Primers, probe and method for rapidly distinguishing HP-PRRS (High pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome) vaccine strain GDr180 from HP-PRRS wild strain
A wild strain, rapid technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, recombinant DNA technology, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems of difficulty in popularization and use, loss of pig farming, low cure rate, etc., and achieve repeatability Good, fast detection speed, good specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1 A primer and probe for rapidly distinguishing the highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome live vaccine GDr180 strain from wild strains
[0045] 1) FMCA primers:
[0046] After screening a large number of primers designed, it was found that the base sequences of the primers SEQ ID NO: 1 and SEQ ID NO: 2 have the best effect on the FMCA method for distinguishing the HP-PRRSV vaccine GDr180 strain from the wild strain. As follows.
[0047] P1: 5'-GGTTGACATGCTGACTTG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 1),
[0048] P2: 5'-CACTGAACCAATGGTGAG-3' (SEQ ID NO: 2).
[0049] 2) Probe
[0050] After screening a large number of designed probes, it was found that the base sequence of the probe, SEQ ID NO: 3, had the best effect on the FMCA method for distinguishing the HP-PRRSV vaccine GDr180 strain from wild strains, and its base sequence is shown below.
[0051] Probe P: 5'-FAM-CCCAAGGATGATTCTCGAGACACCG-BHQ1-3' (SEQ ID NO: 3), or its nucleotide reverse complement. ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2 A detection method for rapidly distinguishing the highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome live vaccine GDr180 strain from wild strains
[0053] FMCA Analysis of Standard Samples
[0054] 1) Extraction of PRRSV standard nucleic acid:
[0055] Take HP-PRRSV vaccine GDr180 strain, add 3mL PBS hydrochloric acid buffer solution to dissolve, take HP-PRRSV wild virus GD strain cell culture solution, take 200μL respectively, and perform nucleic acid extraction according to the instructions of TAKARA's MiniBEST Viral RNA / DNA Extraction KitVer.4.0 extract.
[0056] 2) FMCA operation steps for positive standard samples
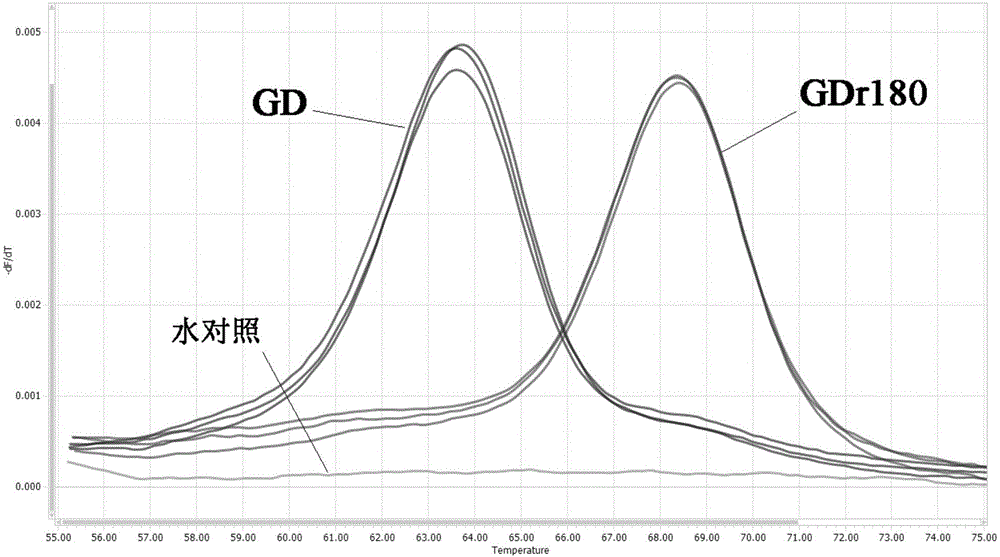
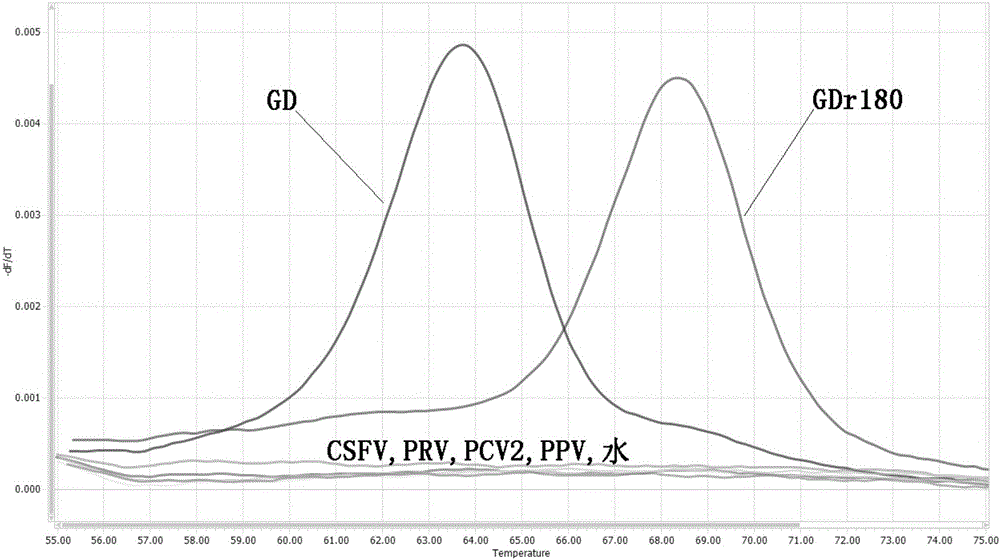
[0057] In order to verify the ability of the designed primers and probes to identify actual samples, HP-PRRSV vaccine strain GDr180 and HP-PRRSV wild virus GD strain were used as standard samples for FMCA analysis. The above-mentioned standard samples were used to extract nucleic acids as nucleic acid templates, and the FMCA am...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Example 3 A method for rapidly distinguishing the highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome live vaccine GDr180 strain from wild strains
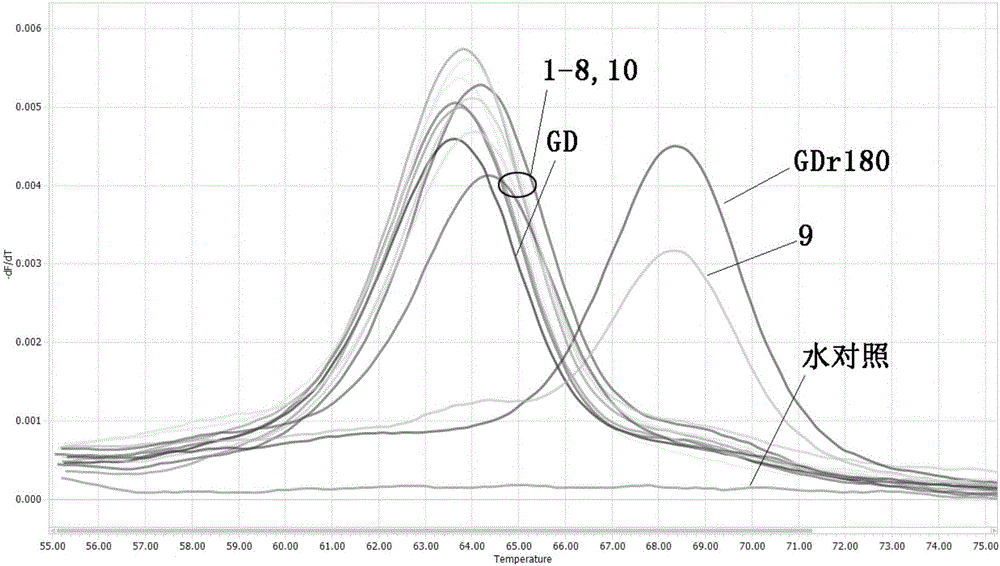
[0067] FMCA analysis of clinical samples
[0068] 1) Extract viral nucleic acid from samples: take 2g of pig lung tissue samples suspected to be infected with HP-PRRSV, add 3mL of PBS hydrochloric acid buffer solution for grinding, centrifuge the ground homogenate at 4000×g for 8 min, and absorb the centrifuged supernatant or 200 μL of serum samples; tissue sample homogenate and serum samples were subjected to nucleic acid extraction according to the instructions of TAKARA’s MiniBEST Viral RNA / DNA Extraction Kit Ver.4.0.
[0069] 2) Using the extracted viral nucleic acid as a template, perform FMCA analysis with the method described in Example 2 above, and the result analysis method is as follows:
[0070] With the standard GDr180 as the positive control, when the absolute value of the melting peak ∆Tm value be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com