Method for preparing (1R, 2R)-2-(3, 4-difluoro phenyl)cyclopropylamine
A technology of difluorophenyl and cyclopropylamine, applied in the field of preparing -2-cyclopropylamine, can solve the problems of loss of raw materials, expensive reagents and high cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
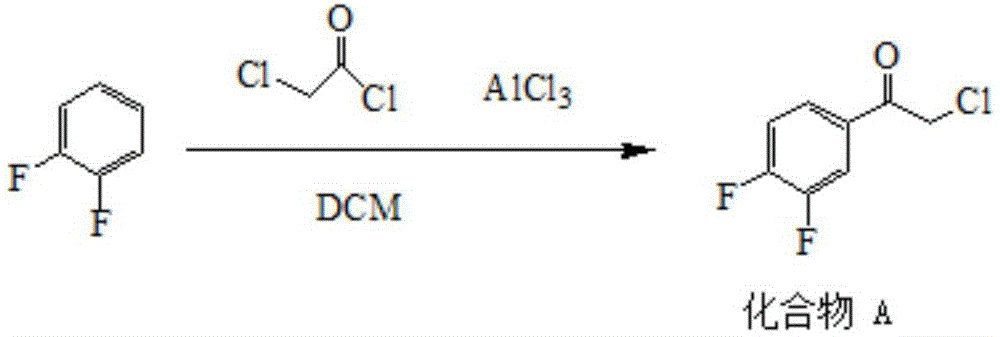
[0050] Embodiment one: the preparation of compound A
[0051]
[0052] 450 ml of dichloromethane and 133.5 g (1 mol) of aluminum trichloride were added to the reaction flask, followed by stirring. Under nitrogen protection, 113 g (1 mol) of chloroacetyl chloride was added dropwise to the reaction solution, and the dropwise addition time was not less than 10 minutes. After the dropwise addition, the reaction solution was heated to reflux for reaction. After 30 minutes of reflux reaction, 97 g (0.85 mol) of 1,2-difluorobenzene was added dropwise under reflux for no less than 2 hours. After the dropwise addition, the reflux reaction was continued for 1 hour. After the reaction was completed, the reaction solution was cooled to 20° C., then slowly poured into 500 g of ice water, and stirred for 30 minutes. After separating the layers, the aqueous layer was extracted with dichloromethane. The combined organic layers were washed with water, saturated sodium bicarbonate and wa...
Embodiment 2
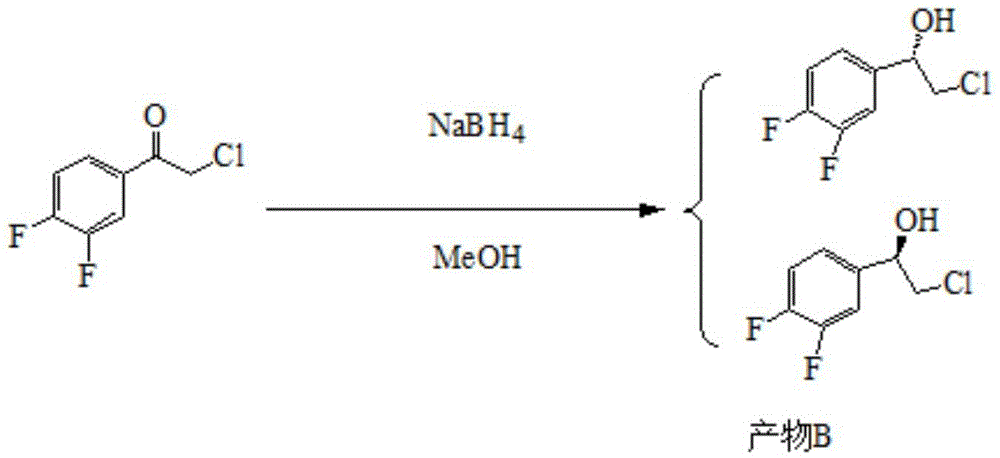
[0053] Embodiment two: the preparation of product B
[0054]
[0055] 50 ml of methanol and 7.6 g (0.04 mol) of compound A were added to the reaction flask. Under the condition of stirring, the reaction solution was cooled to 0°C. Slowly add 0.378 g (0.01 mol) of sodium borohydride to the reaction solution, and the temperature during the addition is less than 5°C. After sodium borohydride was added, the temperature of the reaction solution was raised to room temperature for reaction. After the reaction, the reaction solution was cooled to 0°C, dichloromethane was added, and 10% NH 4 Cl aqueous solution 75ml. After completion of the dropwise addition, the mixture was stirred for 30 minutes. layered. The aqueous layer was extracted with dichloromethane. The combined organic layers were washed with brine. The organic layer was dried and filtered. The organic layer was concentrated to obtain 7.42g of product B with a yield of 96%; 1 H-NMR: δ (ppm): 3.9 (2H, dd); 5.3 (2...
Embodiment 3
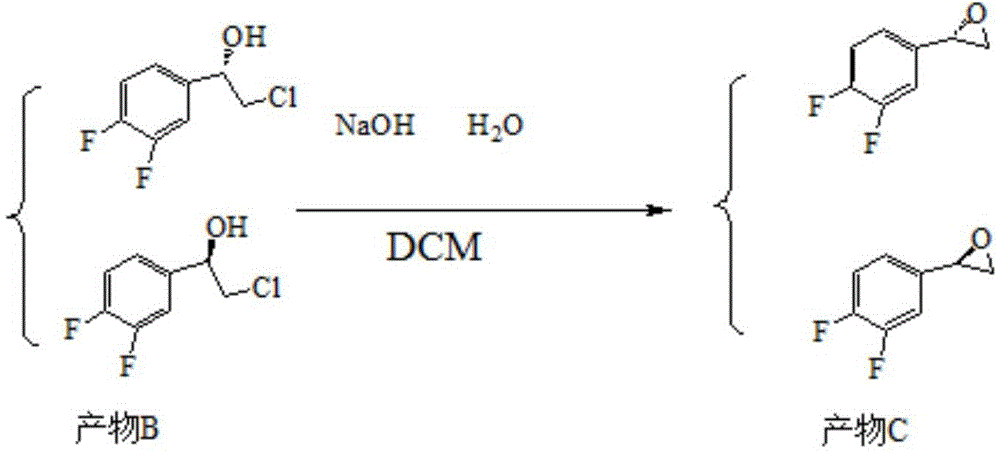
[0056] Embodiment three: the preparation of product C
[0057]
[0058] 10.5 g (0.02625 mol) of 10% aqueous sodium hydroxide solution, 4.813 g (0.025 mol) of product B and 50 ml of dichloromethane (DCM) were added to the reaction flask. React under stirring conditions at room temperature. After the reaction was finished, it was cooled to room temperature, and the layers were separated. The aqueous layer was extracted with dichloromethane; the combined organic layers were washed with water. Dry and concentrate the organic layer to obtain 3.8g of product C with a yield of 97.4%; 1 H-NMR: δ2.71-2.73 (1H, dd); 3.13-3.15 (1H, m); 3.82-3.83 (1H, m); 7.01-7.27 (3H, m).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com