DOA estimation method of nested array based on K-R subspace
A direction-of-arrival estimation and subspace technology, which can be used in direction-determining orientators, radio wave measurement systems, and measurement devices, can solve problems such as large errors in estimation methods such as antenna arrays, and achieve small errors, high resolution, and high The effect of estimating accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0023] Embodiment 1: The K-R subspace-based direction of arrival (DOA) estimation method for nested arrays includes the following steps:
[0024] Step 1: Establish a nested array model according to the equal-spaced linear array signal model;
[0025] Step 2: perform sparse processing on the nested array model established in step 1 according to the principle of K-R product transformation to obtain a sparse matrix Φ;
[0026] Step 3: Optimize and reconstruct the sparse matrix Φ obtained in Step 2 to obtain the estimated value of the incoming wave direction.
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0027] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the signal model of the medium-spaced linear array array in step 1 is specifically:
[0028] X(t)=A(Θ)S(t)+N(t)
[0029] Where X(t) is the received signal, S(t) is the transmitted signal, N(t) is the system noise, t is the time, and A(Θ) is the steering vector matrix.
[0030] Any column vector a(Θ) in matrix A(Θ) i ) is an array in the spatial source signal with a direction of Θ i The direction vector of , and is an M × 1-dimensional column vector, there are:
[0031]
[0032] Other steps and parameters are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0033] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the nested array model established in the step 1 is specifically:
[0034] If D signals are incident on the nested array, the input data vector received by the nested array of M elements is expressed as the linear combination of the incident waveform of the D incident signals and the noise, namely:
[0035]
[0036]
[0037] where x(t) is the received signal vector, a(φ i ) is the steering vector of the array of directions of arrival of the ith signal, s i (t) is the vector of the ith incident signal and n(t) is the vector of system noise.
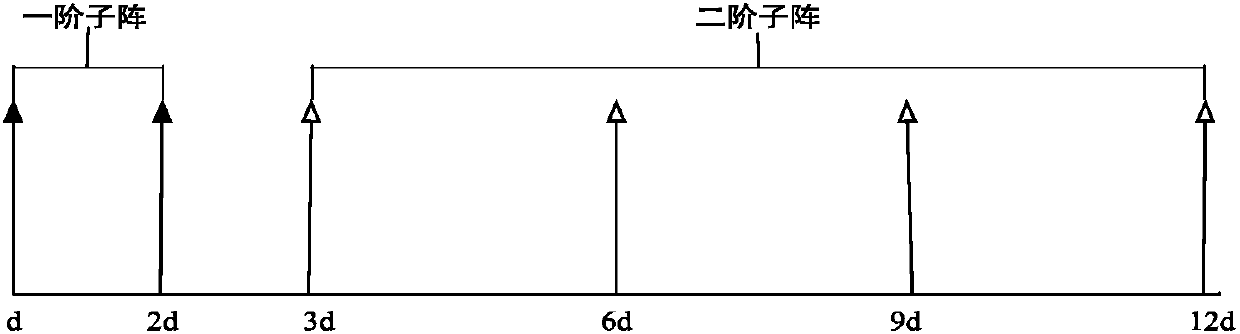
[0038] Since the number of array elements is greater than 4, the position interval of the array elements will inevitably produce redundancy, so scholars are devoted to finding the optimal array to obtain smaller redundancy and degrees of freedom, thus resulting in the concept of minimum redundancy . The arrangement of the nested array is a sp...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Snr | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com