Differential nuclease digestion method and application thereof to detecting mRNA (messenger ribonucleic acid) internal modification through LC-MS (liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry)
A nuclease and differential technology, applied in the field of differential nuclease cleavage combined with LC-MS, can solve problems such as differentiation and achieve the effect of easy operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
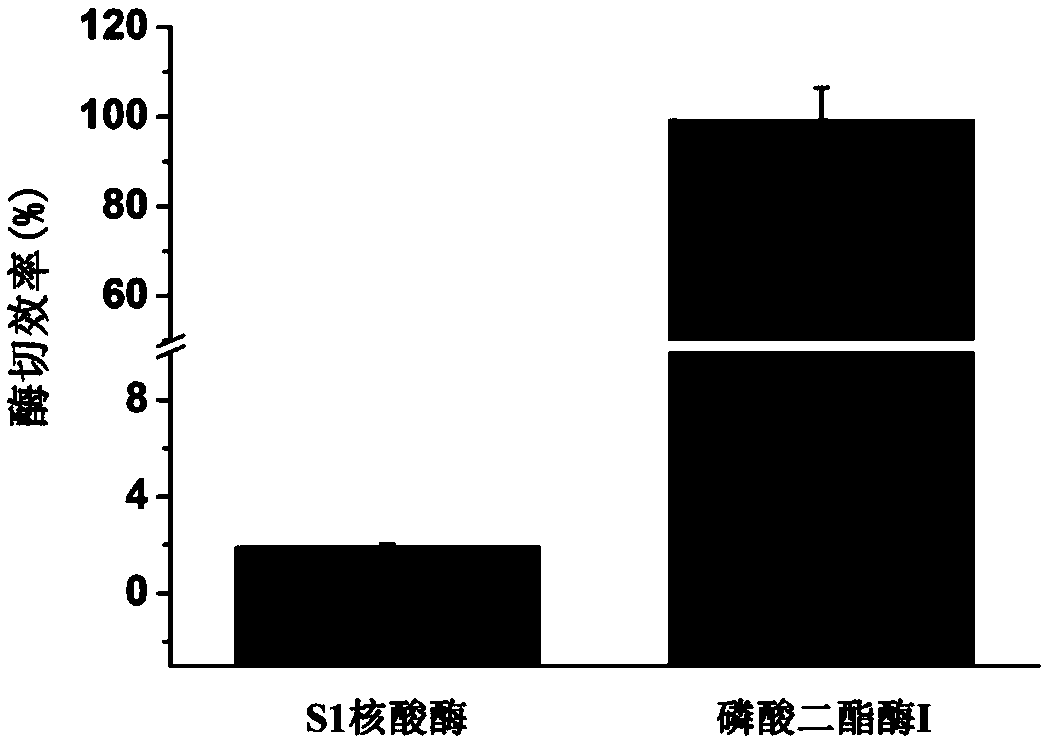
[0034] Embodiment 1: S1 nuclease enzymatic hydrolysis, phosphodiesterase I enzymatic hydrolysis to the enzymatic cleavage efficiency of the 5' end cap structure of mRNA
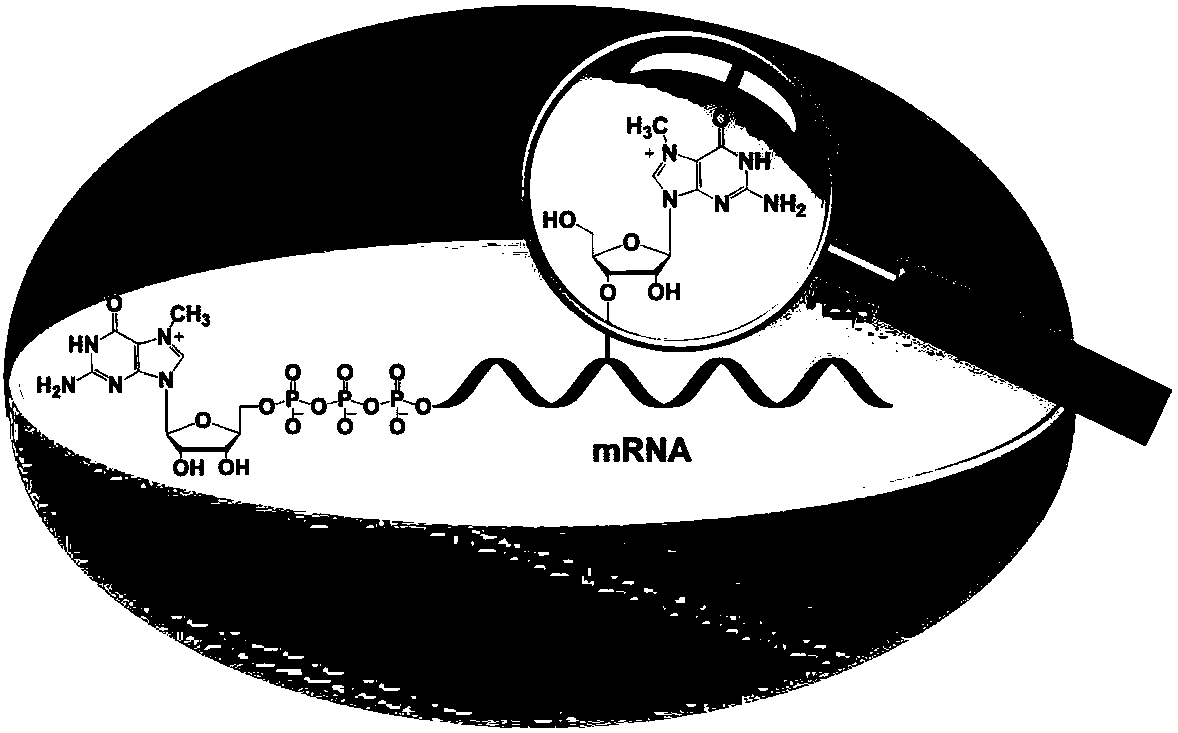
[0035] Use mMESSAGE The T7Kit kit uses double-stranded DNA with a T7 promoter as a template for carrying 5' end m 7 In vitro transcription of RNA with G-cap structure, the 5' end of the RNA is the same as eukaryotic mRNA, and each RNA transcribed contains only one m at the 5' end 7 g. Use S1 nuclease and phosphodiesterase I to enzymolyze the RNA into nucleotides, then use alkaline phosphatase to enzymolyze the nucleotides into nucleosides, remove the protein, freeze and spin dry, and redissolve in 65 μL of water. Inject 50 μL and analyze by LC-MS. The enzymatic efficiency of S1 nuclease enzymatic hydrolysis and phosphodiesterase I enzymatic hydrolysis on the cap structure of the 5' end of mRNA can be calculated. See the results in image 3 , S1 nuclease and phosphodiesterase I have a huge difference in t...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2: Enzymolysis efficiency comparison of S1 nuclease enzymolysis, phosphodiesterase I enzymolysis and other enzymolysis methods
[0037] Use S1 nuclease, phosphodiesterase I, conventional enzymatic digestion (S1 nuclease and phosphodiesterase I share), exonuclease T, exonuclease I and T4 DNA polymerase to digest the same amount of mRNA For nucleotides, use alkaline phosphatase to enzymatically hydrolyze nucleotides into nucleosides, remove protein, freeze and spin dry, redissolve in 65 μL water, inject 50 μL, and analyze by LC-MS. Compare the peak areas of normal nucleosides (A, G, C, U) obtained by different enzymatic hydrolysis methods, the results are shown in Figure 4 .
Embodiment 3
[0038] Example 3: m 7 G standard and internal m of mRNA in rice samples 7 Chromatographic retention time comparison of G
[0039] Total RNA was extracted from rice samples using TRIzol reagent and reused The mRNA IsolationSystem kit is used to isolate and purify mRNA from rice total RNA. After the mRNA was hydrolyzed into nucleotides with S1 nuclease and phosphodiesterase I, the nucleotides were hydrolyzed into nucleosides with alkaline phosphatase, the proteins were removed, freeze-dried, and redissolved in 65 μL of water. Analysis of m by LC-MS 7 G standard, S1 nuclease digest and phosphodiesterase I digest. contrast m 7 Extracted ion chromatograms of G standard, S1 nuclease hydrolyzate and phosphodiesterase I hydrolyzate, the results are shown in Figure 5 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com