Series-parallel walking robot construction method and series-parallel walking robot
A walking robot and construction method technology, applied in manipulators, motor vehicles, program-controlled manipulators, etc., can solve problems such as few degrees of freedom, and achieve the effects of low body height, strong bearing capacity, and easy trajectory planning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 3
[0160] in
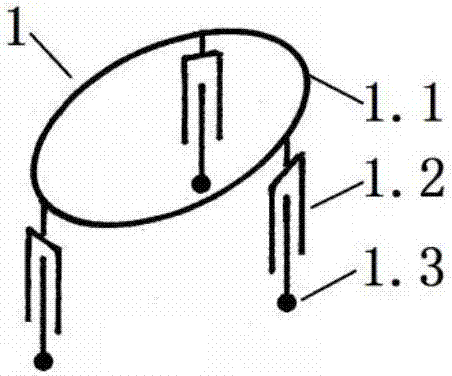
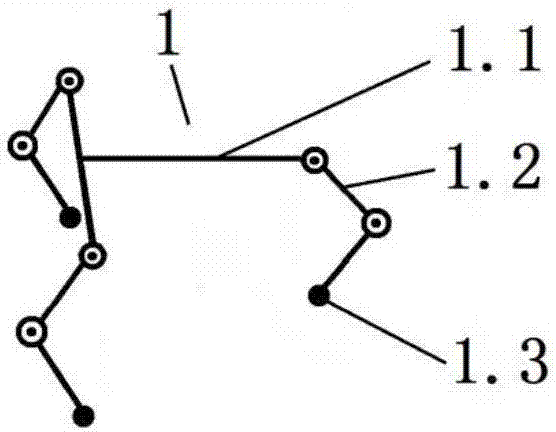
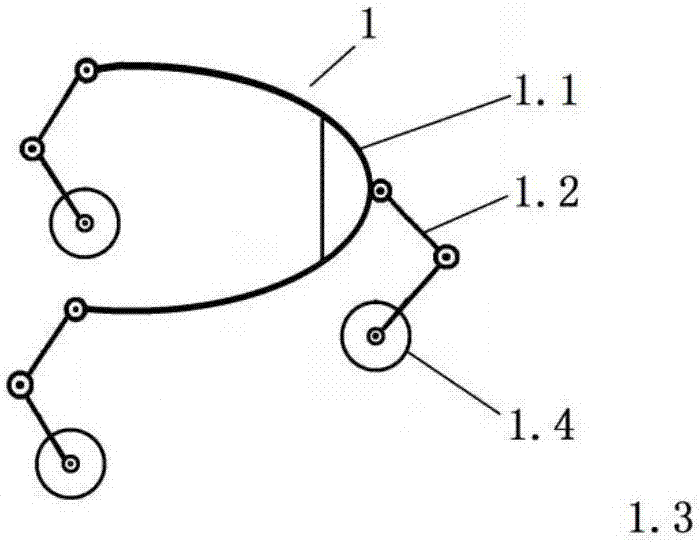
[0161] Ra is the radius of the circumscribed circle of the toe triangle of the A-leg mechanism,
[0162] Rb is the radius of the circumscribed circle of the toe triangle of the B-leg mechanism;
[0163] The first is an isotropic connection scheme, known as the internal and external structure scheme (see embodiment 1, 2); the second is a non-isotropic scheme, called the cross structure scheme (see embodiment 3 , 4).
[0164] For the internal and external structure scheme, if there are two identical leg mechanisms, there will be a phase difference of about 60 degrees when the two upper platforms are connected.
[0165] In the cross structure scheme, the toes of one leg mechanism generally have to fall in the center of the triangle of the other toe.
[0166] In order to provide a hybrid walking robot that can still walk when the body is overturned, including A-leg mechanism, B-leg mechanism and pelvis, the metatarsal branch of the two leg mechanisms of the hybrid w...
Embodiment 1
[0322] Example 1 ( Figure 26 ) is composed of two hybrid leg mechanisms ( Figure 21 ) form the hybrid walking robot 4, the upper platforms of the A-leg mechanism 4.1 and the B-leg mechanism 4.2 (the hip bone planes are staggered by 60 degrees) are connected together to form a pelvis 4.3. The branches of the two thigh mechanisms are on the same level (or on different levels). The thigh branch chains of the two leg mechanisms each occupy a fan-shaped space of about 60 degrees without interfering with each other. The two Y-shaped arch platforms are located at different heights without interfering with each other. Each metatarsal branch occupies a fan-shaped space of about 60 degrees without interfering with each other. The toes on its two leg mechanisms each occupy a fan-shaped space of about 60 degrees. Each toe has independent free working space. This is a hybrid walking robot of inside and outside. The distance between the centers of gravity of the two toe triangles is...
Embodiment 2
[0324] Example 2 ( Figure 27 ) is a hybrid walking robot 4 composed of two hybrid leg mechanisms, one large and one small, and the larger hybrid leg mechanism 4.1 reference Figure 13 , the smaller leg mechanism 4.2 reference Figure 11 . The upper platforms of the two leg mechanisms are connected together to form a pelvis 4.3, the branch chains of the two thigh mechanisms are on the same level, and the pelvis is on another level (also can be on the same level). Thigh branch chain 2.2 all has its own activity space, does not interfere with each other. The two arch platforms are located at the same height, one is a convex triangle, which is larger, and the other is Y-shaped, which is smaller, and the two do not interfere with each other. Each metatarsal branch 1.2 has its own space for movement. If the larger leg mechanism has a larger toe triangle, the toe workspace can be larger. The distance between the centers of gravity of the triangles of the two toes is 0, and the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com