Power grid abnormality quick detection method based on random matrix spectral radius method
A random matrix and detection method technology, which is applied in the direction of detecting faults according to conductor types, complex mathematical operations, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as weak signals, achieve accurate resolution, improve the level of abnormal analysis and processing of power grids, and have high sensitivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0094] Example: Investigate the sampling data of 57 PMUs in a power grid in a certain place under the wide-area measurement system. The power grid is an independent low-voltage distribution network, and all PMUs are configured at the 110V voltage level. Through the selection of points in the early stage, the configuration ensures a considerable system. Under this system, PMU devices are installed in the low-voltage distribution network to complete the system frequency sampling.
[0095] On a certain day in March 2015, two frequency disturbances occurred in this power grid. Analyze the PMU sampling data of each frequency disturbance, and construct a large-dimensional matrix as follows:
[0096] 1. For each PMU node, take continuous 20-second frequency sampling data (T=200), then 57 PMU nodes form an original matrix of 57*200.
[0097] 2. Since the row-to-column ratio of the large-dimensional matrix should be between [0,1] and should not be too small, the data of 0-10 seconds o...
example 1
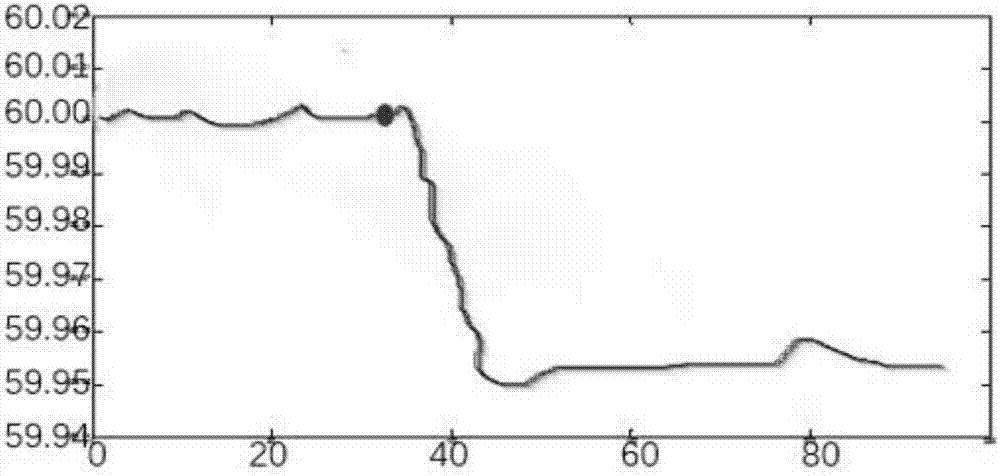
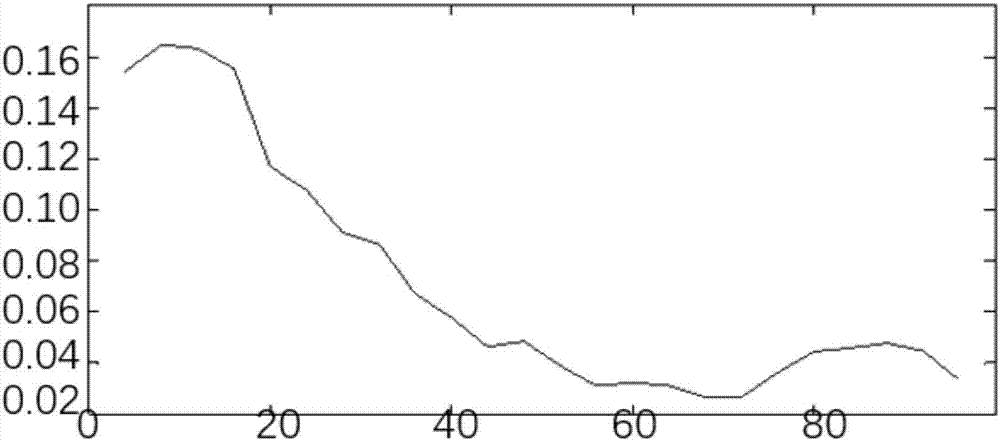
[0100] Example 1: Frequency first perturbation. figure 2 is the time-domain diagram of the first perturbation of the frequency, where the abscissa is the number of sampling points, the unit is unit, and the ordinate is the frequency, the unit is Hertz. The frequency mutation lasts for about 10 seconds, corresponding to about the 800th-900th point, and these 100 points are in figure 2 displayed in . image 3 is the change curve of the inner diameter of each sliding window ring, where the abscissa is the number of sampling points in unit, and the ordinate is the size of the inner diameter. It can be seen that the inner diameter drops sharply when the abnormality occurs, and continues to be at the lowest point at the abnormal moment. Figure 4 The characteristic root donut diagram of the spectral distribution under the selected sliding window shows the characteristic root distribution of each sliding window large-dimensional matrix before and after the anomaly and across the ...
example 2
[0101] Example 2: The frequency is perturbed for the second time. Similar to Example 1, Figure 5 is the time-domain diagram of the second perturbation of the frequency, where the abscissa is the number of sampling points, the unit is unit, and the ordinate is the frequency, the unit is Hertz. The frequency mutation lasts for about 10 seconds, corresponding to about the 800th-900th point, and these 100 points are in Figure 5 displayed in . Image 6 It is the change curve of the inner diameter of each sliding window ring. It can be seen that the inner diameter drops sharply from the beginning of the abnormality, and continues to be at the lowest point at the abnormal moment. Figure 7 is the characteristic root donut diagram of the spectral distribution under the selected sliding window, where the abscissa is the number of sampling points in unit, and the ordinate is the size of the inner diameter. In this example, Δf=59.98Hz-59.95Hz=0.03Hz, the sensitivity is increased by ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com