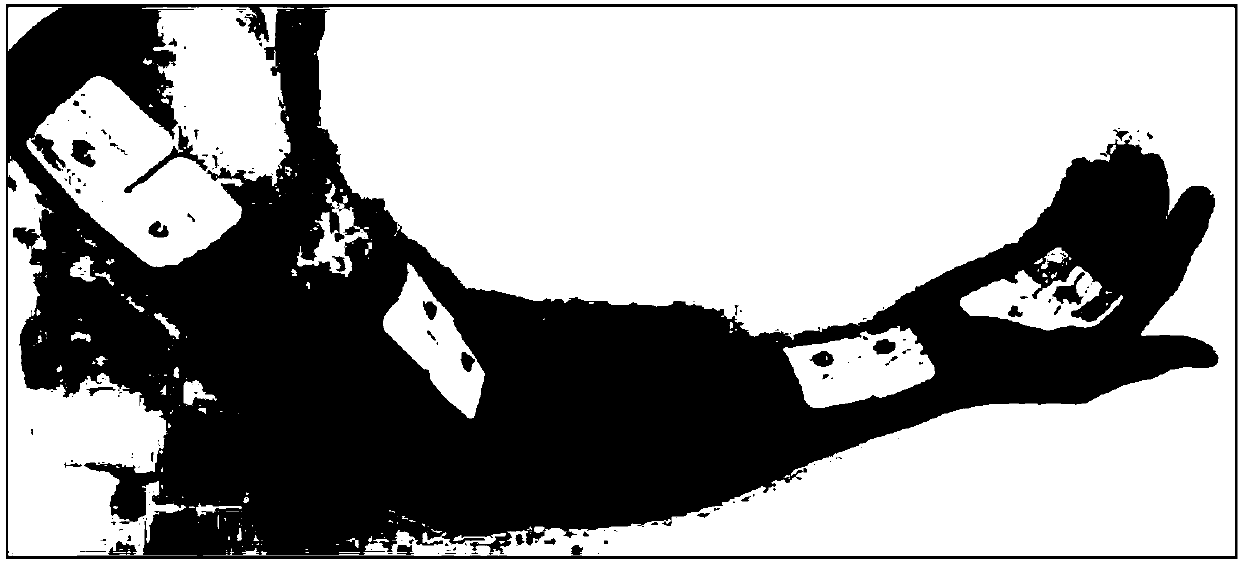
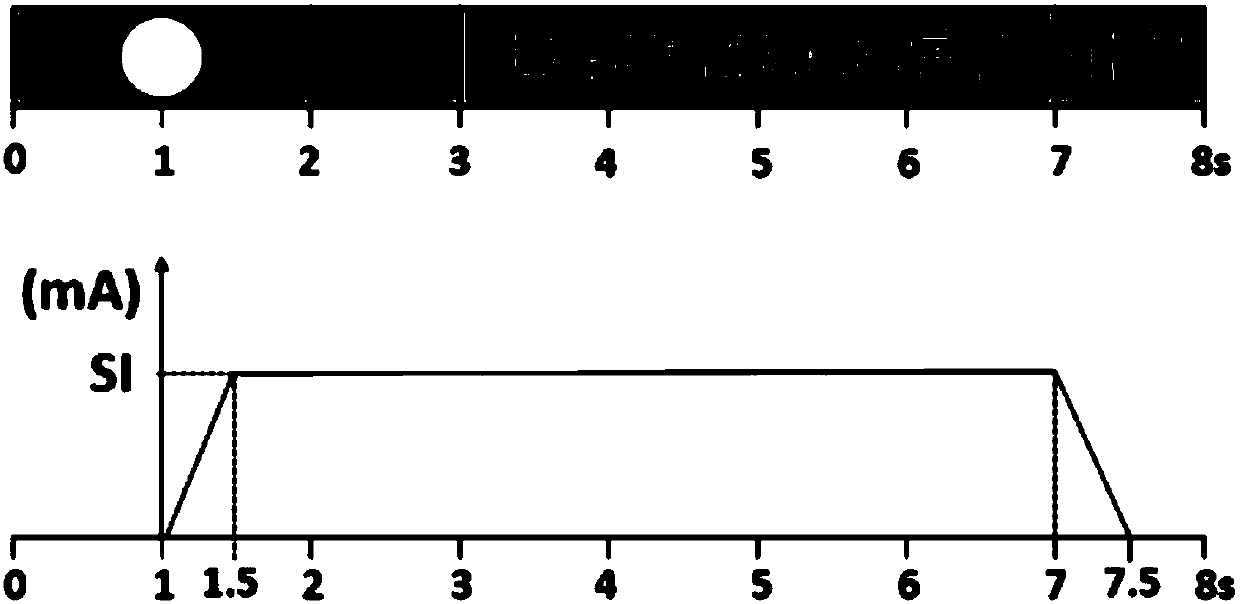
[0039] 101: Four types of actions are designed for different joints of the right upper limb, including: fisting, wrist raising, elbow flexion and shoulder abduction; by placing four types of movements on the palm flexor, wrist median nerve, arm biceps brachii and arm deltoid The electrodes at the same position give electrical stimulation at the beginning of the prompt, and the subjects choose to pay attention to the location of the electrical stimulation while imagining the corresponding action;
[0040] 102: Effectively integrate the event-related desynchronization features of different frequency distributions and the steady-state somatosensory evoked potential features induced by electrical stimulation to form a hybrid paradigm;
[0041] 103: Use an algorithm based on multi-frequency component spatial filtering to extr...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Combined with the specific calculation formula, Figure 1-Figure 3 , the example further introduces the scheme in embodiment 1, see the following description for details:
[0048] 201: The design of different joints of the right upper limb includes four types of movements including fist clenching, wrist raising, elbow flexion and shoulder abduction, by placing four muscles in the palm flexor, wrist median nerve, biceps brachii and deltoid muscles of the arm The electrodes at the same position give electrical stimulation at the beginning of the prompt, and the subjects choose to pay attention to the location of the electrical stimulation while imagining the corresponding action;
[0049] Each person conducts 8 sets of experiments each time, each set of experiments includes 40 single tasks, four types of actions appear randomly, and each 10 single tasks / group. Before formally collecting EEG signals, each subject was required to perform imaginative movement training 3 day...
Embodiment 3
[0066] The embodiment of the present invention further introduces the process of applying stimulation and collecting EEG signals in Embodiment 1-2 in conjunction with the accompanying drawings, see the following description for details:
[0067] The embodiment of the present invention designs four types of actions for different joints of the right upper limb, including: making a fist, raising the wrist, bending the elbow and shoulder abduction. Then, the electrodes placed on the four positions of palmar flexor, wrist median nerve, arm biceps brachii and arm deltoid were simultaneously given electrical stimulation at the beginning of the cue, and the subjects chose to pay attention to the location of the electrical stimulation while imagining the corresponding action. Finally, through the process of feature extraction, pattern recognition, etc., the decision value is output and the voice prompts are fed back to the subjects in time. The structural schematic diagram of the embod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com