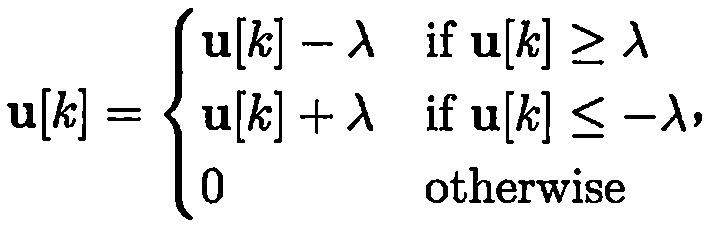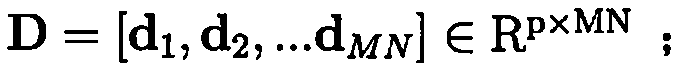Structured sparse coding based coal rock identification method
A technology of sparse coding and coal and rock recognition, applied in character and pattern recognition, instruments, computer parts, etc., can solve problems such as complex structure, damage of mechanical components, sensors and electrical circuits, poor reliability of devices, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0016] specific implementation plan
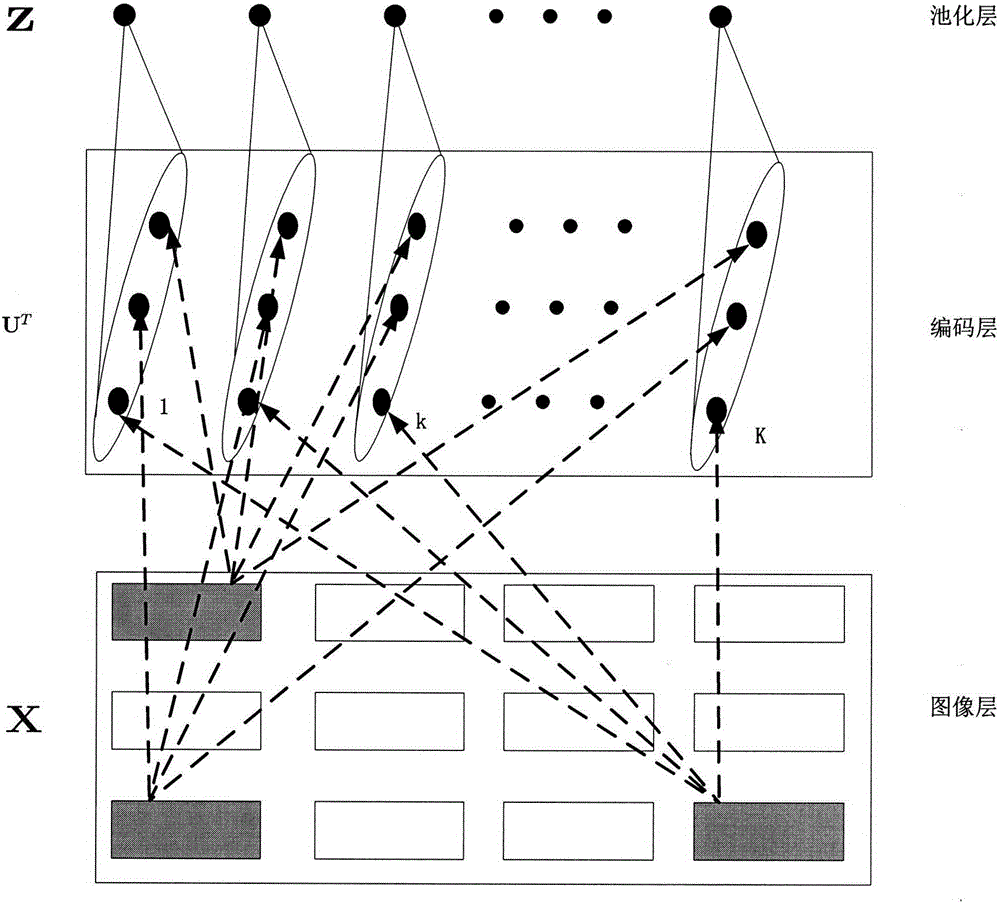
[0017] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the principle of the coal and rock identification method of the present invention, mainly including 3 layers: an image layer, a coding layer and a pooling layer. The image layer provides input to the coding layer. In this embodiment, image blocks are extracted from grayscale images as codes The input of layer; The coding layer calculates the expression coefficient when each image block is expressed with MK primitives, and the present embodiment uses 1 1 -norm optimizes the calculation of expression coefficients, so that there are very few non-zero elements in the expression coefficients, so it is called sparse coding; the pooling layer calculates the statistical characteristics of all expression coefficients and then obtains the feature expression of the input image. The specific implementation steps are as follows:
[0018] A. Collect M+1 coal (or rock) images from the site of the coal rock id...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com