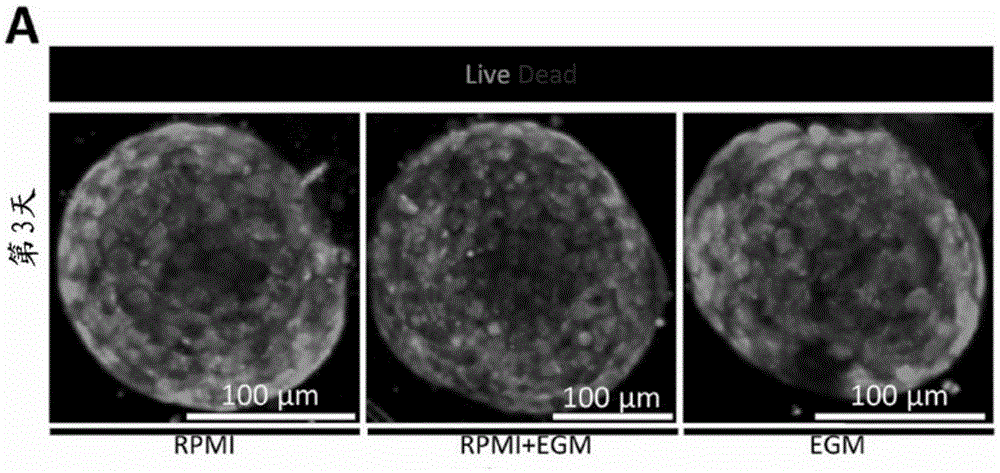
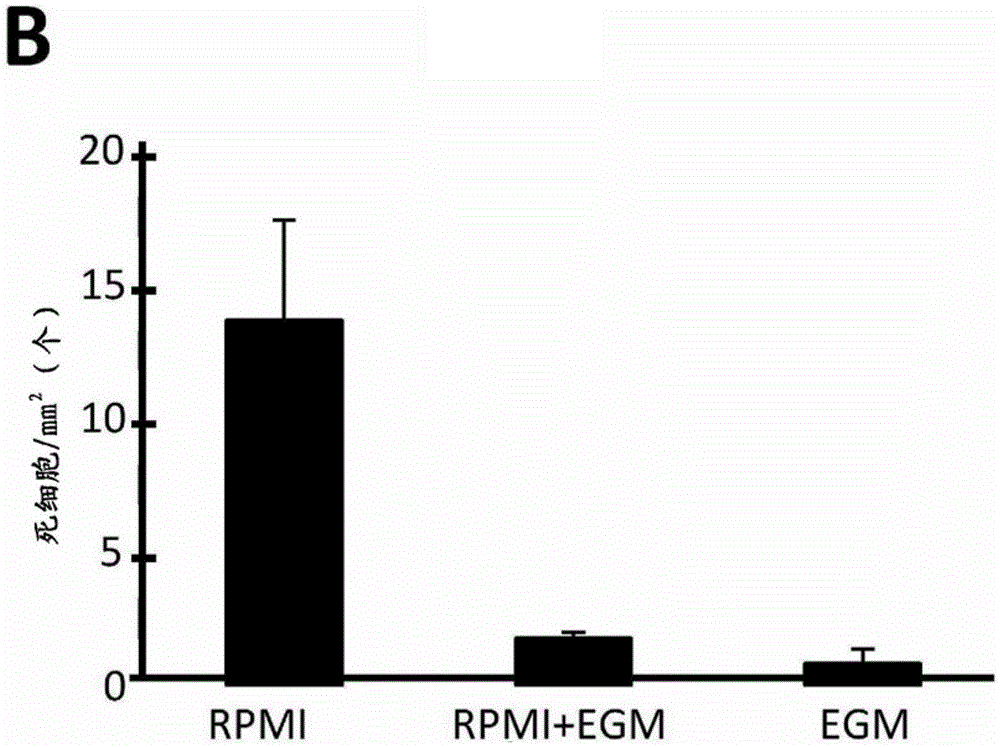
Method for providing vascular system in biological tissue
A vascular system and biological technology, applied in the field of making three-dimensional tissue with vascular network, can solve the problems of independent stent material, unestablished, foreign body reaction of stent material, etc., and achieve the effect of high technical value
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0084] Hereinafter, the present invention will be described in detail.
[0085] The present invention provides a method for imparting a vascular system to a biological tissue in vitro, which comprises co-culturing the biological tissue with vascular cells and mesenchymal cells.
[0086] In this specification, "biological tissue" refers to a structure composed of a plurality of cells, and examples include normal-abnormal tissue or cancer tissue isolated from an individual, self-pluripotent stem cells (artificial pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells) , embryonic stem cells (ES cells), etc.), tissue stem-precursor cells, differentiated cells, etc. induced tissues), etc. Biological tissues can be mainly of human origin, but animals other than humans (e.g., animals used for laboratory animals, companion animals, working animals, racehorses, fighting dogs, etc., specifically, mice, rats, Biological tissues derived from rabbit, pig, dog, monkey, cow, horse, sheep, chicken, shark, ray, ...
Embodiment 1
[0130] [Example 1: Implantation of vascular network in islet tissue]
[0131] 〔method〕
[0132] 【1. Isolation method of mouse islets】
[0133] Isolation of mouse islets was mainly carried out according to the method of Dong et al. (document name: Aprotocolforisletisolationfrommousepancreas). The abdomen of an anesthetized C57BL / 6J mouse (Japan SLC) was sterilized with 70% ethanol using diethyl ether (Wako), and the abdomen was opened, and the ampulla of Farter, which is the junction of the common bile duct and the duodenum, was ligated. Thereafter, a 27G injection needle was inserted into the confluence of the cystic duct and the hepatic duct, and 3 ml of collagenase XI solution (1,000 U / ml) (Sigma, cat. No. C7657) prepared with Hanks buffer (HBSS, GIBCO) was injected, Fill the whole pancreas with collagenase XI solution. Cut out the pancreas, put it into a 50ml tube containing collagenase XI solution, and shake it at 37.5°C for 15 minutes. After digesting the pancreas, ad...
Embodiment 2
[0215] [Example 2: Delivery of vascular network to renal glomeruli]
[0216] 〔method〕
[0217] 【1. Isolation method of mouse glomeruli】
[0218] After the abdomen of a C57BL / 6-Tg mouse (Japan SLC) anesthetized with diethyl ether (Wako) was disinfected with 70% ethanol, the abdomen was opened, and the kidney was removed. The renal epithelium was removed from the excised kidney, and after washing with physiological saline, the kidney was cut with a scalpel wheel. The renal pelvis and medulla were removed with clips, and the cortex was recovered. The recovered cortex was minced on ice, and filtered by adding Hanks buffer (HBSS, GIBCO) containing 0.1% bovine serum albumin (BSA, SIGMA) little by little using a 100 μm mesh cell strainer. The flow-through was filtered through a 70 μm mesh cell filter, and finally, the flow-through was filtered through a 40 μm mesh cell filter. The cell mass remaining on the 40 μm purpose cell filter was collected using Hanks buffer containing 0.1...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com