A horizontal axis wind turbine
A technology of wind power generator and horizontal axis, which is applied in the direction of wind power generator, wind power motor combination, wind power generator consistent with the wind direction, etc. It can solve the problem of low annual operating hours of wind power equipment, increased blade lift resistance, and incoming flow angle of attack. Small problems, to achieve the effect of broadening the range of effective working conditions, increasing the output torque, and improving the lift-to-drag ratio
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
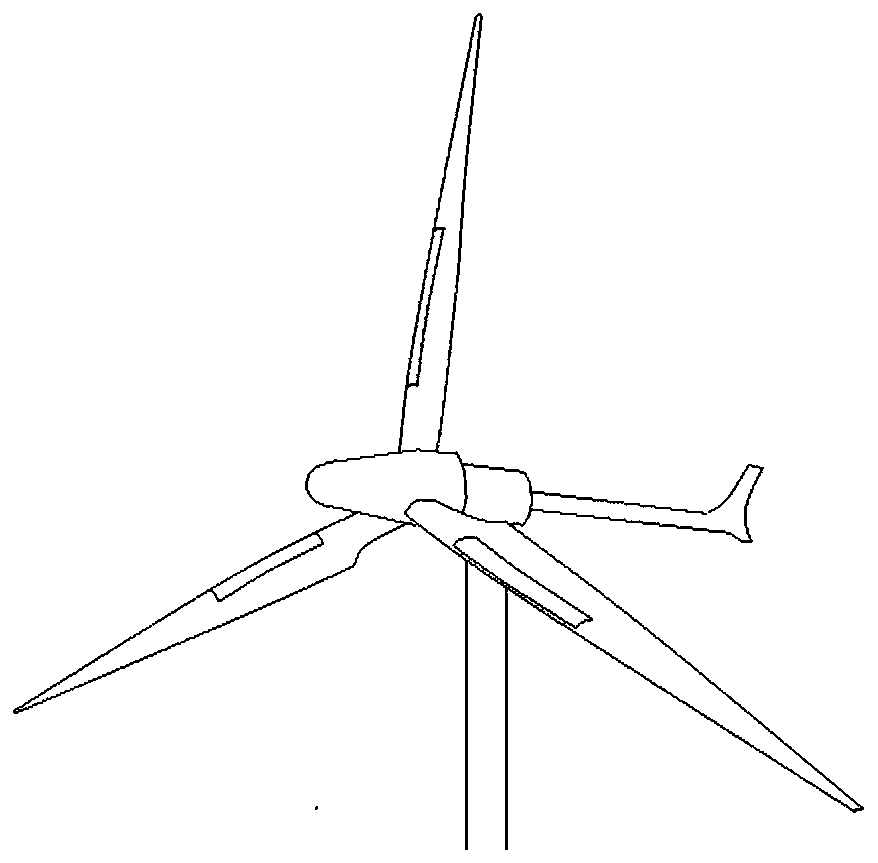
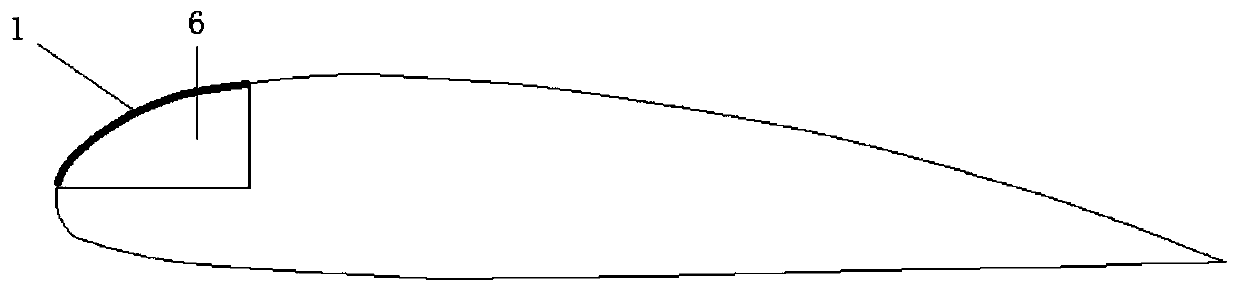
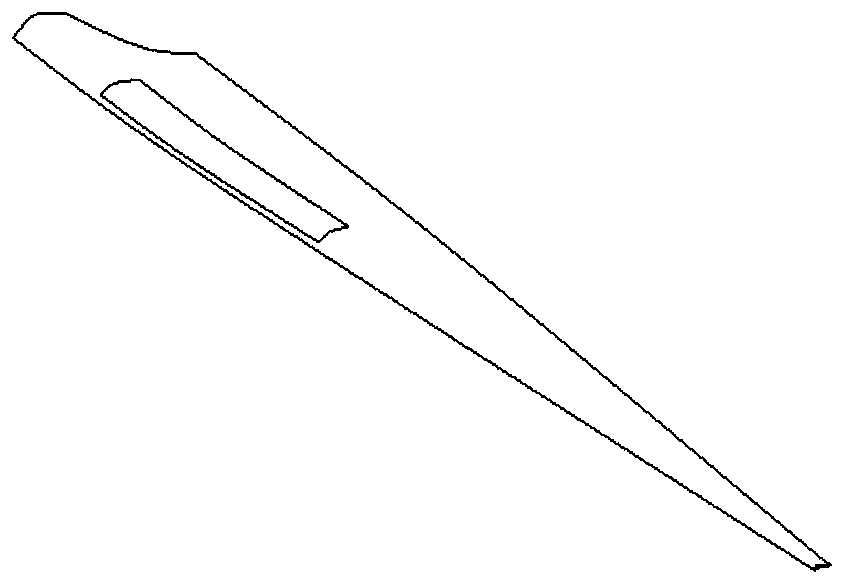
[0030] Such as figure 1 As shown, the wind generator includes a wind turbine, a gearbox, and a generator. The blades of the wind turbine include a rotating shaft and at least two blades. The rotating shaft is installed in a horizontal direction. A cavity 6 with a length of about 1 / 2 of the radial length of the blade is radially provided, figure 2 is a cross-sectional view of a wind turbine blade with a cavity, image 3 It is a schematic diagram of a wind turbine blade with a cavity and a flexible membrane structure. The opening of the cavity 6 is covered with a flexible membrane 1 having the same shape as the cavity opening, and the edge of the flexible membrane 1 is tightly fixed to the edge of the opening of the cavity 6 .
[0031] The cavity 6 is a groove arranged in the blade, or a protrusion arranged on the surface of the blade, and the protrusion is a cavity structure.
[0032] Studies have shown that the lift generated by wind turbine blades mainly comes from the fro...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Such as Figure 4 As shown, it is basically the same as Embodiment 1, the difference is that an exciter 3 is also fixed inside the cavity 6, and a fixing device (such as a crankshaft) 4 on the exciter 3 is connected with one end of the spring 2, and the other end of the spring 2 One end is fixedly connected to the flexible membrane 1, and the spring 2 is stretched and compressed at a certain frequency through the exciter 3, so that the flexible membrane 1 also vibrates at this frequency. The frequency of the exciter 3 is adjustable from 0 Hz to 200 Hz, so that the frequency of the flexible membrane 1 can also be adjusted to adapt to the flow field and further optimize the flow field structure. Wind tunnel tests show that in the range of Ma number 0.01-0.1, the lift coefficient of wind turbine blades using this structural blade shape is increased by 42% compared with the rigid structure blade shape, and the drag coefficient can be reduced by up to 56%.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Such as Figure 5 As shown, it is basically the same as that of Embodiment 1, except that an airbag 5 with a volume adapted to the cavity is also provided inside the cavity 6. On the one hand, the airbag 5 can play the role of supporting the flexible membrane 1 flexibly. On the one hand, the vibration performance of the flexible membrane 1 can be improved. Further, the airbag 5 can be inflated and deflated, and the effect of changing the shape of the blade can be achieved by inflating and deflated the airbag 5 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com