A dna fragment with insecticidal effect and its application in agriculture
A fragment and sequence technology, applied in the field of biological transgenics, can solve the problems of affecting toxin activity, insecticidal effect, and lectin protein activity, etc., to achieve the effect of improving activity and ensuring stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] In the present invention, the expression selection sequence fragments 1, 3, 5, and 7 are sequentially connected in the plant transformation of upland cotton to form the DNA fragment of the present invention. For cotton transgenic methods, please refer to transgenic cotton methods and protocols (edited by Baohong zhang). The CaMV35S promoter is used as the promoter of the present invention, and the target gene is constructed into the vector pCIMBIA2300, and the transgenic process is completed by the tissue culture method mediated by Agrobacterium. The method is very mature and well-known in the art, so it will not be repeated here. The hypocotyls of 23 cotton varieties of China Cotton Research Institute were selected as the recipient material to complete the transgenic process.
[0027] Positive cotton plants were obtained by Kana resistance and PCR detection, cotton needles were selected, total protein was extracted, and whether the protein was expressed in cotton was d...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The present invention is compared with the expression amount and insecticidal effect of the prior art
[0035] The selected sequence fragments 1, 10, 12, and 7 are sequentially connected to form the DNA fragment of the present invention, which is marked as fragment A.
[0036] Selected sequence fragments 9, 12, and 7 are sequentially connected to form a DNA fragment described in the prior art, marked as B. That is to say, the plant secretion leader peptide is connected with chitinase, spider toxin and GNA.
[0037] The above two fragments were used to construct vectors for transgenic comparison of Arabidopsis thaliana.
[0038] Transgenic method: Arabidopsis transgenic method is a mature method in the field of biological research, so it will not be described here. The reference method in this example comes from Simplified Arabidopsis Transformation Protocol, SteveClough and Andrew Bent, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign
[0039] During the transformation proc...
Embodiment 3
[0045] The corresponding transgenic Arabidopsis of the present invention is compared with the transgenic Arabidopsis without auxiliary sequence and the wild type, and the anti-aphid effects are compared.
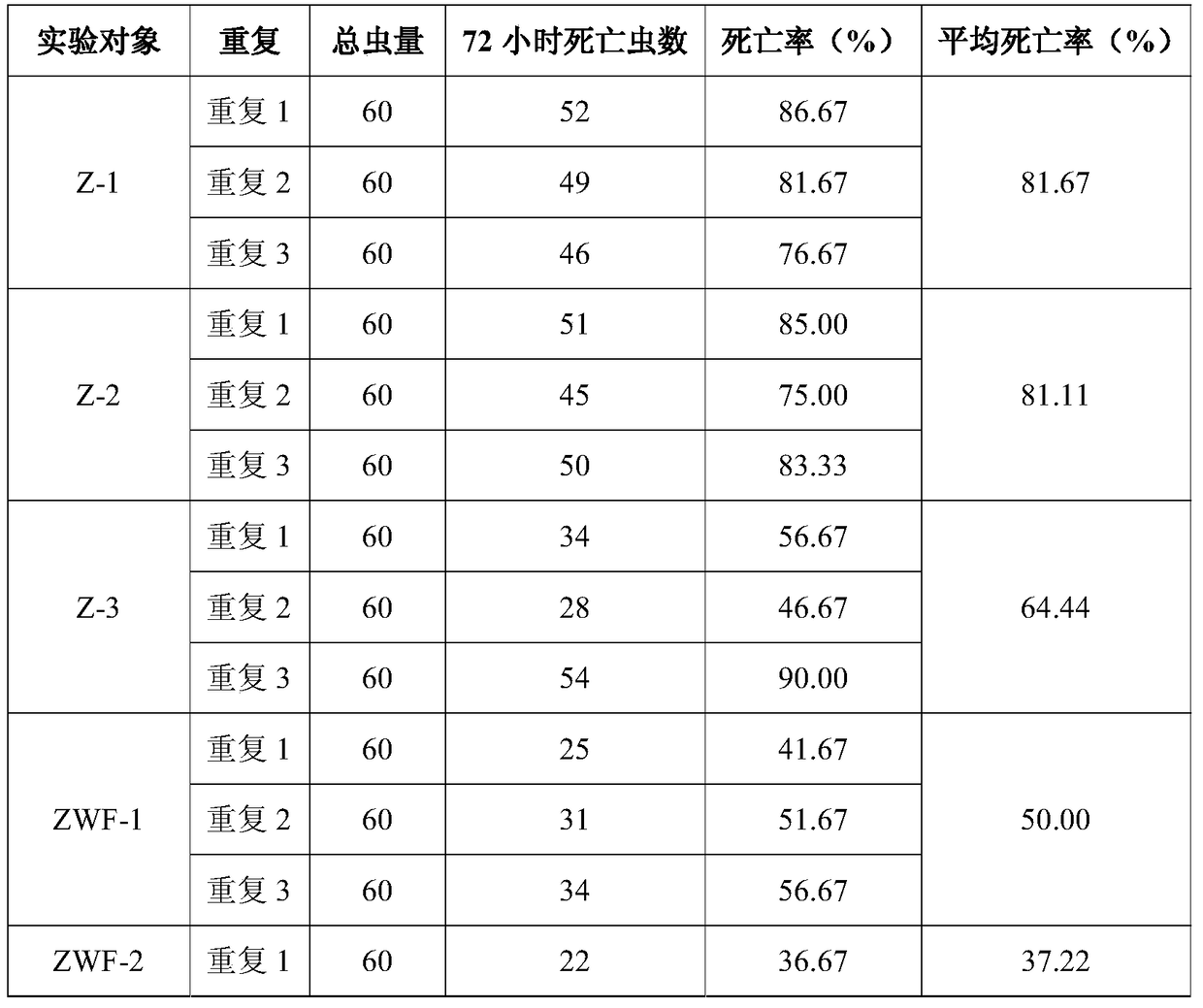
[0046] The present invention: the selected sequence fragments 1, 14, 16, and 7 are sequentially connected to form the DNA fragment of the present invention. Transformation was carried out on Arabidopsis thaliana, and experiments were carried out on the obtained T3 generation plants, and the three strains with high, medium and low expression levels of the fusion protein were named Z-1, Z-2, and Z-3;
[0047] Control 1: The new DNA fragment 1 formed by removing the auxiliary sequence of the above DNA fragments, that is, 1, 16, and 7 in sequence, was transgenic in the same way to obtain T3 generation plants, and the fusion protein expression levels were measured as high, medium and low. The strains were named ZWF-1, ZWF-2, ZWF-3;
[0048] Control 2: wild-type Arabidopsis;
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com