Traveling wave fault locating method based on multi-measuring-information
A technology of traveling wave fault and localization method, which is applied in directions such as fault locations to enhance redundancy and accuracy, prevent ranging failures, and save equipment investment costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
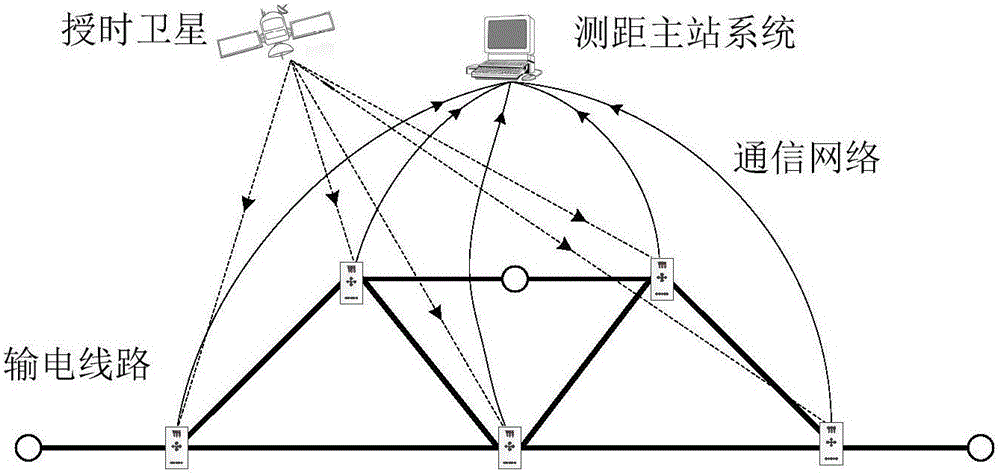
[0028] A traveling wave fault location method based on multi-measurement information, the steps of which are as follows:
[0029] 1) Optimize the configuration of the traveling wave measurement units in the power grid in advance, the traveling wave positioning master station collects the traveling wave data collected by each measurement unit, and selects the data of some measurement units as the information domain of fault location, that is, the fault distance calculation data source;
[0030] 2) Decoupling the phase-mode transformation of the traveling wave signal to obtain the linear mode and zero mode. The trained neural network obtains the zero-mode wave velocity, and preliminarily estimates the time difference between the initial wave head of the zero-mode and line-mode components arriving at the same detection point. fault distance;
[0031] 3) Preliminarily estimate i fault distances based on the traveling wave data recorded by i measurement units in the information do...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com