Artificial breeding production method of trichogramma japonicum
A technology for artificial breeding of Trichogramma, applied in the fields of botanical equipment and methods, horticulture, animal husbandry, etc., can solve the problems such as difficult to remove and make egg cards, difficulty in large-scale production in production mode, and narrow host range. , to achieve the effect of easy large-scale reproduction, convenient large-scale reproduction, and easy source of armyworms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
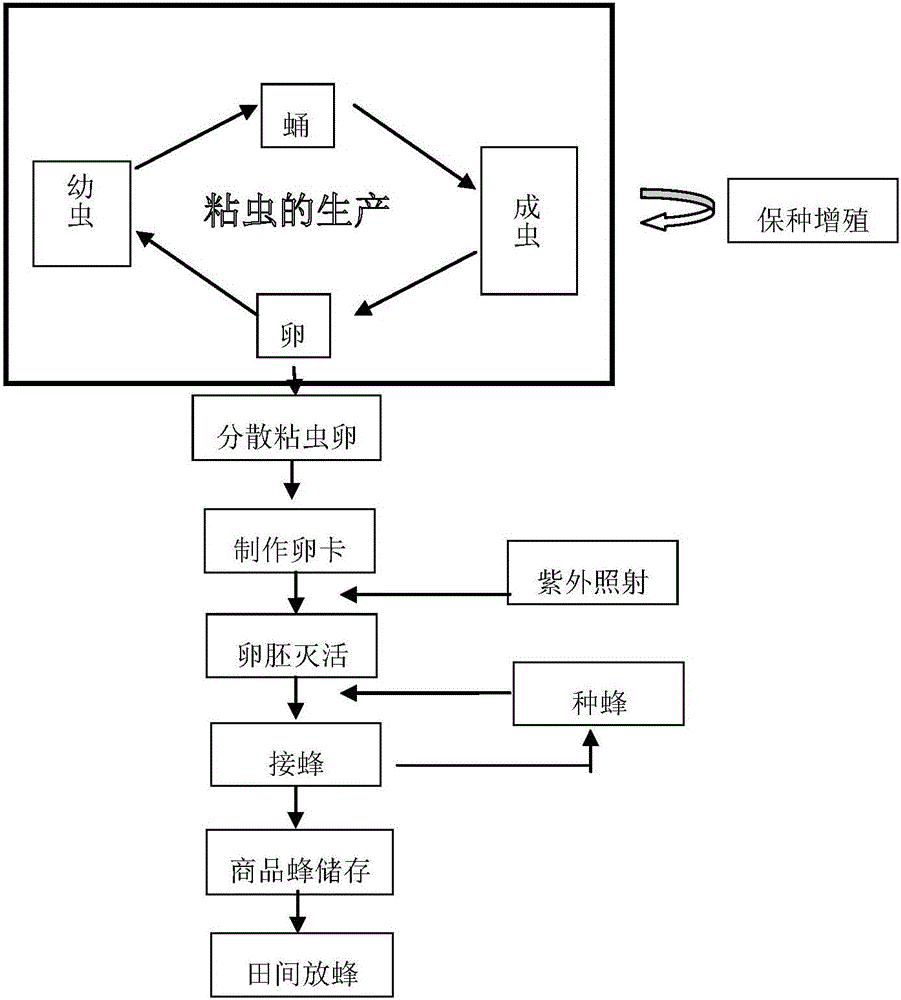
[0061] Embodiment 1 breeding Trichogramma rice borer
[0062] 1) Production of armyworm eggs
[0063] 1.1 For armyworm breeding, the temperature is controlled at 26±1°C and the humidity is about 65%.
[0064] 1.1 Raising larvae: place the soon-to-hatch armyworm eggs on one side of the insect tank, and add an appropriate amount of artificial feed to the other side, and cover with a lid with toilet paper to prevent the larvae from escaping. About 100 larvae per tank;
[0065] 1.2 When the larvae grow to the end of the 3rd instar, they are transferred to the large square box for feeding, and artificial feed is added; the number of larvae in each large square box can be adjusted according to the actual situation. Before pupation, there are about 100 larvae in each large square box. 18 days.
[0066] Before pupation, clean up excess feed and keep the box dry to make it pupate smoothly.
[0067] 1.3 Collect the pupae; about 2 days after the pupation is completed, clean up the ...
Embodiment 2
[0083] Embodiment 2 and the comparison of prior art and cost estimation
[0084] Trichogramma rice borer can parasitize the eggs of corn borer and armyworm, but the eggs of these two insects are in the form of lumps, which are not easy to remove from the egg-laying utensils to make egg cards, which limits the application; the life cycle of diamondback moth is short, and the reproduction Ligao can quickly expand the population in a short period of time and obtain a large number of eggs, but the eggs are small, resulting in a decline in the quality of the bred Trichogramma rice borer. Similarly, diamondback moth eggs are not easy to make egg cards and form standardization; Spodoptera litura The amount of eggs laid is large, and it is easy to make a standard egg card, but the Trichogramma rice borer cannot complete the development after being parasitized. Therefore, screening an alternative host with high production efficiency is an important basis for using Trichogramma as a b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com