Thyristor synchronization signal processing method applicable to changing frequency
A technology for synchronizing signals and changing frequencies, which is applied in general control systems, instruments, computer control, etc., can solve problems such as voltage waveform distortion on the AC side, misjudgment of synchronous signals, and increased difficulty of synchronous signal zero crossings, etc., to improve trigger accuracy, The effect of strong frequency tracking ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] The present invention is described in detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and embodiment:
[0020] A thyristor synchronous signal processing method for changing frequency, it comprises the following steps,
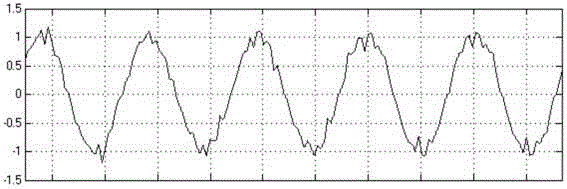
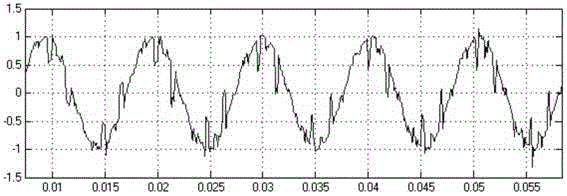
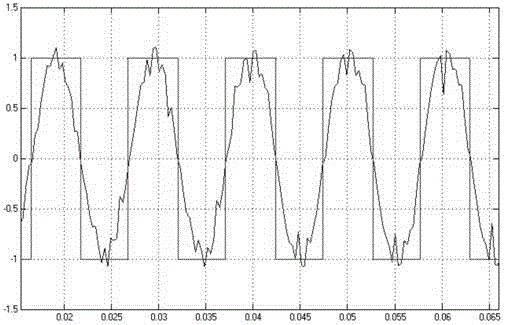
[0021] (1) Use the first-order RC low-pass filter to filter out the high-frequency components of the original synchronous signal. The cut-off frequency of the filter can be selected as 1 / 3 of the fundamental frequency, and the filtered signal will lag behind that before the filter;
[0022] (2) Convert the filtered synchronous signal to a square wave signal through a comparator, input it into the digital signal processor DSP, use the capture unit in the DSP to capture the rising edge of the square wave signal twice, and subtract the counter values of the two rising edges To get the counting difference, divide the counter frequency by the counting difference to get the frequency of the square wave signal;
[0023] (3) According to the cut-off fre...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com