Posterior probability tag collision solution for RFID system
A posteriori probability and conflict resolution technology, applied in electromagnetic radiation induction, instruments, induction record carriers, etc., can solve problems such as inaccurate tag estimation results, affecting tag recognition efficiency, and sending too many commands, so as to save hardware memory resources, improve label recognition efficiency, and avoid conflicting effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
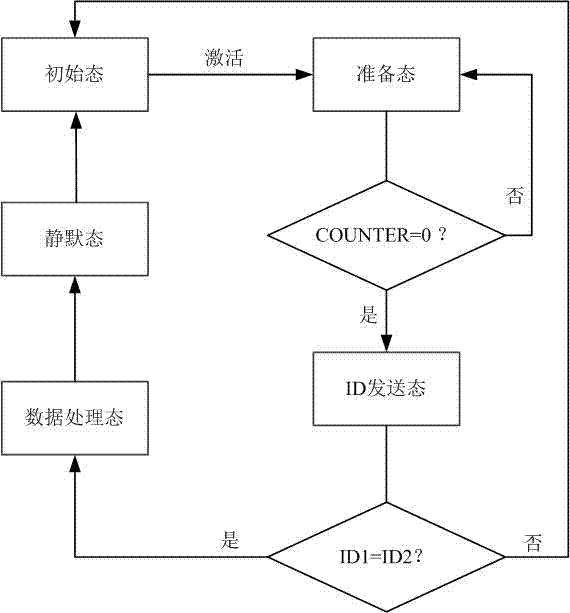
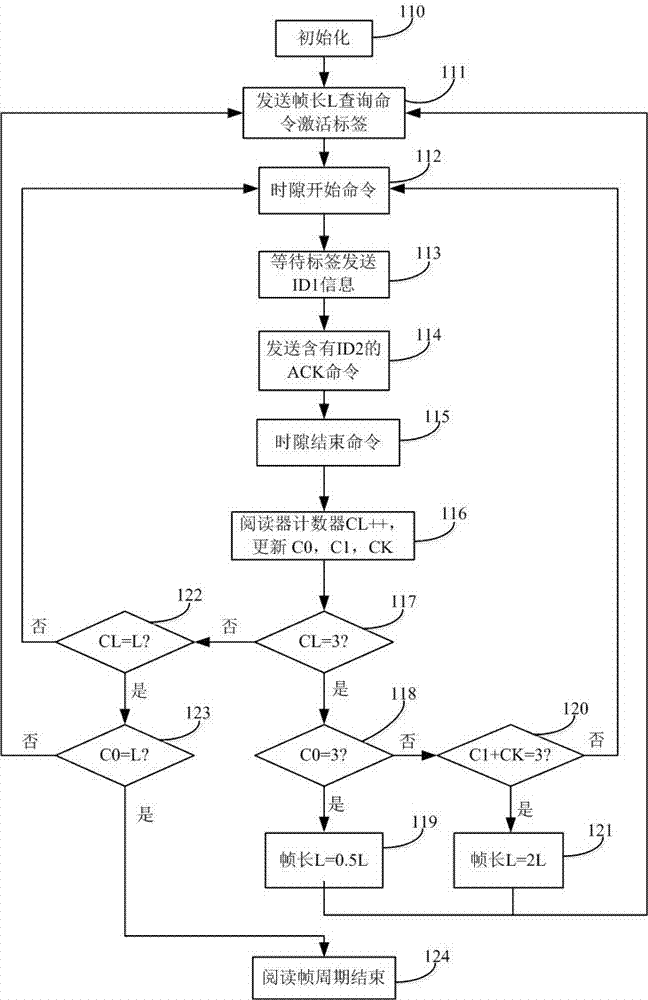
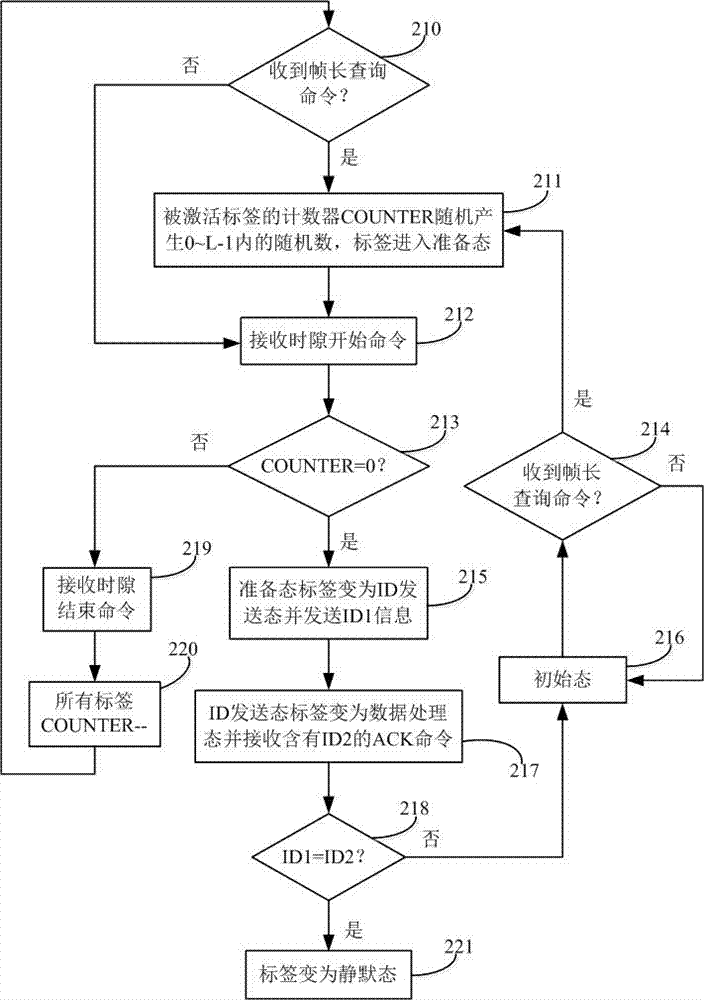
[0045] The RFID system of the inventive method is made up of a reader and a plurality of tags within its coverage area, and the reader first sends out relevant commands, and the tags perform corresponding operations after receiving corresponding commands, and the specific method is:
[0046] ① Set a cycle for the time it takes for a reader and multiple tags to perform a complete communication identification process, and a complete cycle can be divided into the following four stages:
[0047]a. Initial: The reader first sends a continuous carrier signal containing energy to activate all tags within the range, and at the same time sends out a query command;
[0048] b. Send ID information: the tag sends ID information to the reader. If there are more than two tags or no tag sends ID information, the conflict command will be executed immediately, otherwise the data processing stage will be carried out;
[0049] c. Data processing: only one tag sends ID information to the reader, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com