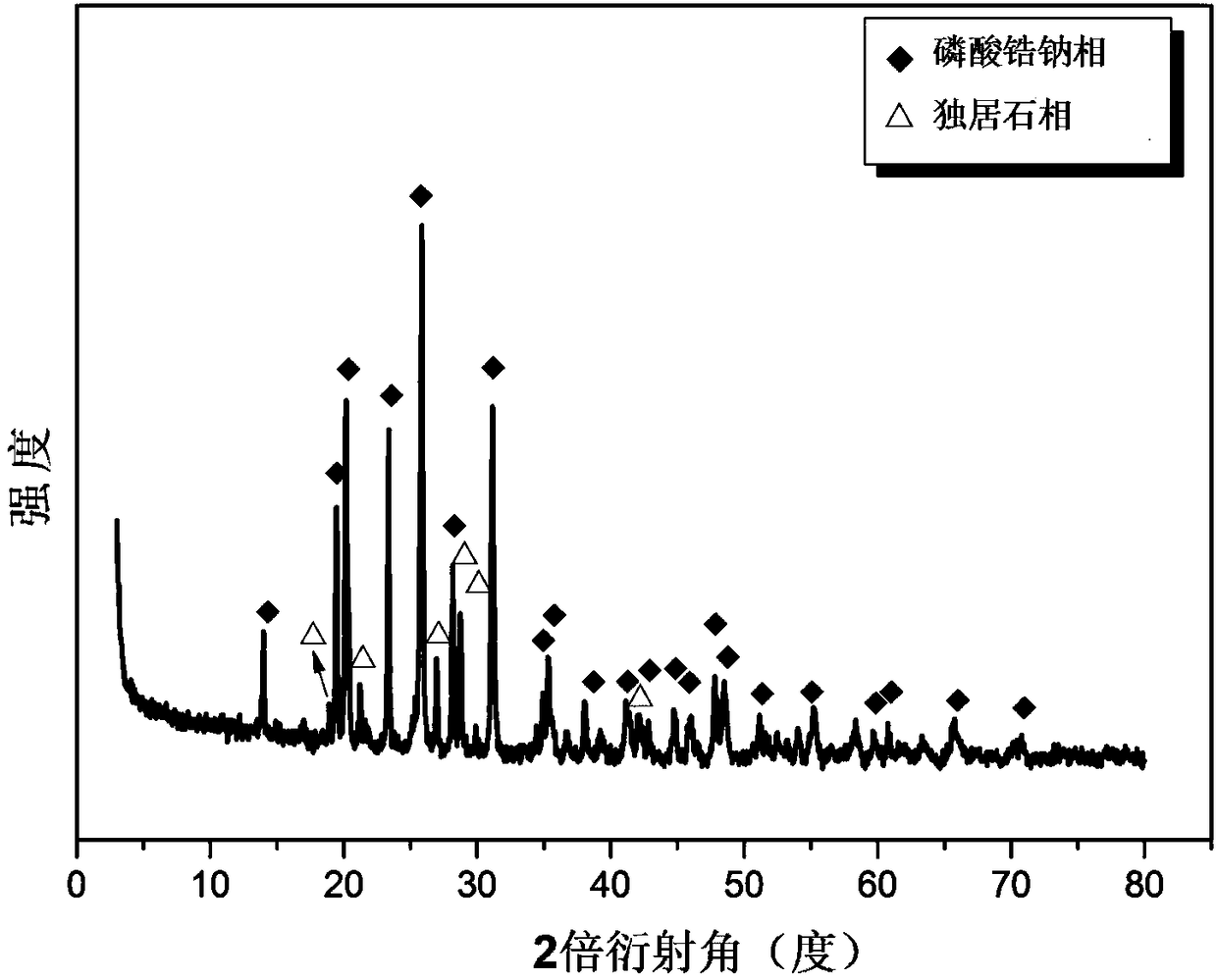
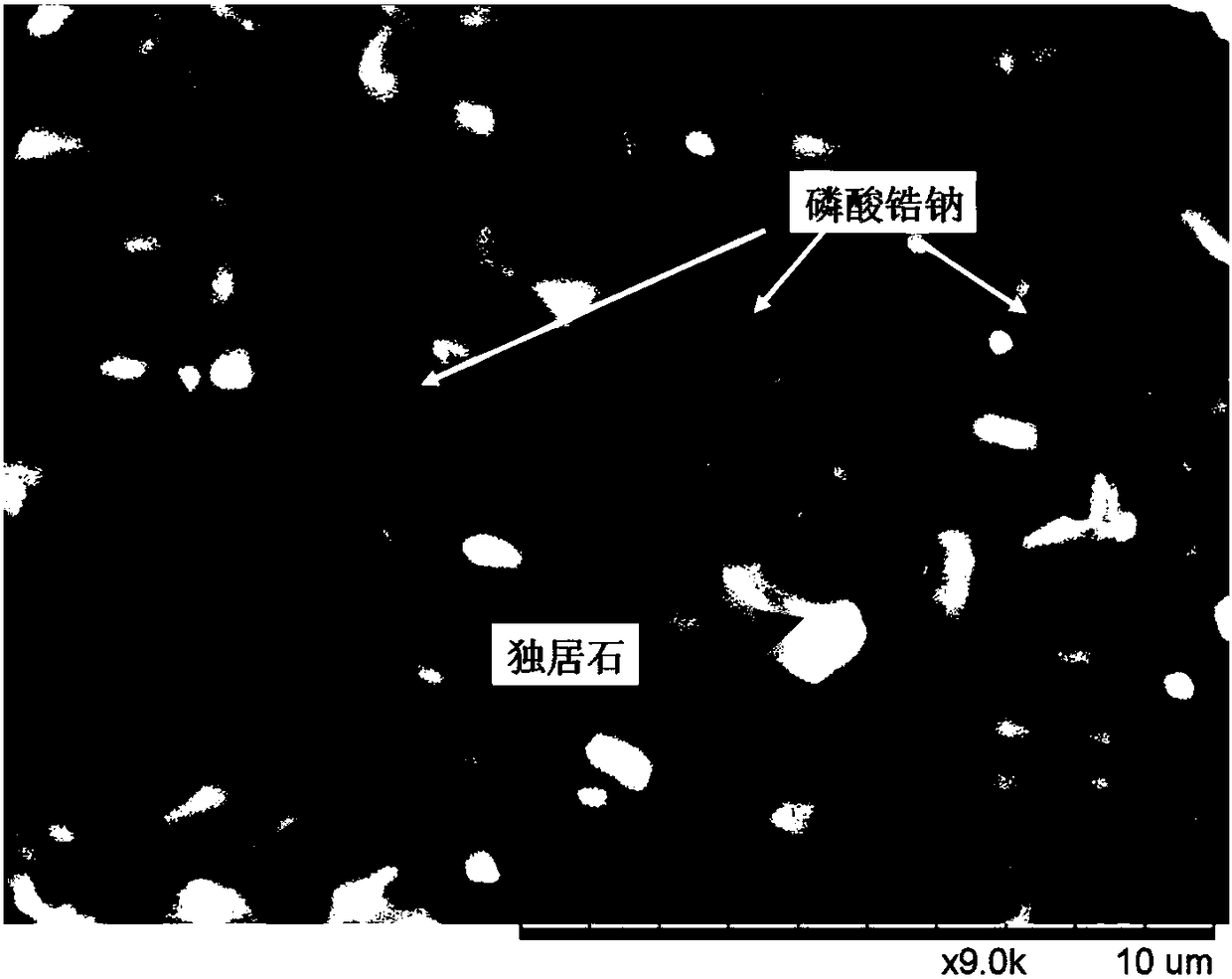
Sodium zirconium phosphate-monazite glass ceramic solidified body and preparation method thereof
A technology of sodium zirconium phosphate and glass ceramics, which is used in radioactive purification, nuclear engineering, etc., can solve the problems of poor radiation stability and thermal stability, reduced stability of solidified body, and low capacity of high-level radioactive waste. Excellent, large volume reduction ratio, high waste bag capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] A preparation method of sodium zirconium phosphate-monazite glass-ceramic solidified body, the steps are as follows:
[0036] (1) Preparation of sodium zirconium phosphate-monazite glass-ceramic substrate raw material powder:
[0037] a. Ingredients: P 2 o 5 , Fe 2 o 3 , B 2 o 3 , CeO 2 , ZrO 2 、Na 2 CO 3 For raw materials, press P 2 o 5 41.64 parts by weight, Fe 2 o 3 28.11 parts by weight, B 2 o 3 2.01 parts by weight, CeO 2 10.10 parts by weight, ZrO 2 14.49 parts by weight, Na 2 CO 3 The proportioning ratio of 3.62 parts by weight is obtained from each raw material;
[0038] b. Mixing: put each raw material into a planetary ball mill and ball mill for 2 hours and mix well;
[0039] c. Pre-burning: Pre-burning the uniformly mixed materials at a temperature of 650°C for 4 hours;
[0040] d. Ball milling: mill the pre-fired material for 4 hours in a planetary ball mill to obtain sodium zirconium phosphate-monazite glass ceramic substrate raw m...
Embodiment 2
[0047] A preparation method of sodium zirconium phosphate-monazite glass-ceramic solidified body, the steps are as follows:
[0048] (1) Preparation of sodium zirconium phosphate-monazite glass-ceramic substrate raw material powder:
[0049] a. Ingredients: P 2 o 5 , Fe 2 o 3 , B 2 o 3 , CeO 2 , ZrO 2 、Na 2 CO 3 For raw materials, press P 2 o 5 41.07 parts by weight, Fe 2 o 3 22.01 parts by weight, B 2 o 3 1.92 parts by weight, CeO 2 9.49 parts by weight, ZrO 2 20.41 parts by weight, Na 2 CO 3 The batching ratio of 5.09 parts by weight gets each raw material;
[0050] b. Mixing: put each raw material into a planetary ball mill and ball mill for 2 hours and mix well;
[0051] c. Pre-burning: Pre-burning the uniformly mixed materials at a temperature of 700°C for 6 hours;
[0052] d. Ball milling: mill the pre-fired material in a planetary ball mill for 5 hours to obtain sodium zirconium phosphate-monazite glass ceramic substrate raw material powder.
...
Embodiment 3
[0059] A preparation method of sodium zirconium phosphate-monazite glass-ceramic solidified body, the steps are as follows:
[0060] (1) preparing sodium zirconium phosphate-monazite glass-ceramic substrate raw material powder;
[0061] a. Ingredients: (NH 4 )H 2 PO 4 , Fe 2 o 3 , CeO 2 , ZrO 2 、H 3 BO 3 、Na 2 CO 3 As raw material, according to (NH 4 )H 2 PO 4 52.43 parts by weight, Fe 2 o 3 17.33 parts by weight, H 3 BO 3 2.68 parts by weight, CeO 2 7.47 parts by weight, ZrO 2 16.07 parts by weight, Na 2 CO 3 The batching ratio of 4.01 parts by weight is obtained from each raw material.
[0062] Others are the same as in Embodiment 2, omitted.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com