Determination device for Seebeck coefficient of flexible thin film material
A technology of flexible thin film materials and Seebeck coefficient, applied in the field of material thermoelectric conversion, can solve the problems of inapplicability of flexible self-supporting thin film performance testing, difficulty in meeting the research needs of flexible thermal management materials, etc., and achieve simple structure, low cost, and easy operation Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
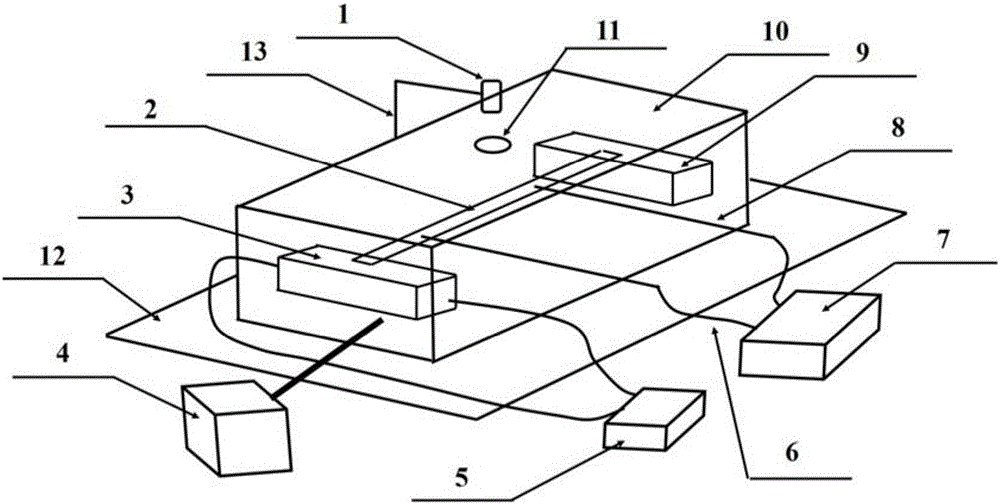
[0020] A device for measuring Seebeck coefficient of a flexible film material, comprising an infrared thermal imager 1, a sample to be tested 2, a heating assembly 3, a vacuum pump 4, a DC power supply 5, a wire 6, a digital source meter 7, an electrode 8, a cooling assembly 9, a vacuum Box 10, infrared window 11, base 12 and support 13, wherein a vacuum box 10 is installed on the base 12, an infrared window 11 is arranged on the top of the vacuum box 10, and a heating device is installed on the base 12 and inside the vacuum box 10. Component 3 and heat dissipation component 9, the heating component 3 and heat dissipation component 9 are used to suspend the sample 2 to be tested, and the vacuum pump 4 connected to the vacuum box 10 is installed on the side of the base 12 to ensure that the sample 2 to be tested is located in the In a vacuum environment, the infrared thermal imager 1 is installed on the base 12 through a bracket 13, and the infrared thermal imager 1 is above the...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Cut a certain area of graphene\polyaniline composite film material prepared by the suction filtration method, (length × width 12cm × 1cm) as the sample to be tested, fix the two ends of the sample on the heating component and the heat dissipation component, use conductive silver paste to reduce Contact resistance. A vacuum pump is used to maintain the internal pressure of the vacuum box at -0.1MPa, and a DC power supply is used to supply DC power to the heating element with a voltage of 6V. An infrared thermal imager is used to measure the temperature at both ends of the sample through the infrared window, and the thermoelectric potential at both ends of the sample is read according to the digital source meter, and the Seebeck coefficient of the sample is calculated to be 47.0 μV / K.
Embodiment 3
[0031] Cut a certain area of graphene\carbon nanotube\PTFE composite film material prepared by the scraping method, (length×width 15cm×1.2cm) as a test sample, fix the two ends of the sample on the heating component and the heat dissipation component, use conductive silver slurry to reduce contact resistance. A vacuum pump is used to maintain the internal pressure of the vacuum box at -0.1MPa, and a DC power supply is used to supply DC power to the heating component with a voltage of 10V. An infrared thermal imager is used to measure the temperature at both ends of the sample through the infrared window, and the thermoelectric potential at both ends of the sample is read according to the digital source meter, and the Seebeck coefficient of the sample is calculated to be 43.5 μV / K.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com