Method for actively detecting defects in metal thin-walled structure part
A thin-walled structural part, active detection technology, applied in measurement devices, analysis of solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic waves, material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic waves, etc. It can solve the problem of low recognition ability and avoid complexity. , Simplified extraction method, easy to measure effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
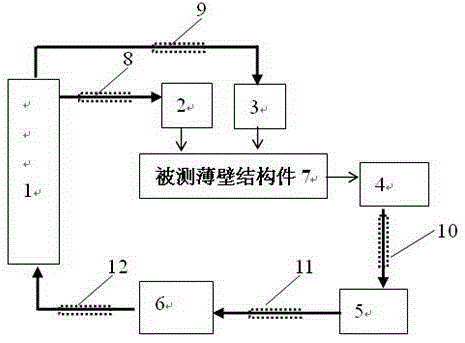
[0018] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination figure 1 Describe this specific embodiment, a method for actively detecting defects in metal thin-walled structural parts described in this specific embodiment The test system includes an arbitrary waveform generator 1, a first transmitting transducer 2, and a second transmitting transducer 3 , non-contact laser vibrometer 4, digital signal oscilloscope 5, computer 6, measured thin-walled structural member 7, first coaxial data transmission line 8, second coaxial data transmission line 9, third coaxial data transmission line 10, The fourth coaxial data transmission line 11 and the fifth coaxial data transmission line 12, the signal output end of the non-contact laser vibrometer 4 is electrically connected to the digital oscilloscope 5 signal input end through the coaxial data transmission line 10, and the digital oscilloscope 5 can Receive and store the signal collected by the non-contact laser vibrometer 4 in real time, the s...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0019] Embodiment 2. The difference between this embodiment and the method for actively detecting defects in metal thin-walled structural parts described in Embodiment 1 is that the first transmitting transducer 2 and the second transmitting transducer 3 are Piezoelectric crystals of the same type and material, the resonant frequency of the first transmitting transducer 2 and the second transmitting transducer 3 is 1MHz, and are vertically coupled with the thin-walled structural member 7 to be tested through epoxy resin.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0020] Embodiment 3. The difference between this embodiment and the method for actively detecting defects in metal thin-walled structural parts described in Embodiment 1 is that the channels of the arbitrary waveform generator 1 include input channels and output channels. The input channel is that the waveform signal can be downloaded into the arbitrary waveform generator 1 through the computer 6, and the output channel is four independent channels, and the transmission signals of different frequencies can be selected at the same time. The present invention only uses the first one of the output channels. output channel and a second output channel.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Resonant frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Resonant frequency | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com