Sulphur cycle-associated denitrifying enhanced biological phosphorus removal (SD-EBPR) utilizing sulphur compounds as electron carriers for biological nutrient removal of wastewater treatment
A technology of electronic carrier and sewage treatment method, applied in biological water/sewage treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, seawater treatment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] overview
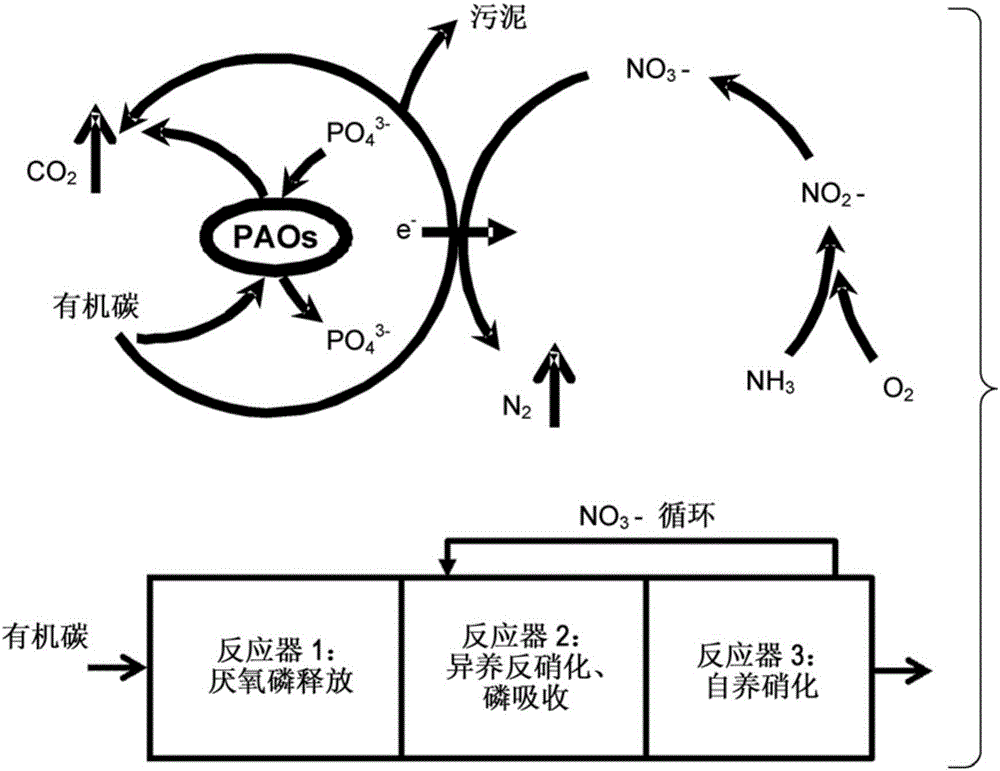
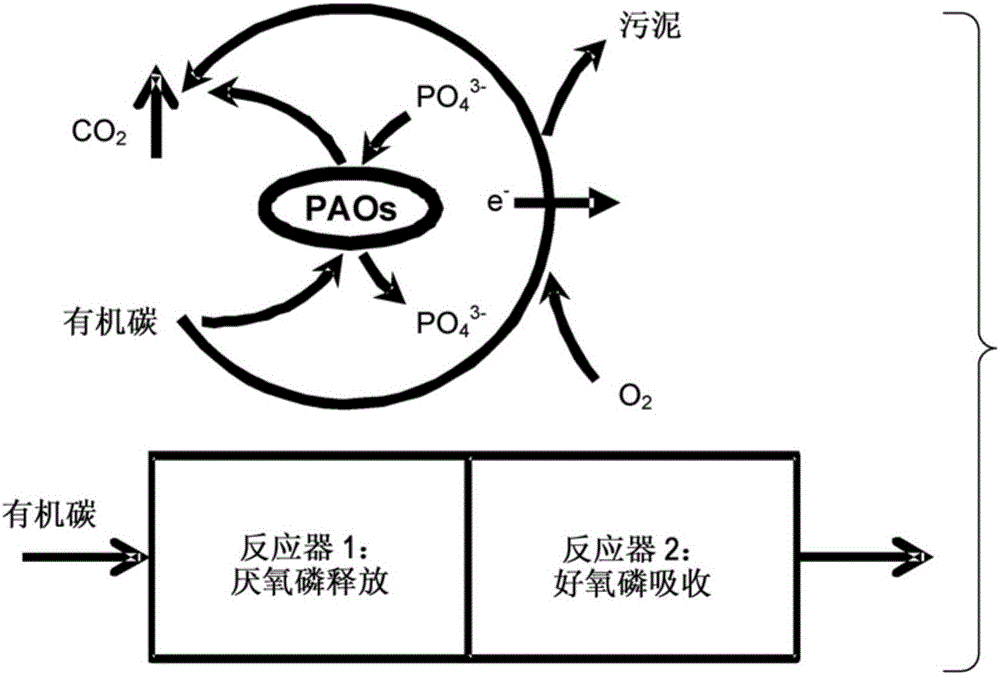
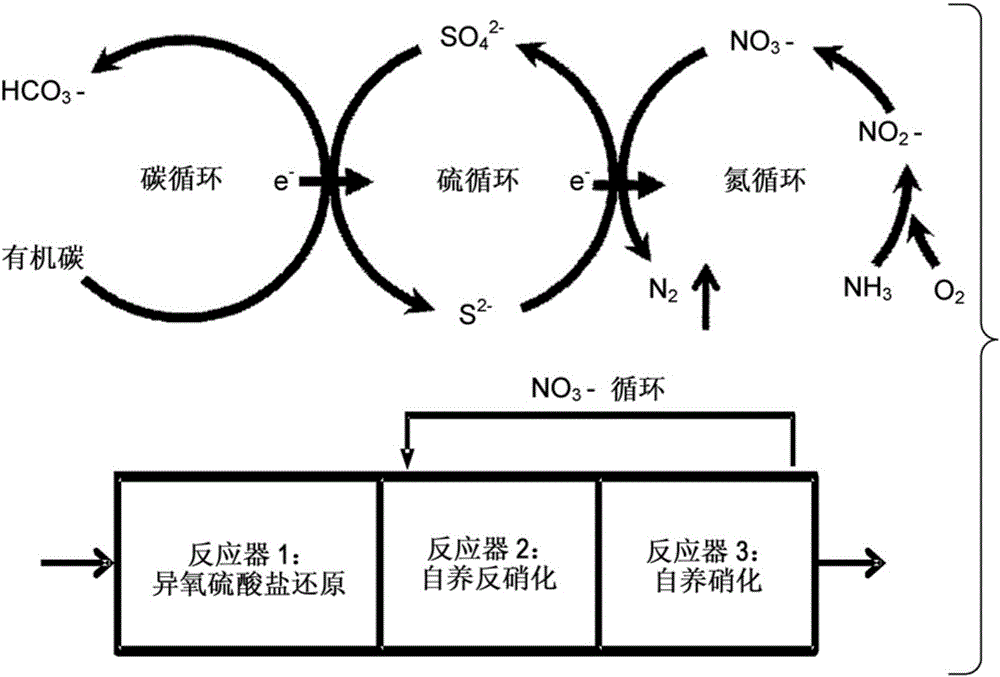
[0035] By introducing the sulfur cycle to the carbon oxidation cycle, develop a sulfur cycle-based denitrification-enhanced biological phosphorus removal (SD EBPR) process that can achieve biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal (BNR) while minimizing sludge generation . Figure 4 is an example of SD-EBPR technique for removing C, N and P. Various forms of elemental sulfur compounds, including sulfate (SO 4 2- ), sulfite (SO 3 2- ), Thiosulfate (S 2 o 3 2- ), sulfide (S 2- ) and elemental sulfur (S 0 ) (the above description is the main form of sulfur in water), can play the role of electron carriers, transfer electrons from organic carbon to oxygen, and its main biological processes include: phosphorus release and absorption, anaerobic Carbon uptake (storage of PHAs), heterotrophic sulfur reduction (storage of polymeric sulfide / sulfur element), heterotrophic / autotrophic denitrification, autotrophic nitrification; the above described process is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com