Nano-cellulose edible coatings and uses thereof
A technology of nanofibrils and cellulose, which can be used in cellulose coatings, food ingredients as coating agents, and protective coatings to protect fruits/vegetables. It can solve problems such as economic losses and juice loss.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
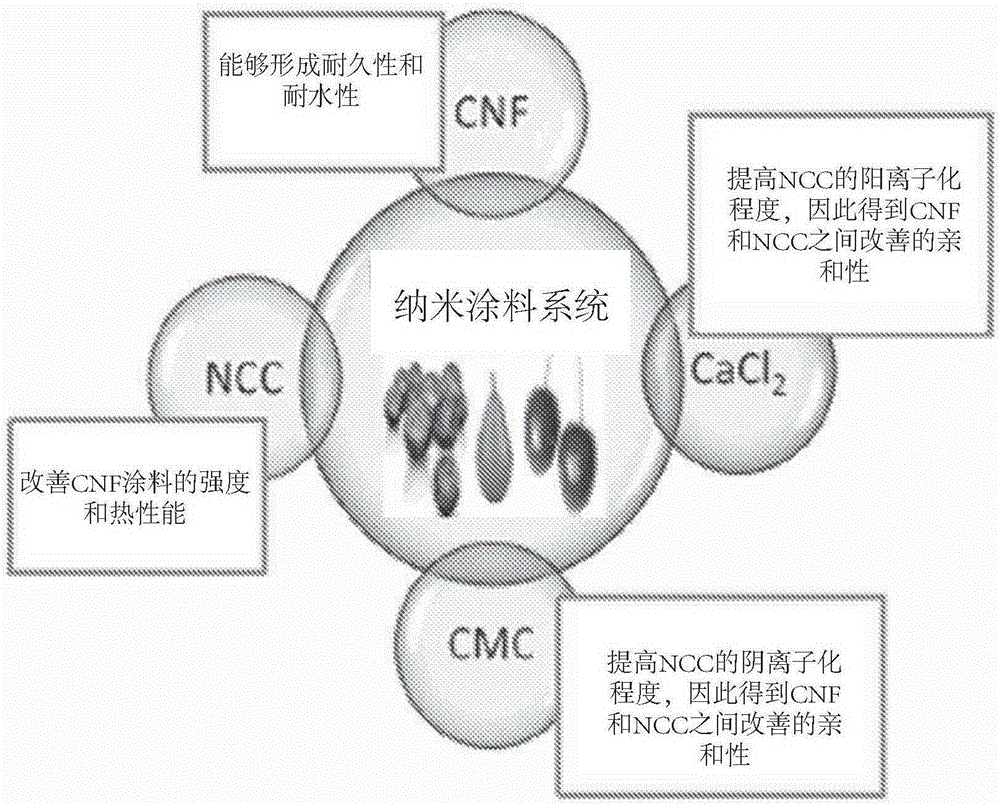
[0173] This example describes compositions for the preparation of cellulose nanofibrils (CNFs) comprising crystalline and amorphous regions, with widths from three to several hundred nm and aspect ratios greater than 50, reminiscent of primary filaments in plant cell walls.
[0174] The CNFs are formed by the fibrillation process with or without chemical pretreatment in the mechanical refining of cellulose, such as but not limited to wood fibers or non-wood plant fibers, with or without residual hemicellulose. In some instances, CNFs are obtained commercially.
[0175] Nanoparticles, nanodots or nanopowder calcium carbonate (NCC) are cubic high surface area particles. Nanoscale calcium carbonate has a particle size of about 60 nm to about 100 nm when examined with a scanning electron microscope (SEM). Existing applications of NCC focus on its application in drug delivery, by making it bear hydrophilic protein-based drugs, and its potential imaging, biomedical and bioscienti...
Embodiment 2
[0181] This example describes the prevention of pigment / nutrient leaching from blueberry fruit using embodiments of the compositions disclosed herein. All embodiments, with or without the addition of nano-calcium carbonate, nearly eliminated the loss of anthocyanin pigments from blueberries (compared to controls) during heat treatments similar to those seen in the industry.
[0182] With different CNF, NCC and CaCl shown in Table 4 2Solution coating of blueberries, either by dipping the fruit in a solution of the composition (dipping the blueberries in the solution of the composition for 1 minute and then drying at room temperature) or by spraying (at 30 psi pressure , the solution of the composition is sprayed onto the surface of blueberries, and then dried at room temperature).
[0183] Uncoated and coated blueberries (or cherries in some embodiments) were filled into glass jars filled with distilled water, placed in a water bath with temperature control, and subjected to o...
Embodiment 3
[0187] This example describes the coating of apples using embodiments of the compositions disclosed herein.
[0188] Peel, core, and slice apples into even-thick slices. The resulting pieces were then dipped in the CNF-containing composition or left uncoated before being frozen in a forced air freezer (-20°C) for 24 hours. Afterwards, the samples were removed from the freezer and thawed at ambient temperature (18-23°C) for about 6 hours. The mass change during freezing (condensation) and the change in the total amount of liquid exuded from the thawed apples (syringe and evaporation) were determined.
[0189] Overall, as shown in Table 5, the total weight loss (%) after thawing of the coated apple slices was lower than the total weight loss after thawing of the uncoated apple slices. In addition, it was found that with coated apples ( Figure 10B ) on uncoated slices caused by the ambient humidity in the thawing chamber formed on thawed apples to a greater extent ( Figure ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com