Dispersion compensation method and apparatus
A dispersion compensation and dispersion value technology, which is applied in the optical field, can solve the problems of inability to recognize received data, decline in reception performance, and inability to lock the dispersion value on the receiving side of the optical module, so as to achieve normal and stable working performance and solve the problem of data interference. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
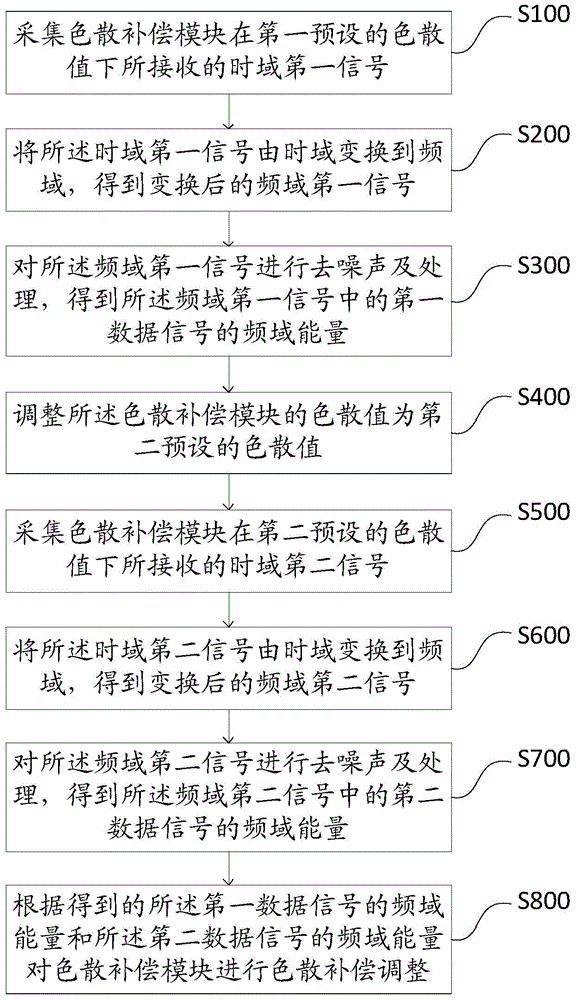
[0099] like figure 1 As shown, one of the flowcharts of the method for chromatic dispersion compensation in the first embodiment of the present invention, the method for chromatic dispersion compensation includes the following steps:
[0100] Step S100: Collect the time domain first signal received by the dispersion compensation module under the first preset dispersion value.
[0101] It should be noted that the actual signal transmission contains noise interference, and the received first signal in the time domain here contains noise interference.
[0102] Step S200: Transform the first signal in the time domain from the time domain to the frequency domain to obtain the transformed first signal in the frequency domain.
[0103] It should be noted that there are many methods for converting a signal from the time domain to the frequency domain. In the embodiment of the present invention, the discrete Fourier transform is used to transform the first signal in the time domain c...
Embodiment 2
[0155] like Figure 7 As shown, it is a schematic diagram of the application of the dispersion compensation method in the embodiment of the present invention to the dual subracks. The transmitting end of the subrack 1 is connected to the receiving end of the subrack 2 through the dispersion compensation module; The receiving end of rack 1 is connected; the connecting line between sub-rack 1 and sub-rack 2 is an optical fiber, and the working steps are as follows:
[0156] Step 1: Set the dispersion value of the dispersion compensation module to -700ps / (nm×km).
[0157] Step 2: The dispersion compensation module performs dispersion scanning on the receiving side to obtain the receiving performance curve.
[0158] Step 3: Perform discrete Fourier transform processing on the performance curve, and perform energy change processing to obtain a frequency domain energy curve.
[0159] Step 4: De-noise the frequency-domain energy curve, remove the energy of the noise part, obtain th...
Embodiment 3
[0163] like Figure 8 As shown, it is a schematic diagram of the application of the embodiment of the present invention in the remote transmission of the single subrack. When the remote signal needs to be transmitted to the receiving end of the device A1, the receiving end of the device A1 and the remote signal are connected by optical fibers, and the transmitting end of the device A1 is connected by optical fiber. not connected. After the optical fiber is connected, it does not need to be changed in future use. The specific steps of implementation are shown in the second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com