Method of repairing and improving secondary salinized soil in facility agriculture
A secondary salinization and soil remediation technology, which is applied in the field of secondary salinization soil remediation and improvement in facility agriculture, can solve the problems of slow effect of straw method, polluted groundwater, and lack of soil nutrients, etc., to promote water permeability, breathability, Effect of reducing salt content and promoting utilization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] In this embodiment, the per-mu application rate of quicklime is 10 kg, the per-mu application rate of organic fertilizer is 1000 kg, and the per-mu application rate of plant ash is 30 kg.
[0052] The following table is the soil pH value comparison and the salt content comparison before and after the treatment of the present embodiment (wherein, the salt content is the percentage of the quality of the salt contained in the soil to the dry soil mass):
[0053] Table 1 Comparison of soil pH value and salt content before and after treatment in Example 1
[0054] project before processing after treatment Soil pH 6.0 6.8 soil salinity 0.67% 0.21%
[0055] As can be seen from the above table, the pH value of the soil treated in this embodiment becomes significantly larger, and the soil changes from an acidic soil unsuitable for crop growth to a neutral soil suitable for crop growth, and the salt content is also significantly reduced. It has dro...
Embodiment 2
[0061] In this embodiment, the per-mu application rate of quicklime is 30 kg, the per-mu application rate of organic fertilizer is 1500 kg, and the per-mu application rate of plant ash is 50 kg.
[0062] The following table is the soil pH value comparison and the salt content comparison before and after the treatment of the present embodiment (wherein, the salt content is the percentage of the quality of the salt contained in the soil to the dry soil mass):
[0063] Table 3 Comparison of soil pH value and salt content before and after treatment in Example 2
[0064]
[0065]
[0066] As can be seen from the above table, the pH value of the soil treated in this embodiment becomes significantly larger, and the soil changes from an acidic soil unsuitable for crop growth to a neutral soil suitable for crop growth, and the salt content is also significantly reduced. It has dropped below 0.3%, which is more suitable for the growth of crops.
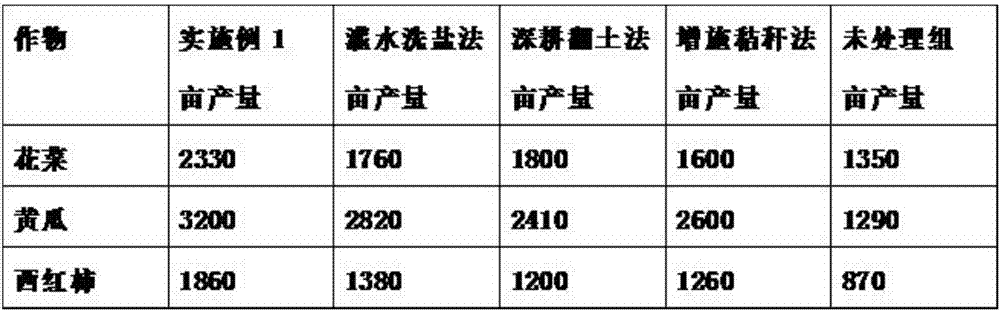
[0067] Cauliflower, cucumber, and...
Embodiment 3
[0072] In this embodiment, the per-mu application rate of quicklime is 50 kg, the per-mu application rate of organic fertilizer is 1200 kg, and the per-mu application rate of perlite is 20 kg.
[0073] The following table is the soil pH value comparison and the salt content comparison before and after the treatment of the present embodiment (wherein, the salt content is the percentage of the quality of the salt contained in the soil to the dry soil mass):
[0074] Table 5 Comparison of soil pH value and salt content before and after treatment in Example 3
[0075] project before processing after treatment Soil pH 5.5 7.2 soil salinity 0.69% 0.18%
[0076] As can be seen from the above table, the pH value of the soil treated in this embodiment becomes significantly larger, and the soil changes from an acidic soil unsuitable for crop growth to a neutral soil suitable for crop growth, and the salt content is also significantly reduced. It has dropp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com