Preparation method of high-throughput cross-linked polyimide solvent-resistant agent nanofiltration membrane and application thereof
A polyimide and nanofiltration membrane technology, applied in the field of membrane separation, can solve the problems of low flux of solvent-resistant nanofiltration membrane and poor solvent resistance of nanofiltration membrane, so as to improve separation performance and pollution resistance, and improve separation Performance and solvent resistance, the effect of increasing the rejection rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
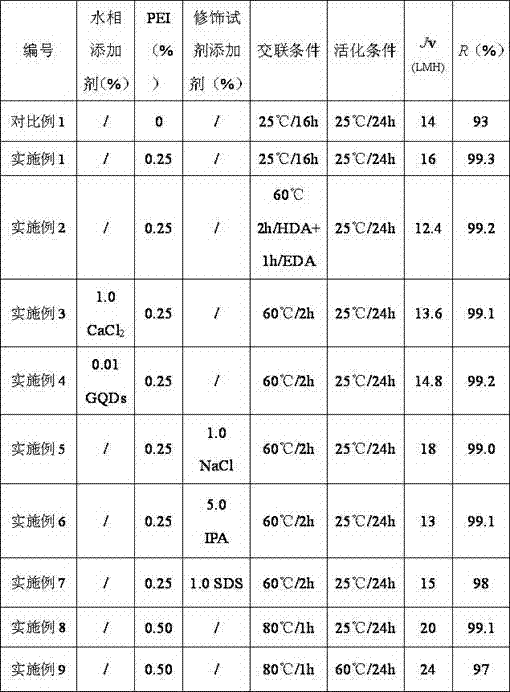
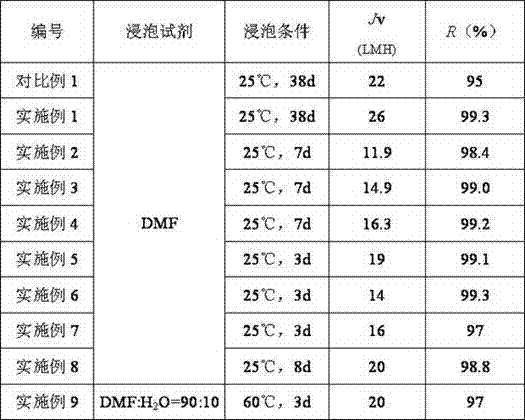
[0082] The difference from Comparative Example 1: After the interfacial polymerization, polyethylenimine modification reagent with a concentration of 0.25% by mass was used to modify the original membrane with polyamine.
[0083] Solution preparation: polyethyleneimine was dissolved in deionized water to prepare a modification reagent with a concentration of 0.25% by mass.
[0084] The preparation steps of the base film are the same as in Comparative Example 1.
[0085] The aqueous phase monomer solution, the oil phase monomer solution, and the crosslinking reagent are all the same as in Comparative Example 1.
[0086] The membrane-making steps and conditions of the solvent-resistant nanofiltration membrane are as follows:
[0087] Step 1: Fully contact the surface of the basement membrane with the aqueous phase monomer solution containing diamine compounds for 30 seconds, remove the excess water phase, and fully contact the surface of the basement membrane after drying with ...
Embodiment 2
[0094] The difference from Comparative Example 1: After the interfacial polymerization, the original eco-membrane was modified with polyamines with an additive-free mass percentage concentration of 0.25% polyethyleneimine modification reagent; the post-crosslinking was secondary crosslinking; first, 10.0% Hexamethylenediamine-isopropanol solution was crosslinked at 60°C for 2h, followed by 5.0% ethylenediamine-isopropanol solution at 60°C for 1h.
[0095] Solution preparation:
[0096] Dissolve polyethyleneimine in deionized water to prepare a modification reagent with a concentration of 0.25% by mass.
[0097] Dissolve ethylenediamine (EDA) in isopropanol to prepare the second cross-linking reagent with a concentration of 5.0% by mass.
[0098] The preparation steps of the base film are the same as in Comparative Example 1.
[0099] The aqueous phase monomer solution, the oil phase monomer solution, and the first crosslinking reagent are all the same as in Comparative Examp...
Embodiment 3
[0103] The difference from Comparative Example 1: During interfacial polymerization, soluble inorganic salts are added to the aqueous phase solution; after interfacial polymerization, a polyethyleneimine modification reagent with a mass percent concentration of 0.25% is used to modify the original ecological membrane with polyamines; the crosslinking conditions are 60°C, 2h.
[0104] Solution preparation:
[0105] Dissolve m-phenylenediamine and calcium chloride in deionized water, mix them evenly, and form an aqueous phase solution with m-phenylenediamine and calcium chloride mass percent concentrations of 2.0% and 1.0% respectively.
[0106] Dissolve polyethyleneimine in deionized water to prepare a modification reagent with a concentration of 0.25% by mass.
[0107] The preparation steps of the base film are the same as in Comparative Example 1.
[0108] The oil phase monomer solution and the crosslinking reagent are the same as those in Comparative Example 1.
[0109] A...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com