Method and device for calculating arterial oxygen saturation through addition of dual-wavelength absolute differences
An absolute difference, dual-wavelength technology, applied in the field of arterial oxygen saturation calculation, can solve the problems of reduced optical path length, complicated calculation, difficult pulse wave positioning, etc. Ability-enhancing effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
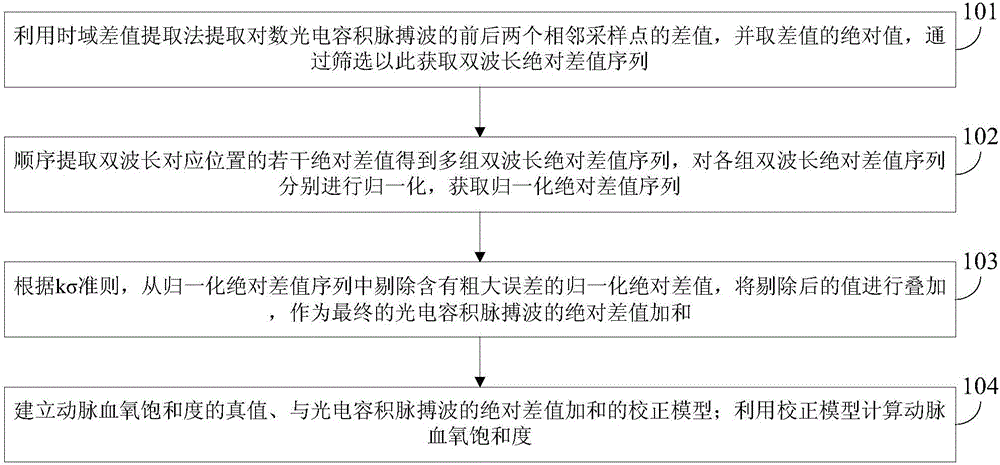
[0064] In order to solve the deficiencies in the dynamic spectrum frequency domain extraction method, the time domain single shot extraction method and the time domain difference value extraction method, the embodiment of the present invention provides a method for calculating the arterial blood oxygen saturation by summing the absolute difference of two wavelengths, see figure 1 , see the description below:
[0065] 101: Using the time-domain difference extraction method to extract the difference between two adjacent sampling points before and after the logarithmic photoplethysmography, and take the absolute value of the difference, and obtain a dual-wavelength absolute difference sequence by screening;
[0066] 102: Sequentially extract a number of absolute differences at positions corresponding to the dual wavelengths to obtain multiple sets of dual-wavelength absolute difference sequences, and perform normalization on each set of dual-wavelength absolute difference sequenc...
Embodiment 2
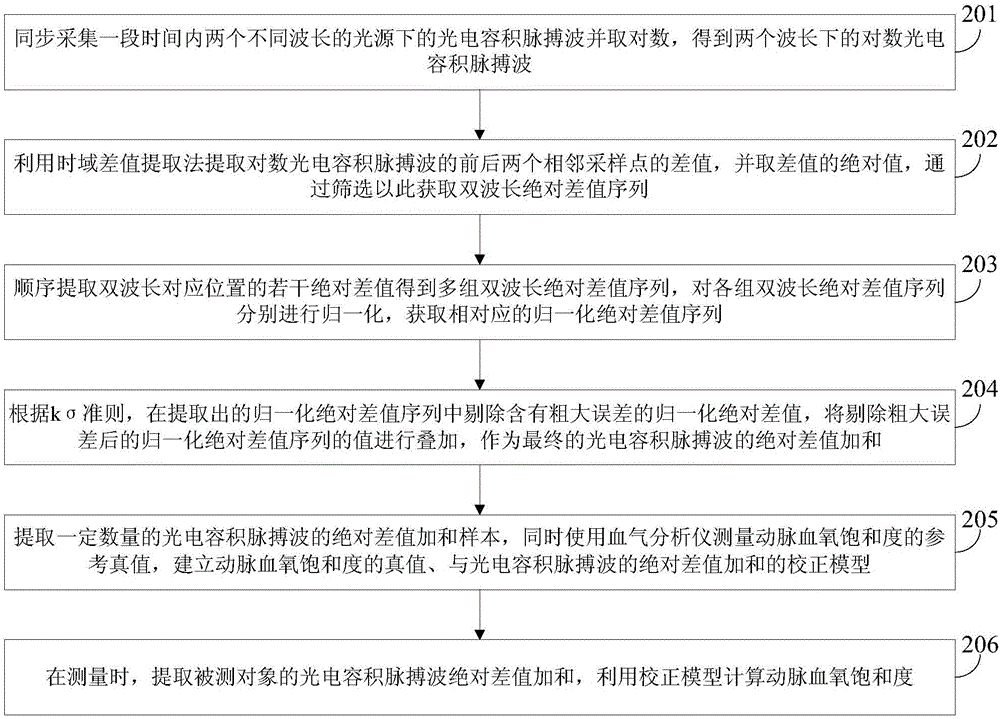
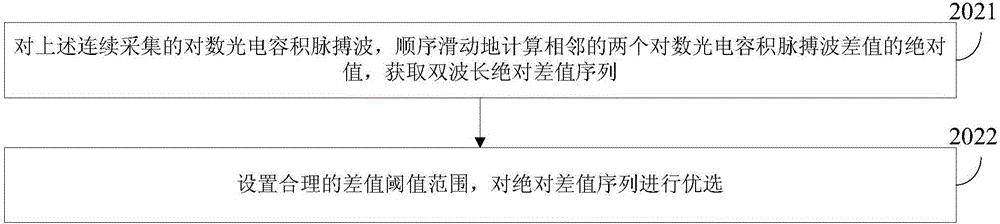
[0080] Combine below figure 1 , figure 2 , the scheme in embodiment 1 is further introduced, see the following description for details:
[0081] 201: Synchronously collect photoplethysmography waves under two different wavelength light sources within a period of time and take logarithms to obtain logarithmic photoplethysmography waves at two wavelengths;
[0082] Wherein, the concrete operation of step 201 comprises the following steps:
[0083] The two light sources with different wavelengths may be anti-parallel light emitting diodes, common anode light emitting diodes or common cathode light emitting diodes, which are not limited in this embodiment of the present invention during specific implementation.
[0084] In practical applications, the manner of driving the LEDs may be time-division driving or frequency-division driving, which is not limited in this embodiment of the present invention.
[0085] Further, the manner of driving the above light-emitting diodes may b...
Embodiment 3
[0119] An embodiment of the present invention provides a device for calculating the arterial blood oxygen saturation by summing the absolute difference of two wavelengths, the device is partly corresponding to the methods in Examples 1 and 2, see Figure 5 , the device consists of:
[0120] The first acquisition module 1 uses the time-domain difference extraction method to extract the difference between two adjacent sampling points before and after the logarithmic photoplethysmography, and takes the absolute value of the difference, and obtains the dual-wavelength absolute difference by screening sequence;
[0121] The second acquisition module 2 is used to sequentially extract a number of absolute differences at the corresponding positions of the dual wavelengths to obtain multiple sets of dual-wavelength absolute difference sequences, and to normalize each set of dual-wavelength absolute difference sequences to obtain normalized absolute differences sequence of values;
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com