Method for research of feeding ecology of cephalopods in different life history stages according to eye crystalline lens
A technology of life history and cephalopods, applied in the field of aquaculture, can solve problems such as the inability to accurately analyze the feeding ecology of cephalopods, and achieve the effects of direct feeding ecology, easy extraction, and high accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0049] Example 1: A method for studying the feeding ecology of cephalopods at different life history stages by using eye lenses
[0050] The operation steps are as follows:
[0051] 1. Extraction: cut the eyeball with a scalpel, and take out a pair of crystals with tweezers;
[0052] 2. Cleaning: Clean the crystal surface with clean water;
[0053] 3. Preservation: put the eye lens processed in step (2) into 75% alcohol for preservation;
[0054] 4. Separation: Take out the crystal, remove the distal end of the crystal, and keep the proximal end of the crystal;
[0055] 5. Soaking: soak the proximal crystal with distilled water for 5 minutes to make it fully absorb water;
[0056] 6. Measurement: Measure the diameter of the proximal crystal processed in step (5) with a vernier caliper;
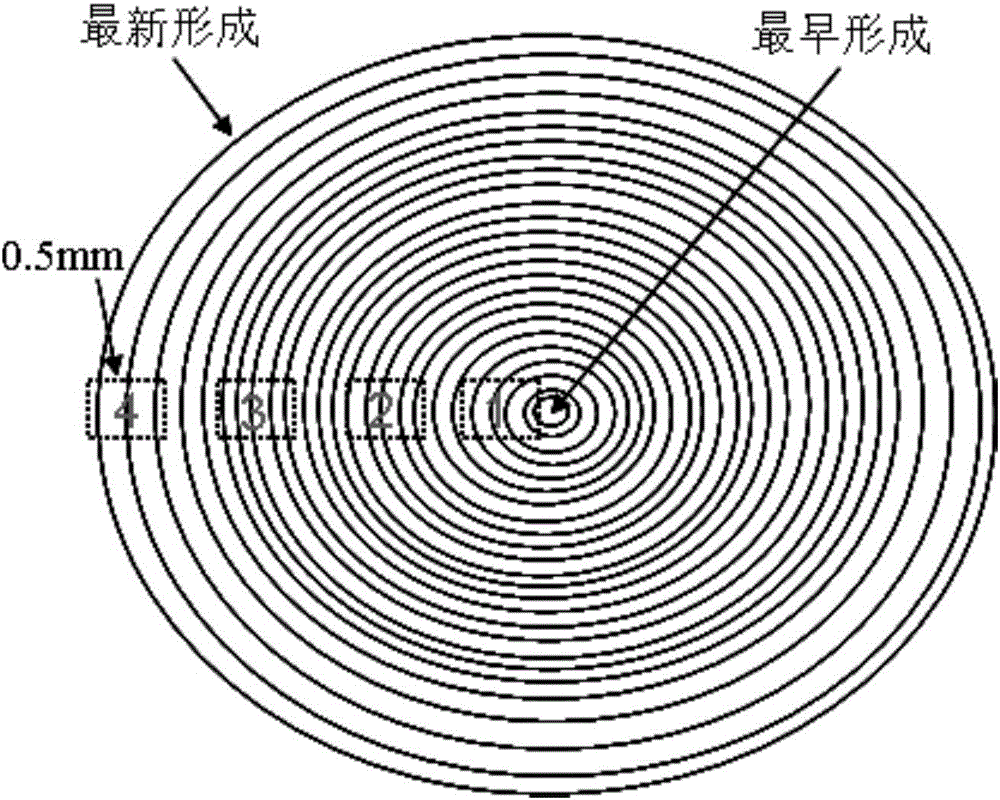
[0057] 7. Micro-sampling: Under a dissecting microscope, use wide-head tweezers sterilized by absolute alcohol to peel off crystals with a width of about 0.5 mm from the outermost layer of...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Embodiment 2: the stripping method of eye lens section in different life history stages of cephalopods
[0069] The operation steps are as follows:
[0070] (1) Separation: take out the crystal, remove the distal end of the crystal, and keep the proximal end of the crystal; remove the smaller distal crystal while retaining the larger near-end crystal to ensure that there is enough crystal volume for micro-sampling. Complete stable isotope determination;
[0071] (2) Soaking: Soak the proximal crystal with distilled water for 5 minutes to make it fully absorb water, which will help the crystal to peel off;
[0072] (3) Measurement: measure the diameter of the near-end crystal that step (2) has processed with a vernier caliper;
[0073] (4) Micro-sampling: Under a dissecting microscope, use wide-head tweezers sterilized by absolute alcohol to peel off crystals with a width of about 0.5 mm from the outermost layer of the crystal to the core of the crystal; before micro-s...
Embodiment 3
[0080] Example 3: Method for Determination of Carbon and Nitrogen Stable Isotopes in Eye Lens Sections in Different Life History Stages of Cephalopods
[0081] The operation steps are as follows:
[0082] (1) Standard sample selection: select USGS 24 (-16.049‰V-PDB) and USGS 26 (53.7‰V-N2) standards as the calibration of stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen;
[0083] (2) Determination of stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen: Determination of stable isotopes of carbon and nitrogen was performed on samples of different cross-sections on an isotope ratio mass spectrometer.
[0084] Wherein, the determination step of stable isotope of carbon and nitrogen in the step (2) is:
[0085] (1) Drying: Put the crystal samples of different cross-sections into the drying oven for drying;
[0086] (2) Grinding: the dried sample is ground into powder in a frozen mixing ball mill, and sieved with a 100-mesh sieve;
[0087] (3) Weighing: Weigh about 1.5 mg of the sieved powder with a mil...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com