Self-heating film based on graphene fiber nonwovens
A graphene fiber, non-woven technology, applied in the direction of fiber chemical characteristics, wet spinning, non-woven fabrics, etc., can solve the problems of low saturation temperature, slow heating speed, and high working voltage, and achieve high saturation temperature, temperature rise and The effect of fast cooling rate and high saturation temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] (1) A graphene oxide dispersion liquid with a concentration of 5 mg / mL is prepared, and the solvent is N, N-dimethylformamide, and it is used as a spinning solution.
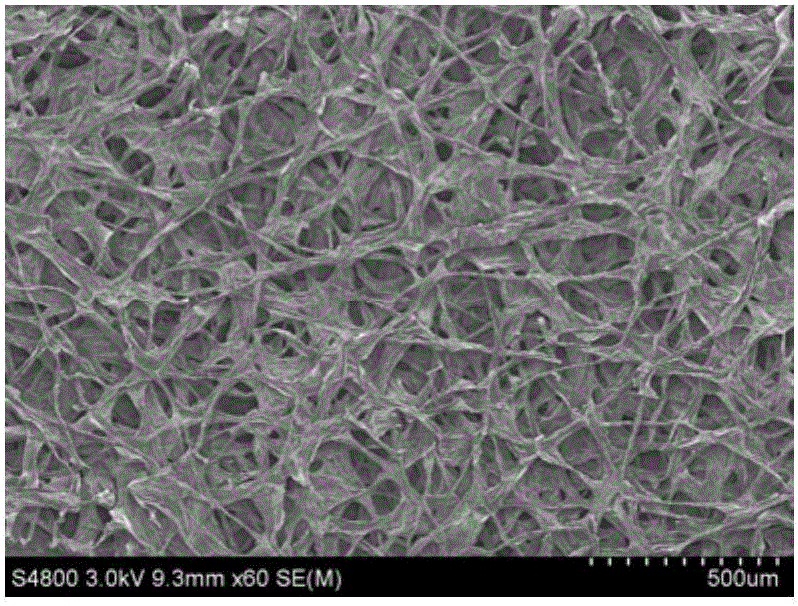
[0030] (2) Make the spinning solution enter the ethyl acetate rotating coagulation solution through a spinning tube with a diameter of 130 μm at an extrusion speed of 0.04 mL / min, soak in the coagulation solution for 30 minutes, and solidify into graphene oxide short fibers with a length of more than 2 mm , collected by vacuum filtration, placed at room temperature for 10 h, and vacuum-dried at 60° C. for 3 h to obtain a film composed of graphene oxide fibers.
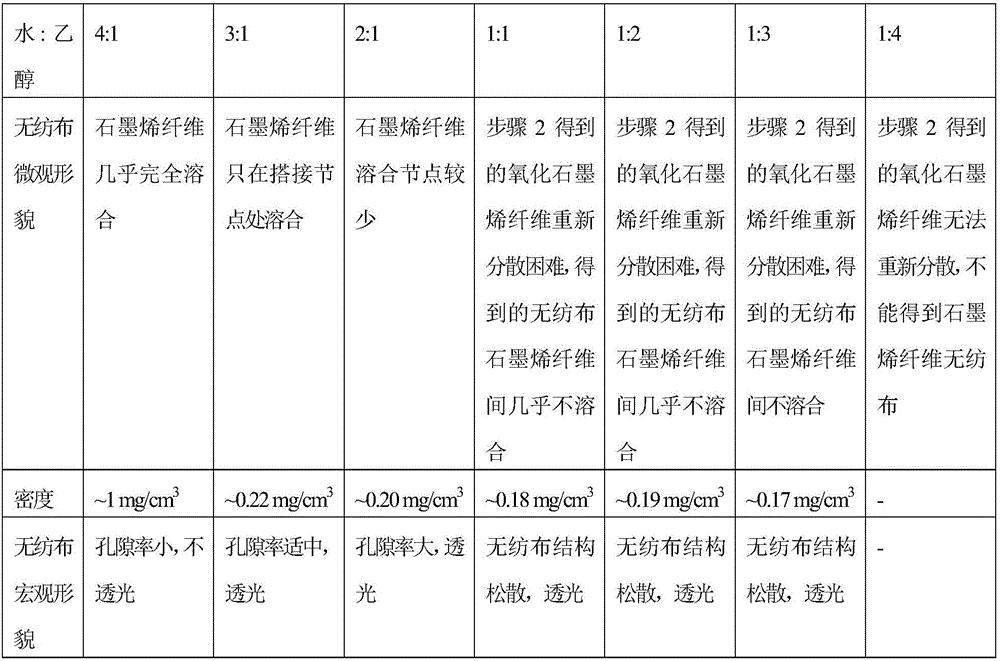
[0031] (3) the film obtained in step 2 is redispersed in water and ethanol in the mixed solution formed by the volume ratio shown in Table 1 to obtain the suspension of graphene oxide fiber, which is filtered and deposited through a filter screen, and graphite oxide is obtained on the filter screen Graphene oxide fiber non-woven fabric; the graphe...
Embodiment 2
[0039] (1) A graphene oxide dispersion liquid with a concentration of 5 mg / mL is prepared, and the solvent is N, N-dimethylformamide, and it is used as a spinning solution.
[0040] (2) Let the spinning liquid enter the ethyl acetate rotating coagulation liquid through a spinning tube with a diameter of 200 μm at an extrusion speed of 0.06 mL / min, soak in the coagulation liquid for 30 minutes, collect it by vacuum filtration, place it at room temperature for 10 hours, and vacuum at 60 ° C. Dry for 3 hours to obtain a film composed of graphene oxide fibers.
[0041](3) redisperse the film obtained in step 2 in water and ethanol in a mixed solution of 3:1 by volume to obtain a suspension of graphene oxide fibers, filter and deposit through a filter screen, and obtain graphene oxide fibers without Woven fabric; the graphene oxide fiber non-woven fabric was washed three times with ethanol and dried at 80°C.
[0042] (4) The graphene oxide fiber non-woven fabric after drying is ob...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Steps 1-5 are the same as in Example 1.
[0048] (6) Paste the 2V solar cells encapsulated in the polymer film on the surface of the graphene fiber non-woven fabric, and connect the electrodes of the photovoltaic film and the non-woven fabric with wires, and install a switch on one side of the circuit, thus obtaining a flexible self- hot film.
[0049] After the above steps, the heating temperature of the obtained self-heating film is 50°C, and the heating rate is 55°Cs when the power is turned on. -1 , the cooling rate is 58℃s when the power is off -1 . When the self-heating film is bent, the heating temperature and rate remain unchanged.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com