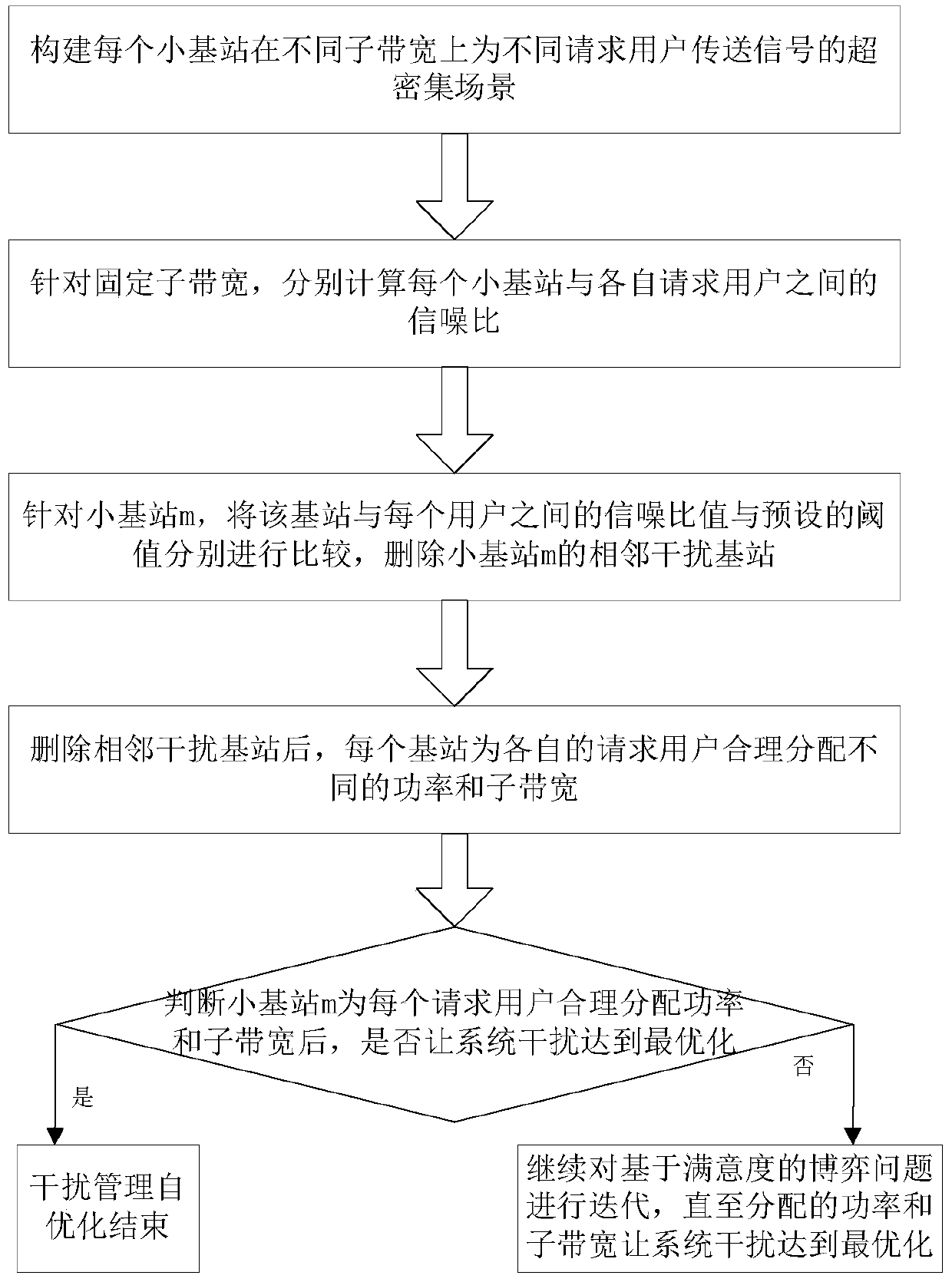
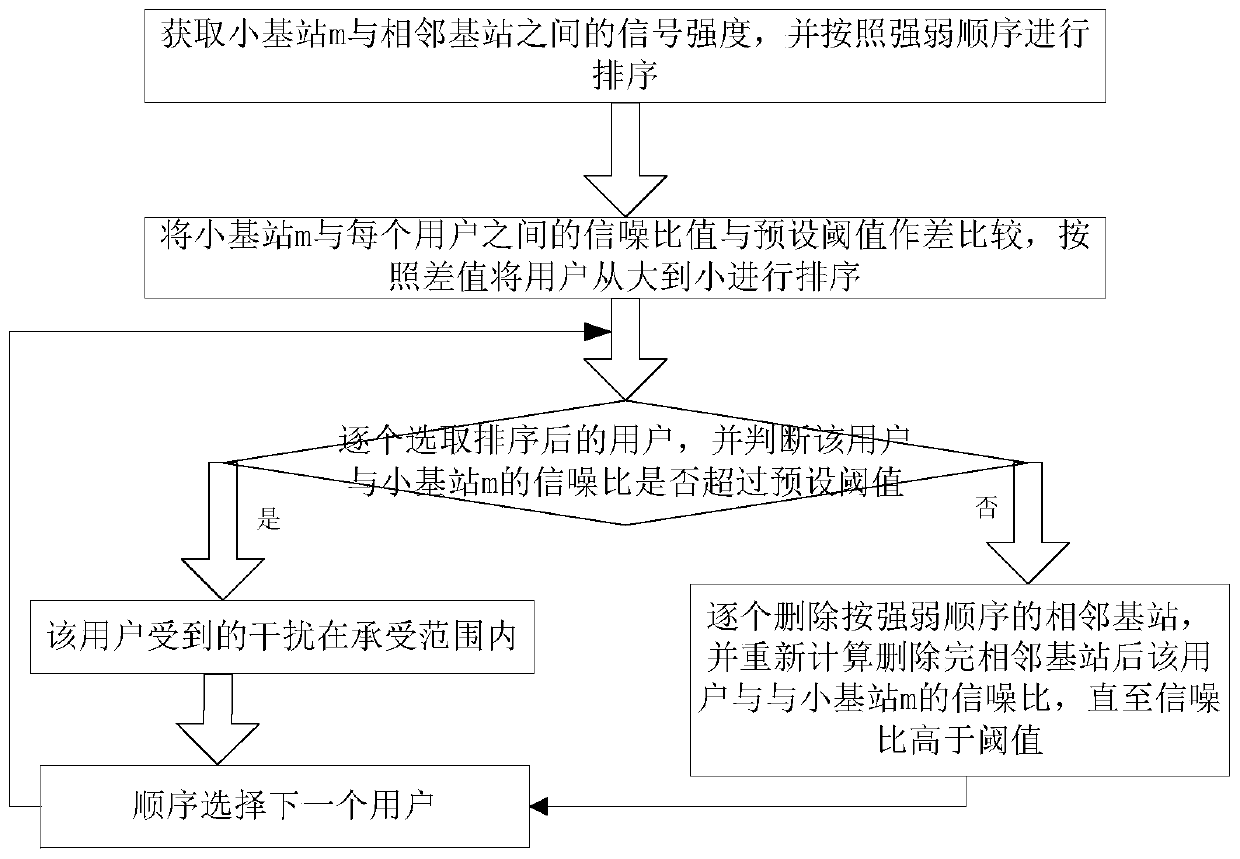
A self-optimization method for interference management based on non-orthogonal multiple access
A non-orthogonal multiple access and interference management technology, applied in the field of interference management self-optimization based on non-orthogonal multiple access, can solve the problems of inapplicable interference optimization scheme, complex interference problems, large signaling overhead, etc. Improve spectral efficiency and system capacity, ensure communication requirements, and reduce interference effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
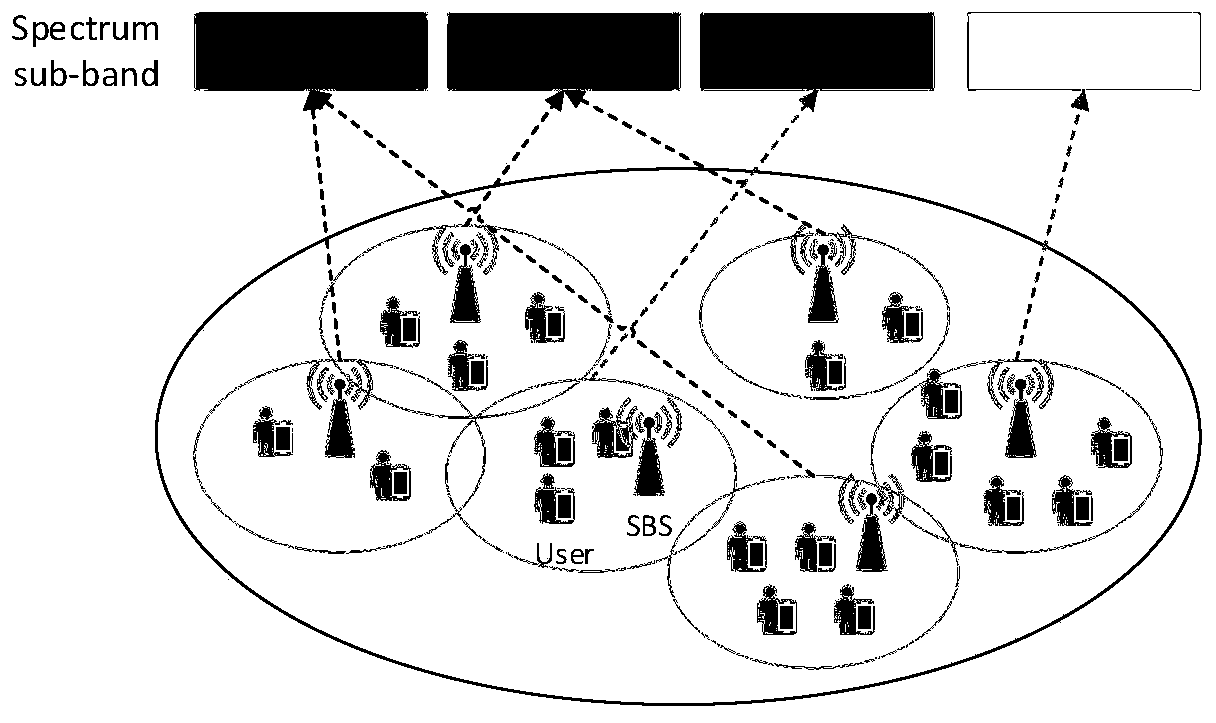
[0130] Consider a square area of 500m*500m, where the distribution density of sub-base stations is 400 / Km2, and the location is fixed, the coverage of each sub-base station is 50m, the distribution density of users is 1000 / Km2, and the system bandwidth is 20MHz. The user channel model adopts the Rayleigh fading model. In addition, the transmit power of each small base station is 24dBm, the thermal noise power is -174dBm, and the carrier frequency is 2.5GHz.
[0131] In order to prove the performance of the multi-dimensional resource allocation mechanism proposed by the present invention, three mechanisms are selected for comparison.
[0132] Mechanism 1 (SORA-OMA): A self-optimization mechanism for interference management based on orthogonal multiple access technology, with low resource utilization.
[0133] Mechanism 2 (DRA-WSO): The distributed interference management mechanism does not consider self-optimization technology, and the network management efficiency is low. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com