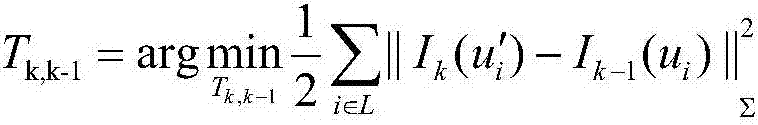Depth camera-based visual mileometer design method
A visual odometry and depth camera technology, applied in the field of computer vision technology research, can solve problems such as poor real-time performance, large amount of calculation, and limited robustness improvement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the embodiments and the accompanying drawings, but the embodiments of the present invention are not limited thereto.
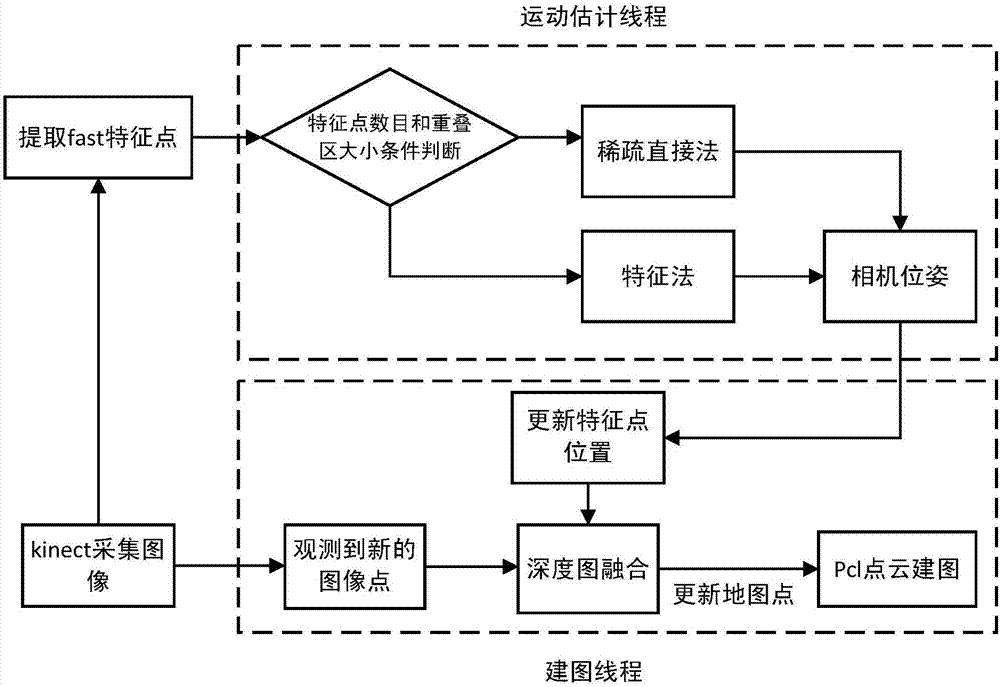
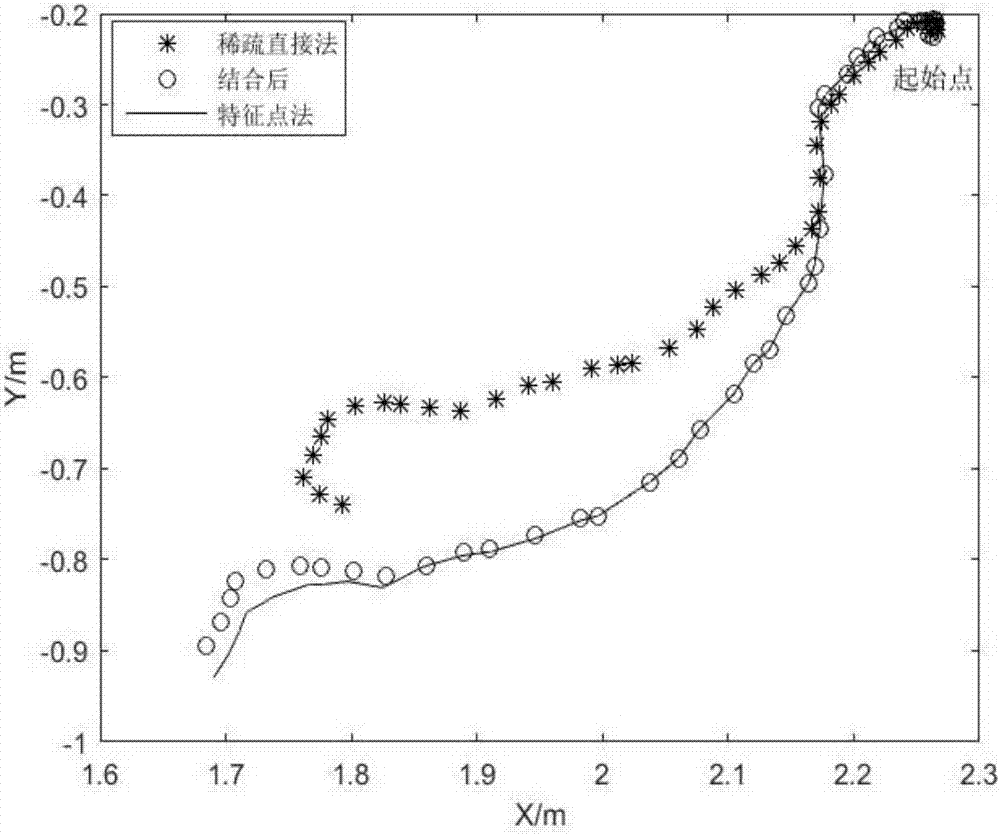
[0040] In order to solve the problem of loss of pose and poor robustness in the process of fast movement in the visual odometry based on the sparse direct method, a design method of the visual odometry based on the depth camera is proposed. This method combines the sparse direct matching method and the feature point matching method, which can improve the real-time and robustness of visual odometry.
[0041] In this method, a threshold is set for the overlapping area between two frames, and the size of the overlapping area can reflect the camera motion to a certain extent. If the overlapping area is large, the sparse direct method is used to estimate the camera pose during gentle motion, and if the overlapping area is small, the feature matching is performed and the camer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com