Fiber-reinforced polycarbonate composition and preparation method thereof
A polycarbonate, fiber reinforced technology, applied in the field of engineering plastics, can solve the problems of not being able to achieve the balance of rigidity and toughness, reducing material toughness, affecting dimensional stability and processing fluidity, etc., achieving reduced damage, excellent low temperature toughness, and increased application The effect of functionality and practicality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-9 and
[0053] Embodiment 1-9 and comparative example 1-7 follow the steps below, to prepare polycarbonate composition:
[0054] Step 1: Prepare raw materials according to the following components: polycarbonate, polysiloxane-polycarbonate copolymer, glass fiber, release agent and additives;
[0055] Step 2: Dry the raw materials in step 1, the drying temperature is 120-130°C, and the drying time is 4-6h;
[0056] Step 3: Add the dried polycarbonate, polysiloxane-polycarbonate copolymer, mold release agent and auxiliary agent into a high-speed mixer for mixing at a temperature of 30-50°C and a mixing time of 5-15min, obtain the mixed material, stand-by;
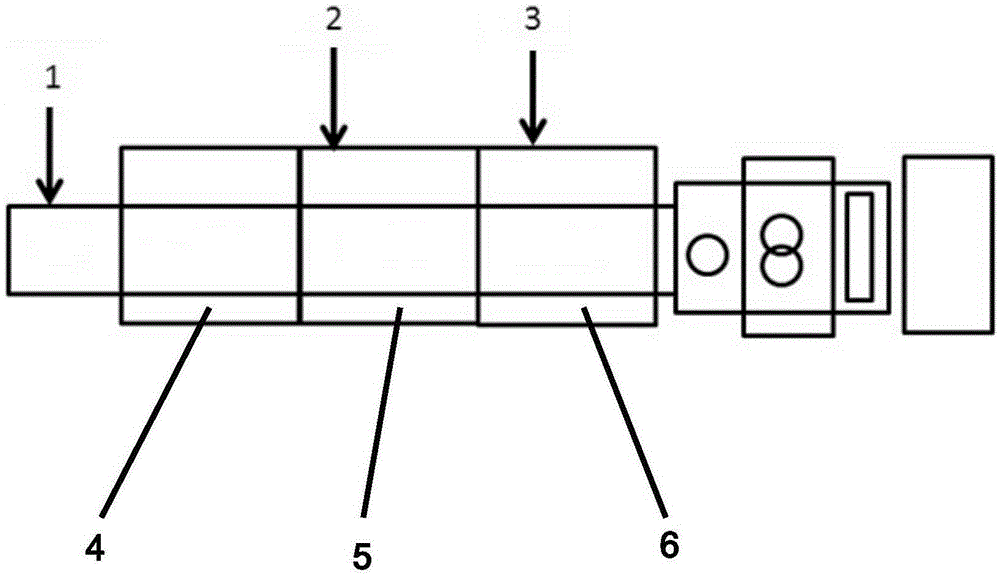
[0057] Step 4: Add the mixed material in step 3 to the first feeding port 1, add the glass fiber to the first feeding port 1, the second feeding port 2 or the third feeding port 3, and in the first screw barrel 4 , Stay in the second screw barrel 5 or the third screw barrel 6 for a certain period of time, the number of parts added ...
Embodiment 1-9
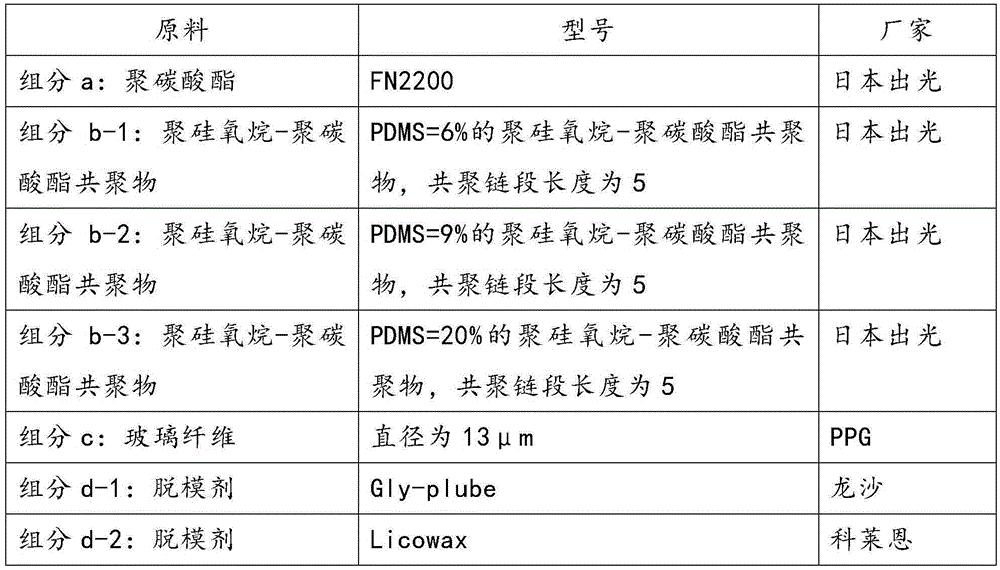
[0082] The proportioning of the used raw material of embodiment 1-9 sees the following table:
[0083]
[0084]
[0085] Wherein embodiment 1,4 and 7: based on the glass fiber gross weight, the glass fiber that accounts for glass fiber gross weight 50% adds from the first feeding port 1, and the residence time in the first screw barrel 4 is 20- 30s; Based on the glass fiber gross weight, the glass fibers that account for 50% of the glass fiber gross weight are from the second feeding port 2, and the residence time in the second screw barrel 5 is 8-15s; obtain embodiment 1, embodiment 4. The composition of Component I and Component II of Example 7 comprising specific glass fiber length distribution and weight ratio;
Embodiment 2
[0086] Embodiment 2, 5 and 8: Based on the total weight of glass fibers, the glass fibers accounting for 80% of the total weight of glass fibers are added from the first feeding port 1, and the residence time in the first screw barrel 4 is 20-30s Based on the glass fiber gross weight, the glass fiber that accounts for 20% of the glass fiber gross weight is from the second feeding port 2, and the residence time in the second screw barrel 5 is 8-15s; obtain embodiment 2, embodiment 5 Compositions of Component I and Component II comprising specific glass fiber length distributions and weight ratios of Example 8;
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com