Strain of auricularia auricula
A technology of black fungus and strains, applied in the direction of fungi, microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of poor quality, small holes, difficult to form a single piece, low yield, etc., and achieve the effect of good promotion prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1: Select local black fungus "Xinke" and "916" as hybrid parents, and obtain F1 generation hybrid strains through single-single hybridization and single-double hybridization techniques. After laboratory mycelium growth observation and cultivation tests, the strains were screened out. For strains with vigorous silk growth, solitary fruiting bodies, and higher yield than the parent, the fruiting bodies are collected to obtain the second-generation strains through tissue separation technology; further cultivation experiments are carried out to screen and obtain excellent strains with relatively stable target agronomic traits, and hybrid strains are obtained after tissue separation The number "X6" was screened and entered into the cultivation test. This strain has good early maturity, solitary fruiting bodies, and less back tendons. Afterwards, a stable strain was obtained after single-plant screening. This strain improved the shortcomings of the old variety "Xinke",...
Embodiment 2
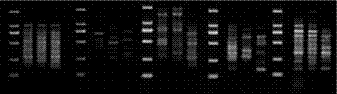
[0044] Example 2: RAPD method was used to compare the DNA differences between the strain and its parent.
[0045] Detection basis: According to the agricultural industry standard of the People's Republic of China "NY / T 1743-2009 Authenticity Identification of Edible Fungus Strains - RAPD Method", the strain DNA was extracted and the optimal primer was determined.
[0046] Materials submitted for inspection: 3 black fungus strains, among which the strain to be inspected is Lier No. 3, and 2 control strains are "Xinke" and "916".
[0047] Inspection method: The experimental primer sequence (Table 6) was synthesized by Qingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. in accordance with "NY / T 1743-2009 RAPD method for authenticity identification of edible fungus strains".
[0048] The mycelium activation, cultivation, genomic DNA extraction, quality inspection, PCR amplification and electrophoresis detection of the strains to be tested are all in accordance with the Agricultural Industry Standard o...
Embodiment 3
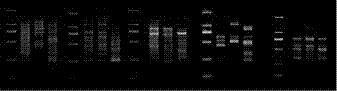
[0053] Example 3: Comparison of DNA differences between the bacterial strain and its parent using the antagonistic reaction method.
[0054] Test basis: Inoculation, culture and observation of the samples to be tested are carried out according to the Agricultural Industry Standard of the People's Republic of China "NY / T 1845-2010 Differential Identification of Edible Fungi Species Antagonism Reaction".
[0055] Materials submitted for inspection: 3 black fungus strains, among which the strain to be inspected is Lier No. 3, and 2 control strains are "Xinke" and "916".
[0056] Inspection method: Strictly follow the aseptic operation, use a Φ5 mm hole punch to punch out the edge of the colony of the appropriate age after activation as the inoculation block, and place the two inoculation blocks at a distance of 30 mm, and place them at a distance of 15 mm from the center of the PDA plate. Wire up. At a temperature of 25°C, ventilated and protected from light, cultured until the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com