Recombinant microorganism of genus escherichia with l-threonine productivity, and method for producing l-threonine using same
A technology of microorganisms and threonine, applied in the direction of recombinant DNA technology, bacteria, peptides, etc., can solve the problems of no production relationship, high homology of galP gene, etc., and achieve improved productivity, high yield, and increased growth speed Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0039] The present invention also provides a preparation method of L-threonine, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: cultivating the transformed recombinant microorganism belonging to the genus Escherichia; and isolating L-threonine from the microorganism culture solution.
[0040] Cultivation of the recombinant microorganism belonging to the genus Escherichia of the present invention can be carried out by a conventional method. Specifically, raw sugar can be contained in whole or in part or glucose as a carbon source medium to inoculate the microorganisms and culture. The culturing process can be performed under appropriate media and culture conditions known in the art. Such culture procedures can be easily adjusted and used by those skilled in the art according to the selected strain. Examples of the culture method include batch culture, continuous culture and fed-batch culture, but are not limited thereto. The medium used in the cultivation should s...
Embodiment 1
[0066] Example 1: Production of recombinant vectors comprising iolT1 and iolT2 genes derived from coryneform bacteria
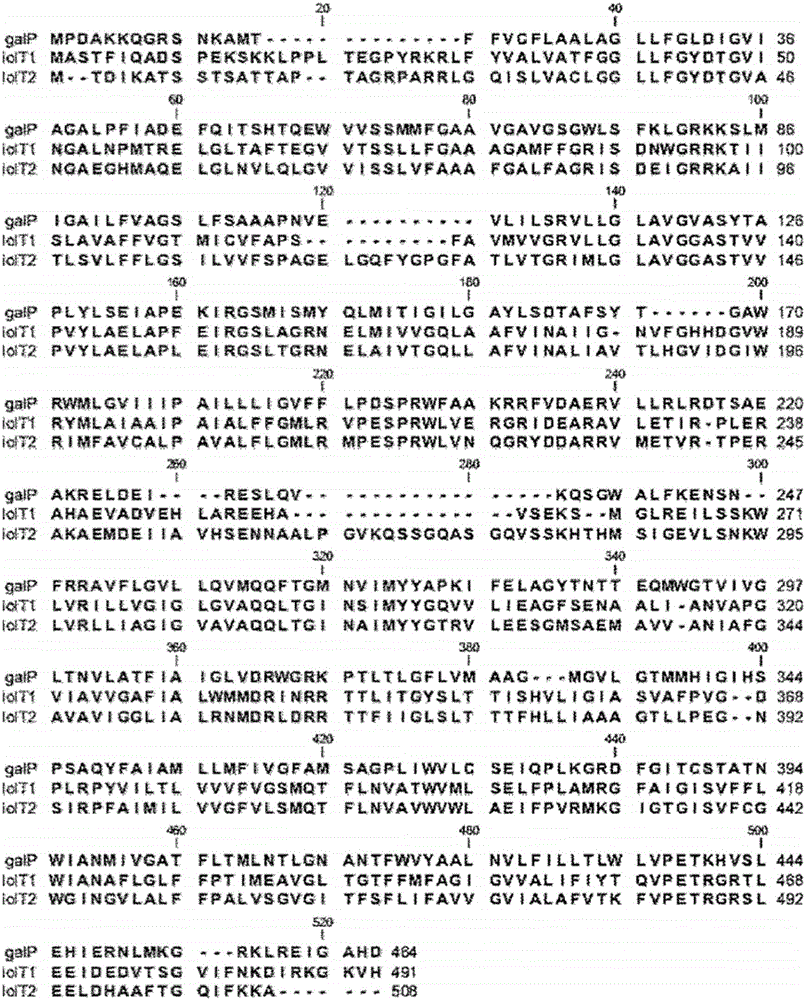
[0067] (1) Homology comparison with Escherichia coli glucose permease (galP)
[0068] It has been reported that the iolT1 and iolT2 genes encoding inositol permease in Corynebacterium glutamicum have similar homology to the galP gene encoding glucose permease in Escherichia coli. From the genome of wild-type Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032, a gene homologous to the galP gene derived from Escherichia coli was found and compared, and the results are shown in figure 1 middle.
[0069] The amino acid sequence encoded by galP derived from Escherichia coli showed 34% homology with the amino acid sequence encoded by iolT1 derived from Corynebacterium glutamicum, and showed 31% homology with the amino acid sequence encoded by iolT2.
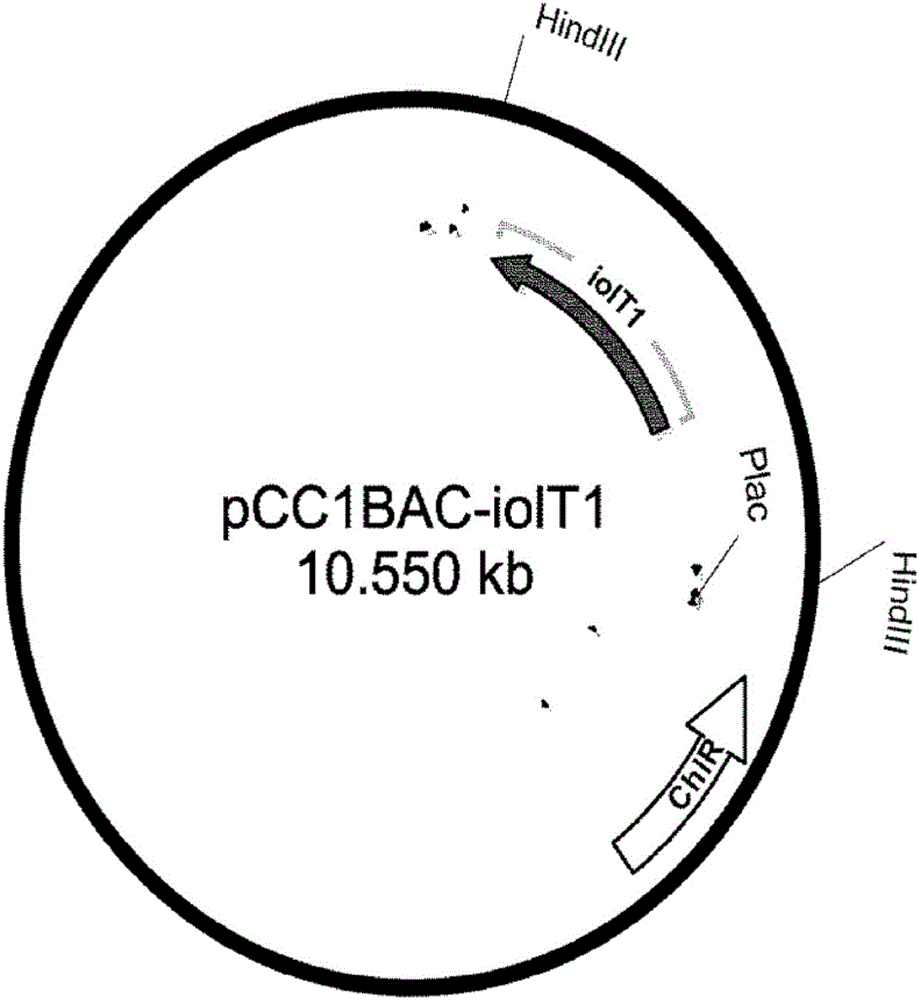
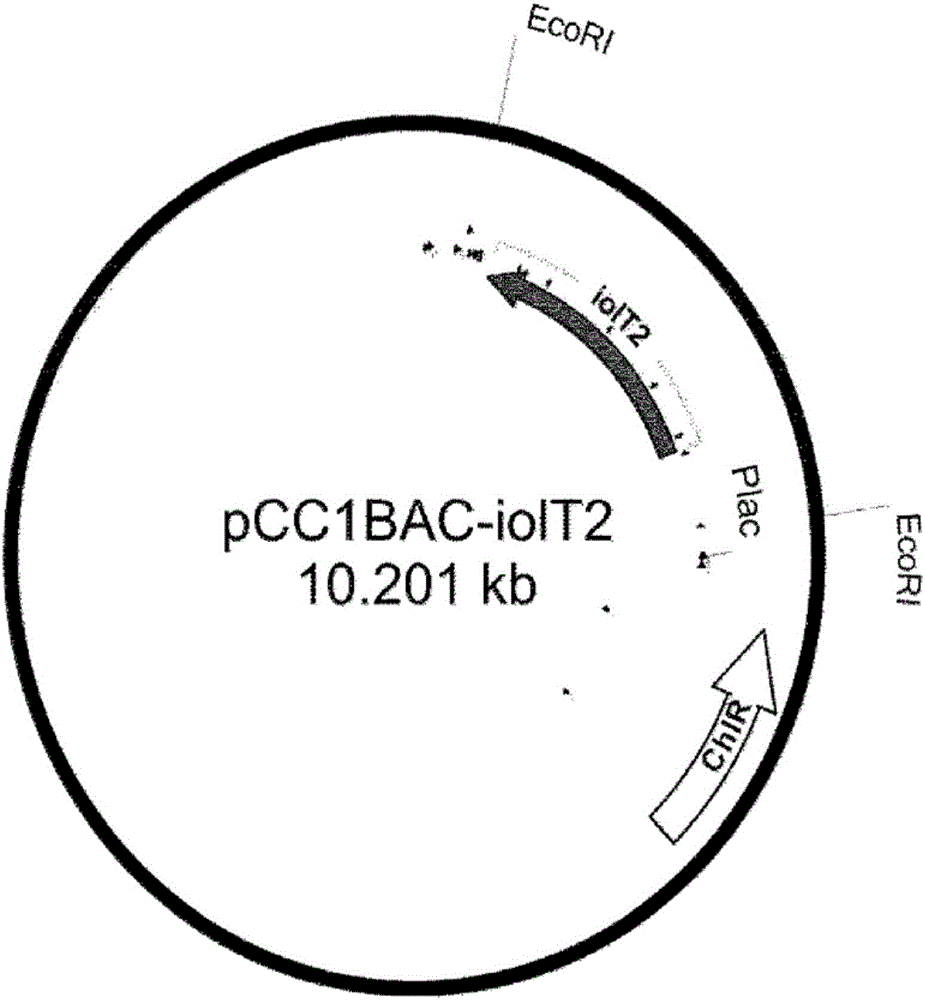
[0070] (2) Production of iolT1 gene fragment
[0071] In order to obtain a 1.5kb fragment comprising the open reading frame...
experiment example 2
[0085] Experimental example 2: Preparation of transformed recombinant strains and comparison of L-threonine productivity
[0086] (1) Preparation of recombinant strains utilizing wild-type Escherichia coli
[0087] The recombinant vectors pCC1BAC-iolT1, pCC1BAC-iolT2, and pCC1BAC-iolT1-iolT2 prepared in Example 1 were introduced into the overexpression vector pBRThrABCR3 (LeeKH et al., Molecular Systems In the wild-type Escherichia coli MG1655 of Biology (2007) 3:149), the Escherichia coli was spread on a solid medium containing 100 μg / ml ampicillin and 15 μg / ml chloramphenicol, and a single colony was selected.
[0088] The selected strains were named MG1655 / pBRThrABCR3 / pCC1BAC-iolT1, MG1655 / pBRThrABCR3 / pCC1BAC-iolT2 and MG1655 / pBRThrABCR3 / pCC1BAC-iolT1-iolT2, respectively.
[0089] The L-threonine productivity of these strains was confirmed by the same method as (3) of Comparative Example 1 using the threonine titer medium prepared according to the composition of Table 1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com