Fusobacterium nucleatum tyrosine phenol lyase mutant, gene, vector, engineering bacteria and application thereof
A technology of Fusobacterium nucleatum and genetically engineered bacteria, applied in the directions of genetic engineering, lyase, carbon-carbon lyase, etc., can solve the problem that the catalytic efficiency needs to be improved, and achieve the effect of excellent catalytic performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1 Obtaining of TPL gene
[0034] The whole genome DNA of Fusobacterium nucleatum (F.nucleatum subsp.CGMCC 1.2526, purchased from China Industrial Microorganism Culture Collection Management Center) was extracted with a DNA extraction kit. Using the DNA as a template, the upstream primer (5'GCTGA GGATC C ATGAGATTTGAAGATTATCCAGC 3’ ) and downstream primer (5'GCATC CTCGAG TTATTTTTTTATTCCAAATCTAGC 3’ ) as primers for PCR amplification reaction. The amount of each component in the PCR reaction system (total volume 50 μL): 10 μL of 5×PrimeSTARTM HS DNA polymerase Buffer, 4 μL of 10 mM dNTP mixture (2.5 mM each of dATP, dCTP, dGTP and dTTP), 1 μL of each upstream primer and downstream primer at a concentration of 50 μM , genomic DNA 1 μL, PrimeSTARTMHS DNA polymerase 0.5 μL, nucleic acid-free water 32.5 μL. The PCR reaction conditions were as follows: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 1min, followed by a temperature cycle of 95°C for 10s, 56°C for 90s, and 72°C for 1...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2 Error-prone PCR construction of TPL mutation library
[0036] Using the TPL gene obtained in Example 1 as a template, the mutant sequence was obtained by error-prone PCR amplification. Amplification primers are (5'GCTGA GGATCC ATGAGATTTGAAGATTATCCAGC 3’ ) and (5'GCATC CTCGAG TTATTTTTTTATTCCAAATCTAGC 3’) .
[0037] The amplification system is: 50μl reaction system:
[0038] 10xTaq polymerase buffer: 5μL;
[0039] Mg 2+ (25mM): 2-8μL;
[0040] Mmm 2+ (25mM): 2-8μL;
[0041] 10mM dNTP mixture (dATP, dCTP, dGTP and dTTP each 2.5mM) 4μ;
[0042] 1 μL each of the upstream primer and the downstream primer at a concentration of 50 μM,
[0043] DNA template: 1 μL;
[0044] Taq DNA polymerase: 10U;
[0045] Make up the system with double distilled water.
[0046] The PCR reaction conditions were as follows: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 1min, followed by a temperature cycle of 95°C for 10s, 56°C for 90s, and 72°C for 1min, a total of 30 cycles, and finall...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3 Screening of TPL mutant library
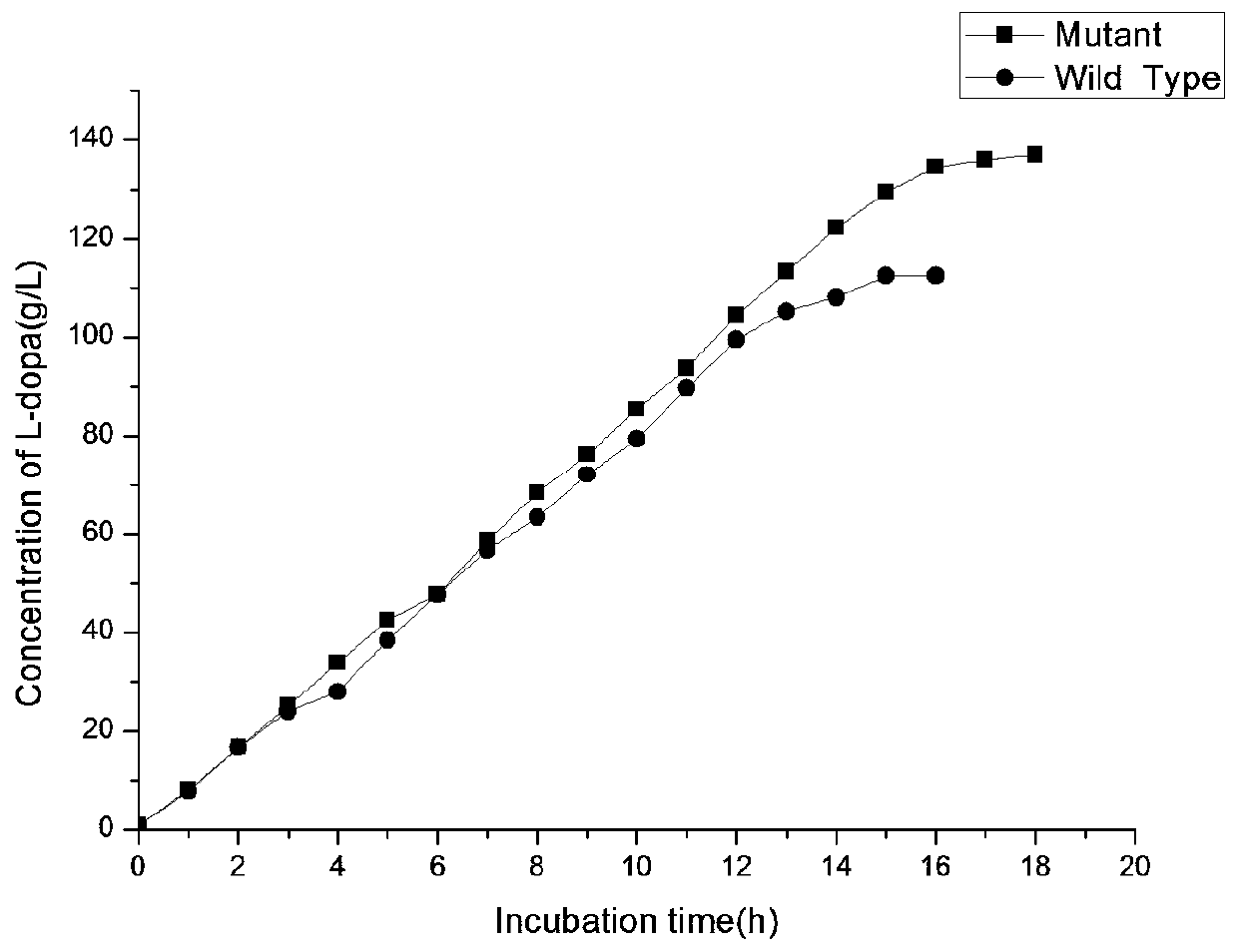
[0048] The screening of the TPL mutation library was as described in the literature (Choi, et al., Kor. J. Microbiol. 2006, 34:58-62). Using the enzyme before mutation as a reference, positive clones with improved activity were obtained through primary screening, which were further determined by liquid chromatography. After the first round of mutation, the mutant with the highest activity was obtained, and sequencing showed that the obtained mutant was E84K. Extract the plasmid containing the E84K mutant as a template, and perform the second round of error-prone PCR, as in Example 2, after transforming into Escherichia coli, and then screen the mutant library to obtain a mutant with improved activity compared with E84K, which is shown by sequencing. The mutant is double mutant E84K / T129I, the amino acid sequence of which is SEQ ID No.4, and the nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID No.3.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| optical purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| optical purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com