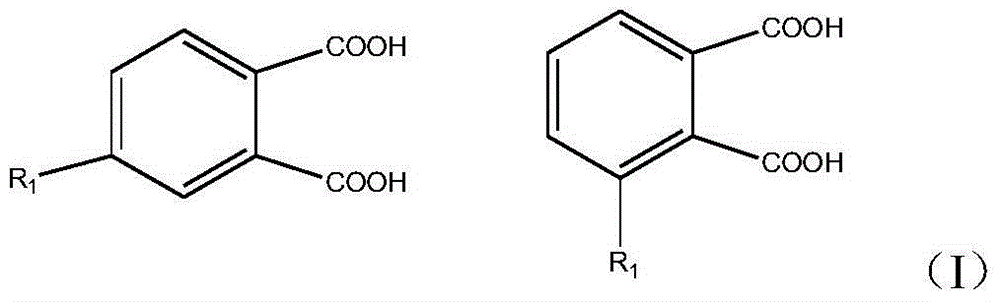
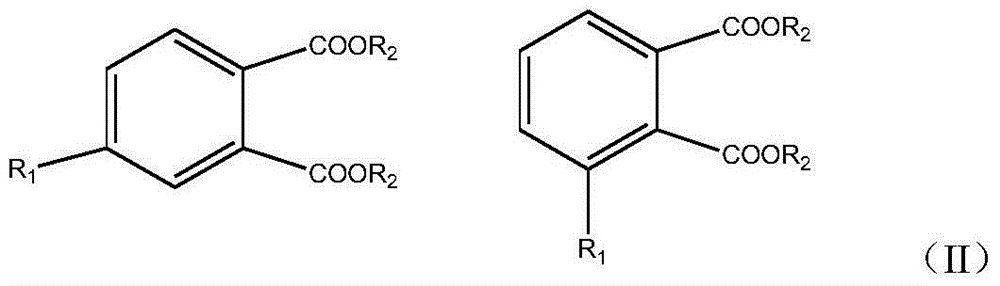
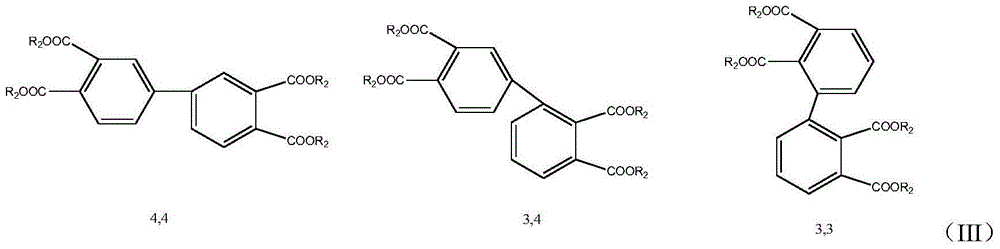
Preparation method for biphenyltetracarboxylic dianhydride mixture
A biphenyl dianhydride and mixture technology, which is applied in the field of preparing biphenyl dianhydride mixtures, can solve the problems of low efficiency and high cost, and achieve the effects of low cost, increased efficiency, and reduced cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Dissolve phthalic acid (1 mmol) in 20 ml of aqueous acid solution, stir for 1.5 hours, pass chlorine gas into it, react for 3 hours, drain all solvents, add 50 ml of ethyl acetate, and wash the resulting solution with saturated brine for 3 After separation of the organic phase, the aqueous phase was extracted twice with ethyl acetate (50 mL). The organic phases were combined, dried with a desiccant, filtered off the desiccant, and evaporated to dryness to obtain the corresponding ortho- and meta-substituted phthalic acid chlorides (yield 100%, GC purity (two isomers) 99 %).
[0032] Dissolve phthalic acid chloride (1 mmol) in 20 ml of methanol, add alkali solution, stir for 1.5 hours, drain all solvents, add 50 ml of ethyl acetate, wash the resulting solution 3 times with saturated brine, and remove the organic phase After separation, the aqueous phase was extracted twice with ethyl acetate (50 mL). The organic phases were combined, dried with desiccant, filtered off ...
Embodiment 2
[0036] 1 Dissolve phthalic acid (1 mmol) in 20 ml of aqueous acid solution, stir for 1.5 hours, pass bromine gas into it, react for 3 hours, drain all solvents, add 50 ml of ethyl acetate, and wash the resulting solution with saturated salt After washing with water three times, the organic phase was separated, and the aqueous phase was extracted twice with diethyl ether (50 mL). The organic phases were combined, dried with a desiccant, filtered off the desiccant, and evaporated to dryness to obtain the corresponding ortho- and meta-substituted phthalic acid chlorides (yield 100%, GC purity (two isomers) 98 %).
[0037] Dissolve phthalic acid chloride (1 mmol) in 22 ml of isopropanol, add alkali solution, stir for 1.5 hours, drain all the solvent, add 50 ml of ether, wash the resulting solution 3 times with saturated saline, and the organic phase After separation, the aqueous phase was extracted twice with ether (50 mL). The organic phases were combined, dried with desiccant,...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Dissolve phthalic acid (1 mmol) in 20 ml of aqueous acid solution, stir for 1.5 hours, pass bromine gas into it, react for 3 hours, drain all solvents, add 50 ml of ethyl acetate, and wash the resulting solution with saturated saline 3 times, after separation of the organic phase, the aqueous phase was extracted twice with dichloromethane (50 mL). The organic phases were combined, dried with a desiccant, filtered off the desiccant, and evaporated to dryness to obtain the corresponding ortho- and meta-substituted phthalic acid chlorides (yield 100%, GC purity (two isomers) 99 %).
[0042] Dissolve phthalic acid chloride (1 mmol) in 25 ml of ethanol, add alkali solution, stir for 1.5 hours, drain all solvents, add 50 ml of dichloromethane, and wash the resulting solution 3 times with saturated brine, and the organic phase After separation, the aqueous phase was extracted twice with dichloromethane (50 mL). The organic phases were combined, dried with desiccant, filtered...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com