A kind of chromium-free passivating agent and its preparation method and application
A chromium-free passivation agent and solution technology, applied in the direction of metal material coating process, etc., can solve the problems of increased silicon content, phosphorus pollution, unstable passivation solution, etc., and achieve passivation performance improvement, less side reactions, and corrosion. The effect of current reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] First, the electrolytic manganese is prepared in a diaphragm tank by electrolysis: stainless steel is used as the cathode plate, and a lead-silver alloy plate is used as the anode plate. Electrolysis conditions: ammonium sulfate 120g / L, manganese sulfate 36.91g / L, selenium dioxide 0.05g / L catholyte, catholyte pH is about 6.8~7.0, current density is 350A / m 2 , the electrolysis temperature was 38°C, and the electrolysis time was 1.5h. The prepared electrolytic manganese product was used for subsequent passivation experiments and performance evaluation of the passivation layer.
[0049] The percentage by weight of each component of the passivator is: stearic acid 16.4%, stearic acid diethanolamide 81.9%, ascorbic acid 1.7%. Stearic acid, stearic acid diethanolamide and water are heated and stirred at 80° C. to dissolve first, and then ascorbic acid is added to stir and dissolve to obtain a chromium-free passivation solution (concentration: 3%) for surface treatment of elec...
Embodiment 2
[0079] The preparation of electrolytic manganese metal is the same as in Example 1.
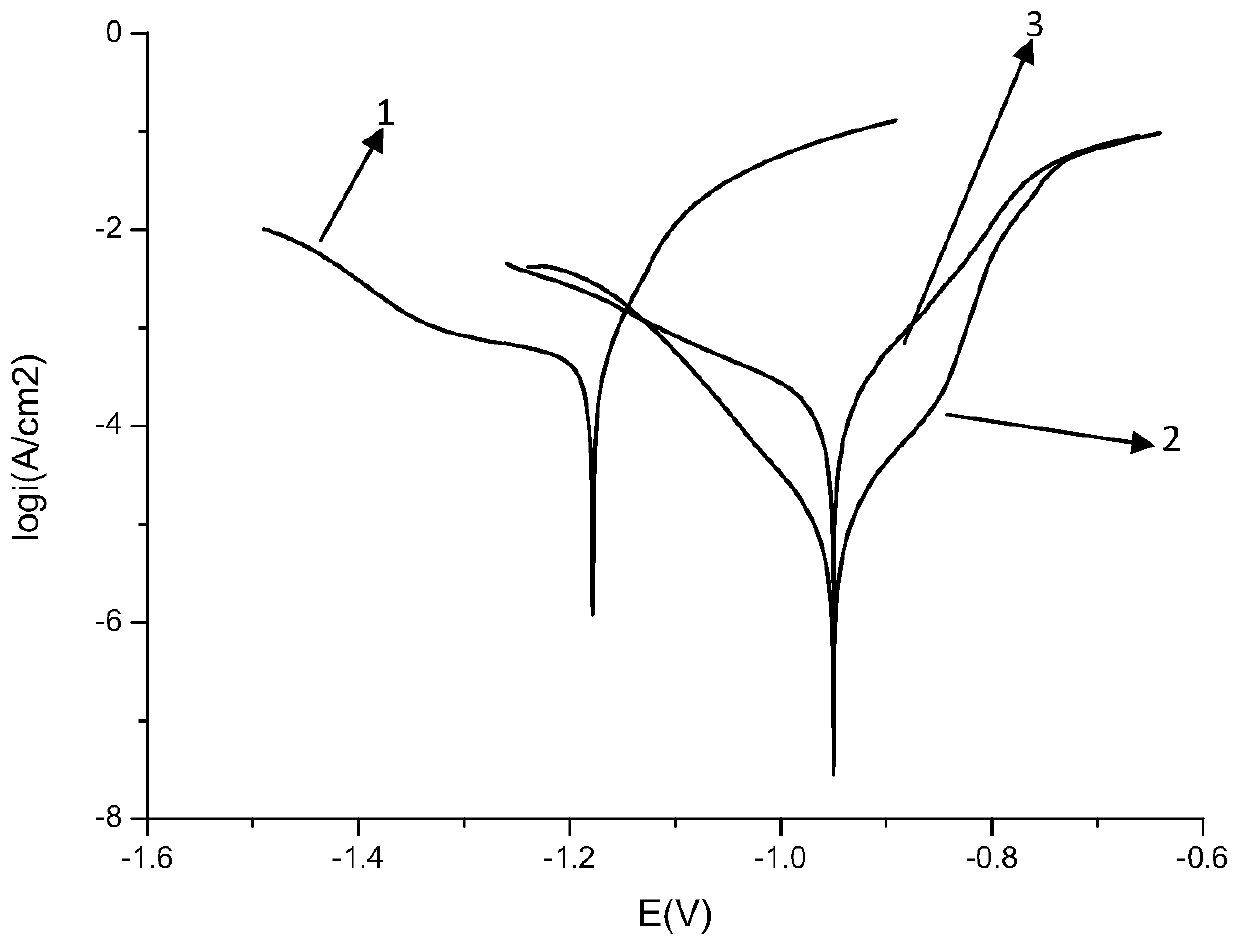
[0080] The percentage by weight of each component of the passivator is: 16% of lauric acid, 82.4% of oleic acid diethanolamide, and 1.6% of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid. First, lauric acid, oleic acid diethanolamide and water were heated and stirred at 80° C. to dissolve, and then ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid was added to obtain a chromium-free passivation solution (concentration: 3%) for surface treatment of electrolytic manganese metal. The passivation agent was used to conduct passivation and electrochemical performance tests on electrolytic manganese, and the polarization curve results are shown in Table 5.
[0081] Table 5 lauric acid and other passivation polarization curve results
[0082]
[0083] In the potassium permanganate nitric acid drop test, the discoloration time of the potassium permanganate drop was 87s.
Embodiment 3
[0085] The preparation of electrolytic manganese metal is the same as in Example 1.
[0086] The percentage by weight of each component of the passivator is: 16% of palmitic acid, 82.4% of stearic acid diethanolamide, and 1.6% of triethanolamine. Palmitic acid, stearic acid diethanolamide and water are heated and stirred at 80° C. to dissolve, and then triethanolamine is added to obtain a chromium-free passivation solution (concentration: 3%) for surface treatment of electrolytic manganese metal. The passivation solution was used to conduct passivation and electrochemical performance tests on electrolytic manganese, and the polarization curve results are shown in Table 6.
[0087] Table 6 Passivation polarization curve results
[0088]
[0089] In the potassium permanganate nitric acid drop test, the discoloration time of the potassium permanganate drop was 79s.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com