Artificial muscle-driven and structurally decoupled robotic joints
A technology of robotic joints and artificial muscles, applied in manipulators, manufacturing tools, program-controlled manipulators, etc., can solve problems such as nonlinear stiffness, low-frequency flutter, and increase the difficulty of control, avoiding interference, high stiffness, and low stiffness. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
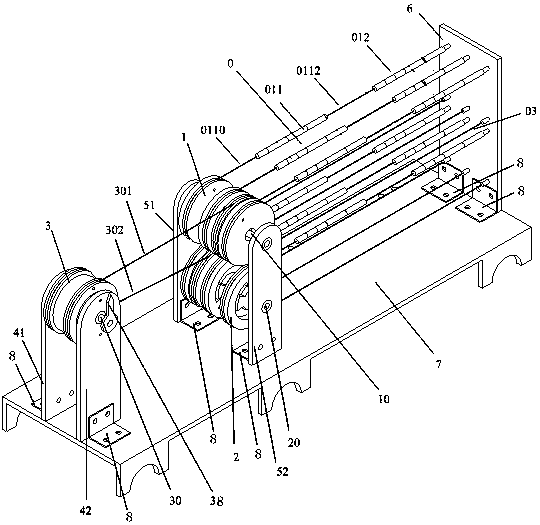
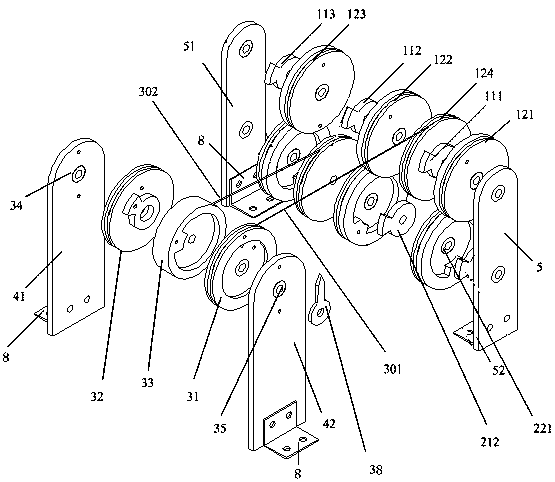
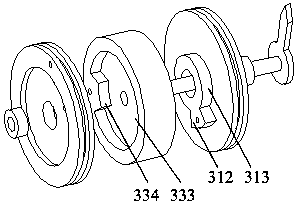
[0030] The present invention adopts the SMA spring as the artificial muscle actuator unit. Since the SMA spring has only two states of contraction and relaxation, in the contraction state, the stiffness is large, and in the relaxation state, the stiffness is small; according to the electrothermal driving characteristics of the SMA spring, by controlling the SMA spring The current of each SMA spring in the spring group is turned on and off to drive the auxiliary joint drive wheel set connected to it, and then drive the main joint drive wheel set to turn a certain angle to realize joint control. The artificial muscle group of the present invention is a series-parallel structure , in this embodiment, it is composed of 12 SMA springs, 6 groups are arranged in parallel and each group is arranged in series, 3 groups of artificial muscles are distributed in each of the two auxiliary joint pulley groups, and the SMA springs are connected by artificial ligament units, as As a special ca...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com