A water-resistant and degradable plant nutrient slow-release material and its preparation method
A slow-release material and nutrient technology, applied in organic fertilizers, fertilizer mixtures, agriculture, etc., can solve the problems of multiple fertilization and nutrient loss, and achieve the effects of easy degradation, load reduction, and industrialized large-scale production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] The water-resistant degradable plant nutrient sustained-release material of this embodiment is prepared as follows:
[0034] (1) Weigh 20 g of corn starch into 5 g of distilled water, then add 12 g of citric acid and 8 g of glycerin, stir evenly and then stand for 24 hours to obtain modified corn starch.
[0035] Add 45 g of modified corn starch to 10 mL of distilled water to prepare a starch solution; put the starch solution in a three-necked flask and stir while heating at 95°C for 0.5 h to obtain gelatinized starch;
[0036] Weigh 5 g of PVA, add 1.25 g of distilled water, heat to dissolve at 97°C, and cool the resulting solution to 80°C to prepare a PVA solution.
[0037] Add the PVA solution to the gelatinized starch, and then stir while heating at 95°C for 0.5h, and the resulting product is cooled to below 80°C to obtain the binder;
[0038] (2) Measure 2mL of glacial acetic acid in a 100mL volumetric flask, dilute with distilled water to make the volume; add 2g of chitosan...
Embodiment 2
[0045] In this example, the nutritional sustained-release material was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the volume of the porogen DBP in step (3) was 12 mL.
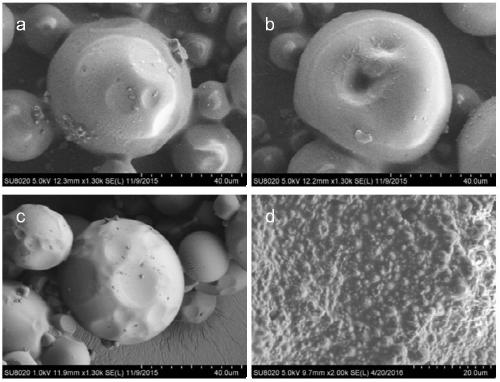
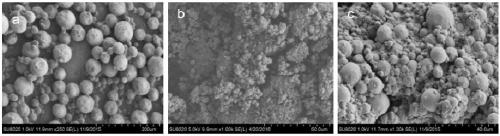
[0046] The scanning electron micrograph of the porous composite microspheres obtained in this example is as follows figure 1 (b) Shown.
Embodiment 3
[0048] In this example, the nutritional sustained-release material was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1, except that the volume of the porogen DBP in step (3) was 16 mL.
[0049] The scanning electron micrograph of the porous composite microspheres obtained in this example is as follows figure 1 (c) and figure 2 (a) Shown.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com