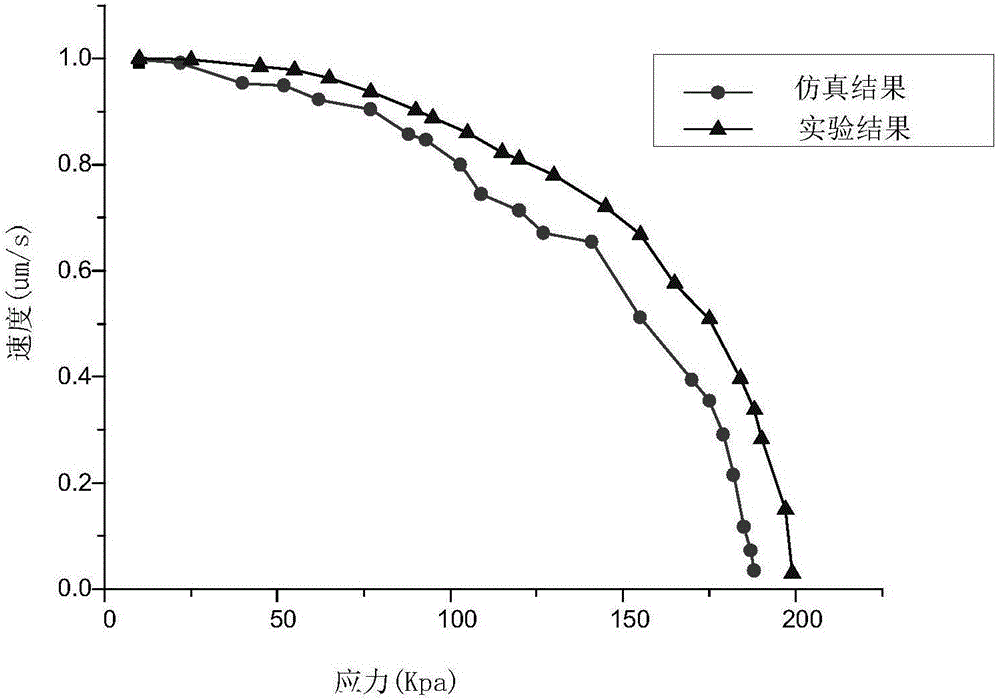
Method for establishing joint cartilage two-phase model on the basis of hyperelastic solid phase characteristics
A technology for articular cartilage and method of establishment, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., and can solve problems such as differences and failures of articular cartilage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0092] A method for establishing a two-phase model of articular cartilage based on superelastic solid phase properties, comprising the following steps:
[0093] Step 1, geometric model and mesh division:
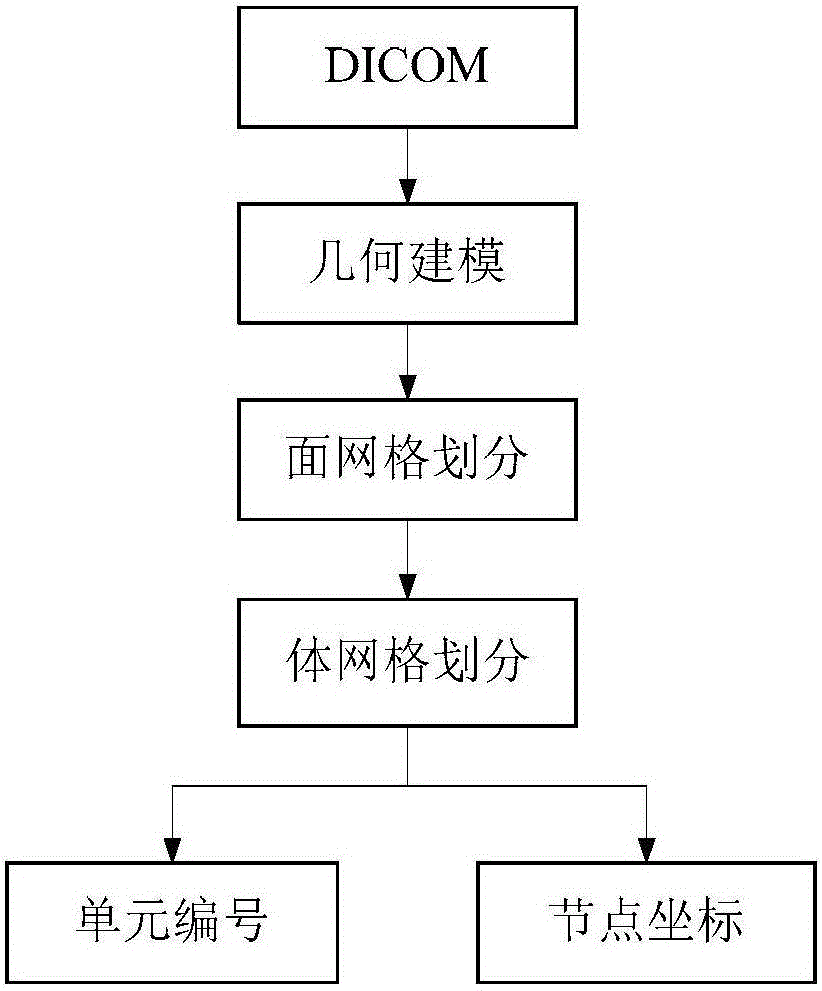
[0094] Taking the joint as the research object, by obtaining the CT data of the joint, the obtained data is output in DICOM format and stored in the computer; through the image segmentation function in MIMICS, the articular cartilage area in the CT data is separated from other tissues, and the three-dimensional Reconstruct the geometric model of the human tissue to be studied;
[0095] From DICOM data to generating the grid model and obtaining the model’s unit number and node coordinates as the original data for deformation calculation input, the acquisition process is as follows: figure 1 shown;
[0096] Step 2, establishing a two-phase model of articular cartilage based on the mixture theory and a control equation based on the v-p variable, including the following steps:...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0173] The specific process of establishing the articular cartilage mechanical balance equation in step 3.3 described in this embodiment is as follows:
[0174] The unit type of the finite element solution is tetrahedral unit, and the shape function is selected as the weight function of the differential equation and boundary conditions, and the weight functions in the weighted residual integral expression are respectively N J and -N J , to obtain the corresponding weighted residual expression, and the simplified weighted residual integral expression obtained through the Gauss divergence theorem and the definition of the total traction force is:
[0175] ∫ Ω { ▿ N J T : σ ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0192] The specific process of solving the articular cartilage mechanical balance equation described in step 3.4 of the present embodiment is as follows:
[0193] Numerical calculation of articular cartilage mechanical balance equation (34) by finite difference method:
[0194] First, the incremental method is used in the time domain to discretize the time t into several time points, namely:
[0195] 0=t 0 1 n n+1 N =t (35)
[0196] The time increment is expressed as:
[0197] Δt n+1 = t n+1 -t n (36)
[0198] Using the complete Lagrangian method, let the initial time t 0 = 0 as the reference configuration, and the reference configuration does not change with time; at t n+1 Moment formula (34) is written as:
[0199] Y n+1 v n+1 +M n+1 = f n+1 (37)
[0200] By the Newton-Raphson method, the linearized form of M is obtained by the following recursion:
[0201] M n ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com