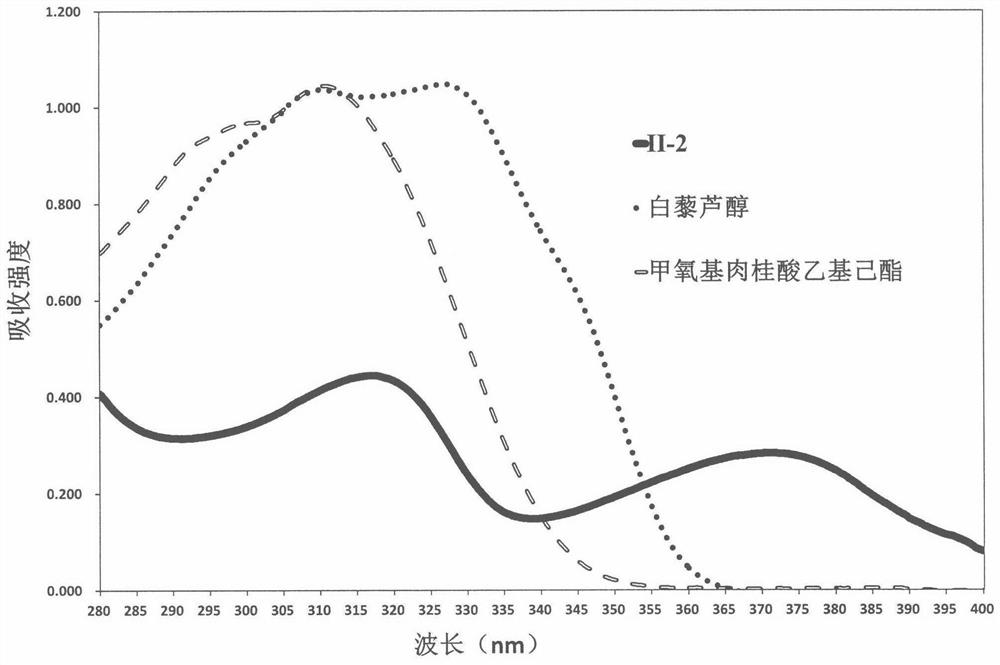
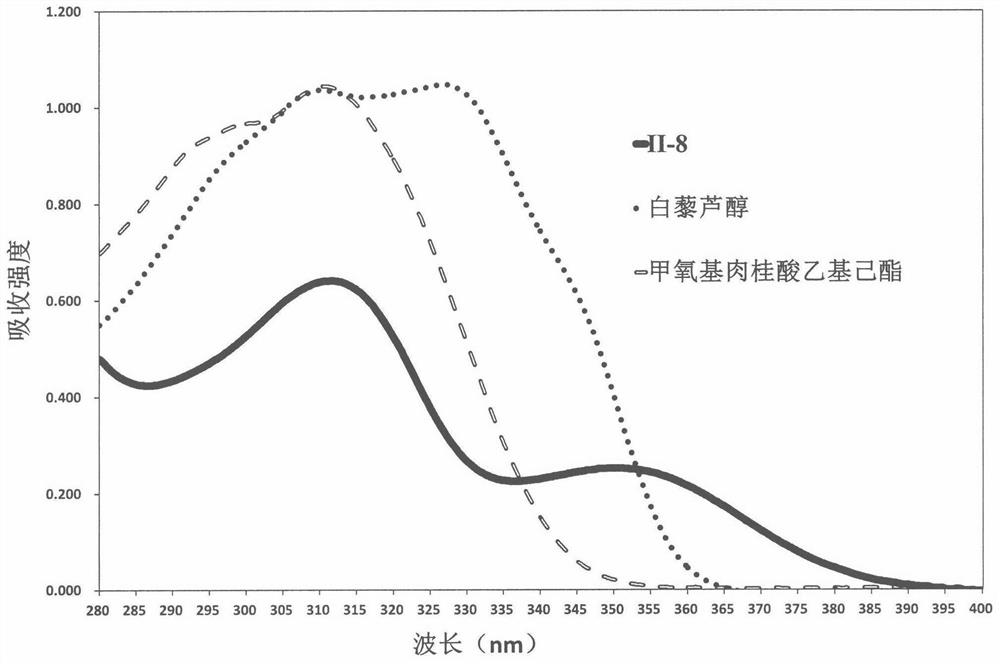
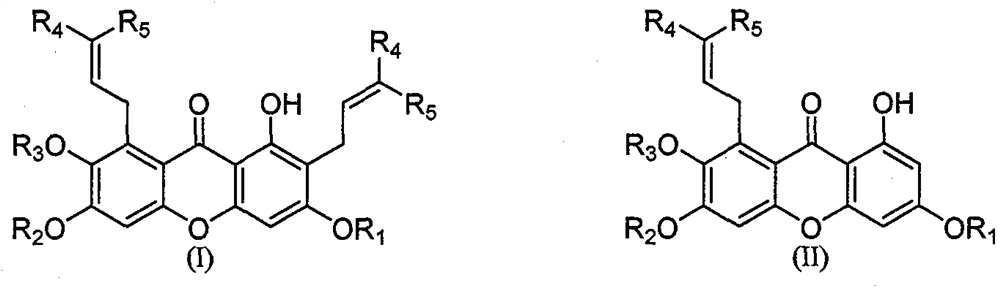
A 1,3,6,7-tetrahydroxyxanthone derivative and its preparation method and use
A technology of tetrahydroxyxanthone and derivatives, applied in the field of acid sphingomyelinase inhibitors, sunscreen agents, 1, can solve the problem of insufficient inhibitory activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Example 1: Preparation of (trans, trans)-3,6-dimethoxy-1,7-dihydroxy-2,8-bis-(2-heptenyl)-9H-xanthone (I-1 )
[0052] Dissolve 2 g (5.43 mmol) of 3,6-dimethoxy-1,7-dihydroxy-2,8-diallyl-9H-xanthone in 3 mL of anhydrous dichloromethane, add 1,3 -Bis(2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)-2-(imidazolidinylidene)(dichlorobenzylidene)(tricyclohexylphosphine)ruthenium 15mg, 1-hexene 13.6mL (108.6mmol ), under the protection of nitrogen, reacted at 50°C for 4h, stopped the reaction, concentrated, and purified by column chromatography to obtain 1.82g of yellow solid I-1 with a yield of 70%.
[0053] 1 H NMR (300MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ0.85, 0.93 (3H each, s, -CH 3 ), δ1.31 (8H, m, -CH 2 CH 2 -×2), δ1.95 (4H, m, -CH 2 ×2), δ3.35 (2H, d, J=6.9Hz, -CH 2 -), δ3.90 (3H, s-OCH 3 ), δ3.99 (3H, s-OCH 3 ), δ4.14 (2H, d, J=6.7Hz, -CH 2 -), δ5.54(4H, m, -CH=×4), δ6.31(1H, s, Ar-H), δ6.73(1H, s, Ar-H), δ13.5(1H, s, Ar-OH); ESI-MS (m / z): 481 [M+H] + .
Embodiment 2
[0054] Embodiment 2: Preparation (anti)-4-[2,3,6-trimethoxy-8-hydroxyl-7-[(anti)-3-carboxy-2-propenyl]-2-butenoic acid (I -6)
[0055]Dissolve 2 g (5.23 mmol) of 3,6,7-trimethoxy-1-hydroxy-2,8-allyl-9H-xanthone in 3 mL of anhydrous dichloromethane, add 1,3-bis( 2,4,6-trimethylphenyl)-2-(imidazolidinylidene)(dichlorobenzylidene)(tricyclohexylphosphine)ruthenium 15mg, acrylic acid 14.4mL (209.2mmol), under nitrogen protection, React at 50°C for 4h, stop the reaction, concentrate, and purify by column chromatography to obtain 2.07g of yellow solid I-6 with a yield of 82%.
[0056] 1 H NMR (300MHz, DMSO), δ3.25 (2H, d, J=6.48Hz, -CH 2 -), δ3.38, 3.87, 3.92 (3Heach, s, -OCH 3 ), δ4.02 (2H, s, -CH 2 -), δ4.85 (2H, d, J=15.06Hz, -CH=×2), δ5.57 (1H, m, -CH=), δ6.58 (1H, m, Ar-H), δ6 .76(1H, m, -CH=), δ7.06(1H, m, Ar-H), δ12.08(1H, s, -COOH), δ13.5(1H, s, -COOH); ESI -MS(m / z): 471[M+H] + .
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3: 3,6,7-trimethoxy-1-hydroxyl-2,8-di-[(trans, trans)-4-methyl-4-hydroxyl-2-pentenyl]-9H-xanyl Xanthone (I-7)
[0058] Dissolve 2 g (5.23 mmol) of 3,6,7-trimethoxy-1-hydroxy-2,8-allyl-9H-xanthone in 3 mL of anhydrous dichloromethane, add 1,3-bis( 2,4,6-Trimethylphenyl)-2-(imidazolidinylidene)(dichlorobenzylidene)(tricyclohexylphosphine)ruthenium 15mg, 2-methyl-3-butene-2- Alcohol 11mL (104.6mmol), reacted at 50°C for 4h under nitrogen protection, stopped the reaction, concentrated, and purified by column chromatography to obtain 1.95g of yellow solid I-7 with a yield of 75%.
[0059] 1 H NMR (300MHz, CDCl 3 ): δ1.04(2H, s, -CH×2), δ1.22(12H, s, -CH 3 ×4), δ3.81 (2H, d, J=5.43Hz, -CH 2 -), δ3.51 (2H, d, J=5.7Hz, -CH 2 -), δ3.74 (3H, s-OCH 3 ), δ3.92, 3.96 (3Heach, s-OCH 3 ), δ5.64, 5.74 (2H, m, -CH=×2), δ6.81 (1H, s, Ar-H), δ7.5 (1H, s, Ar-H), δ13.07 (1H , s, Ar-OH); ESI-MS (m / z): 497 [M-H] - .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com