Feedback method and device
A technology of feedback information and division method, applied in the field of mobile communication, can solve the problem of high feedback overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0230] Embodiment one (method embodiment):
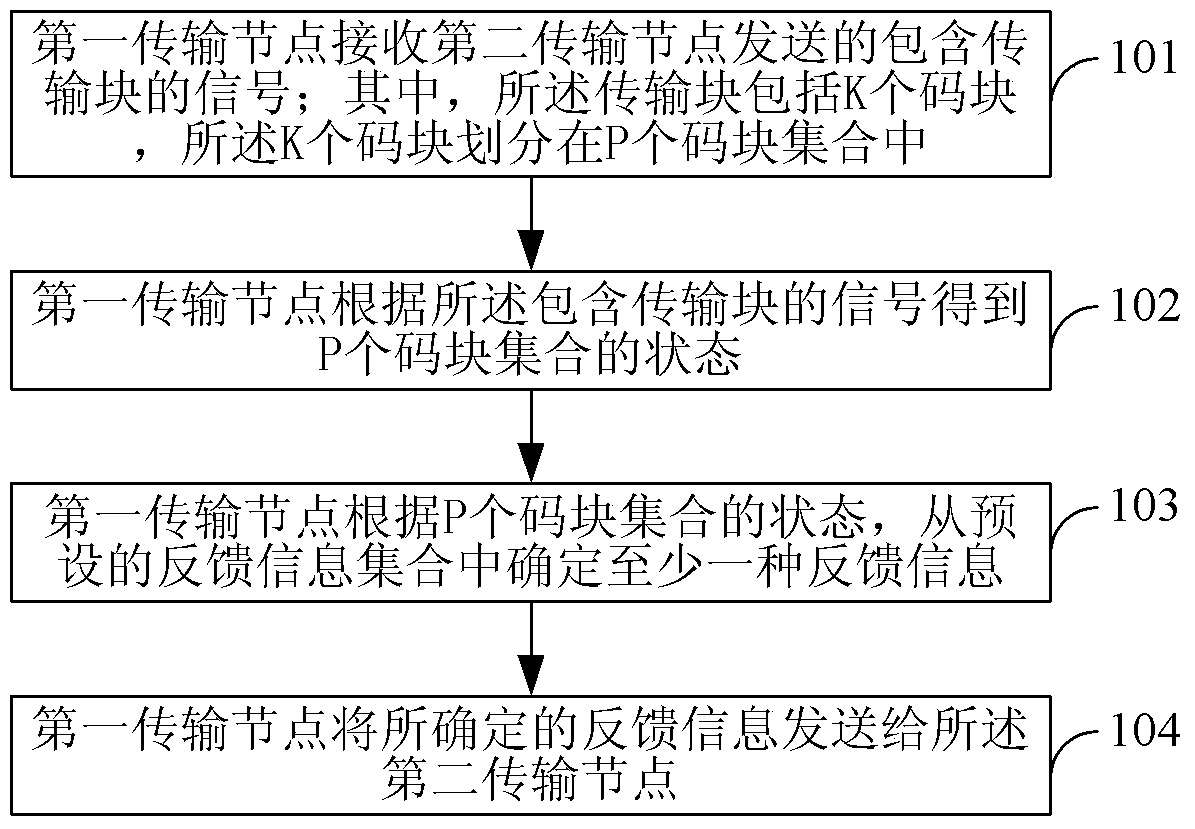
[0231] This embodiment proposes a feedback method, which is applied to the first transmission node, such as image 3 Shown, including:
[0232] Step 101: The first transmission node receives a signal containing a transmission block sent by a second transmission node; wherein, the transmission block includes K code blocks, and the K code blocks are divided into P code block sets; wherein , K and P are positive integers, K≥3, 2≤P≤K;
[0233] Step 102: The first transmission node obtains the status of P code block sets according to the signal including the transmission block;
[0234] Step 103: The first transmission node determines at least one type of feedback information from a preset feedback information set according to the status of the P code block sets;
[0235] Step 104: The first transmission node sends the determined feedback information to the second transmission node. Wherein, the feedback information set includes at least: correc...
example 1
[0280] In this example, the first transmission node is a terminal, and the second transmission node is a base station:
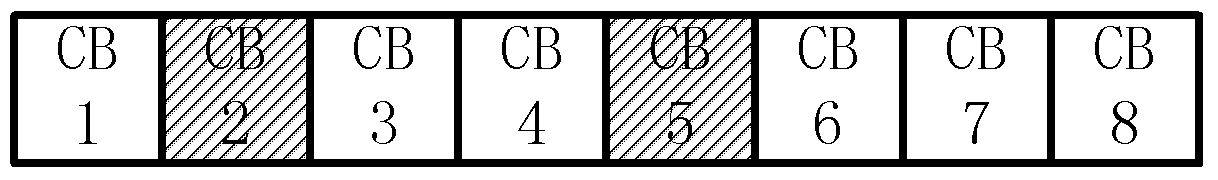
[0281] Step A1: The terminal receives the signal containing the transmission block sent by the base station, where the transmission block includes K=8 code blocks, and the 8 code blocks are divided into P=2 code block sets. Such as Figure 4 As shown, code block set (CBset) 1 includes code blocks CB1, CB2, CB3, and CB4; code block set 2 includes code blocks CB5, CB6, CB7, and CB8. In this example, the code block set adopts a continuous division method. The number of code block sets P=2 is configured by the base station, and the base station selects P=2 from a set of preset values {2, 3, 4, 5}, and sends it to the terminal through downlink signaling.
[0282] Step A2: The terminal determines at least one type of feedback information from the feedback information set according to the status of the two code block sets, and sends the feedback information to the ba...
example 2
[0286] The difference between this example and example one is that, in this example, the number of code block sets P is determined by the size of the transmission block. In this example, the size of the transmission block belongs to the preset value interval, and the number of The number of code block sets corresponding to the value interval is P=2. At this time, the number P of code block sets does not need to be sent through signaling between the base station and the terminal.
[0287] Another difference between this example and the second example is that both code block set 1 and code block set 2 receive errors. At this time, the number of correct code block sets is less than the preset threshold 1, or the data of the error code block set is greater than The preset threshold is 1, or the correct rate of the code block set is lower than the preset threshold 0.5, or the error rate of the code block set is higher than the preset threshold 0.5. In this case, if the retransmitted d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com