Metal doped carbon points with high fluorescence quantum yield and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of metal doping and carbon dots, applied in the field of nanomaterials, can solve the problems of low fluorescence quantum yield, etc., and achieve the effects of high fluorescence quantum yield, less raw material consumption, and less by-products and intermediate products.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] (a) Take 0.735g of sodium citrate and 0.0617g of cuprous chloride, dissolve in 25mL of deionized water and stir for 5min to obtain a precursor solution;
[0058] (b) Place the obtained precursor solution in a 50ml polytetrafluoroethylene-lined stainless steel autoclave, seal it and react at a temperature of 200°C for 6h, and cool it naturally to room temperature to obtain a suspension;
[0059] (c) Filter the suspension with a cylindrical membrane separation filter with a molecular weight cut-off of 3 kDa, collect the filtrate, and dry to obtain copper-doped carbon dots with a high fluorescence yield.
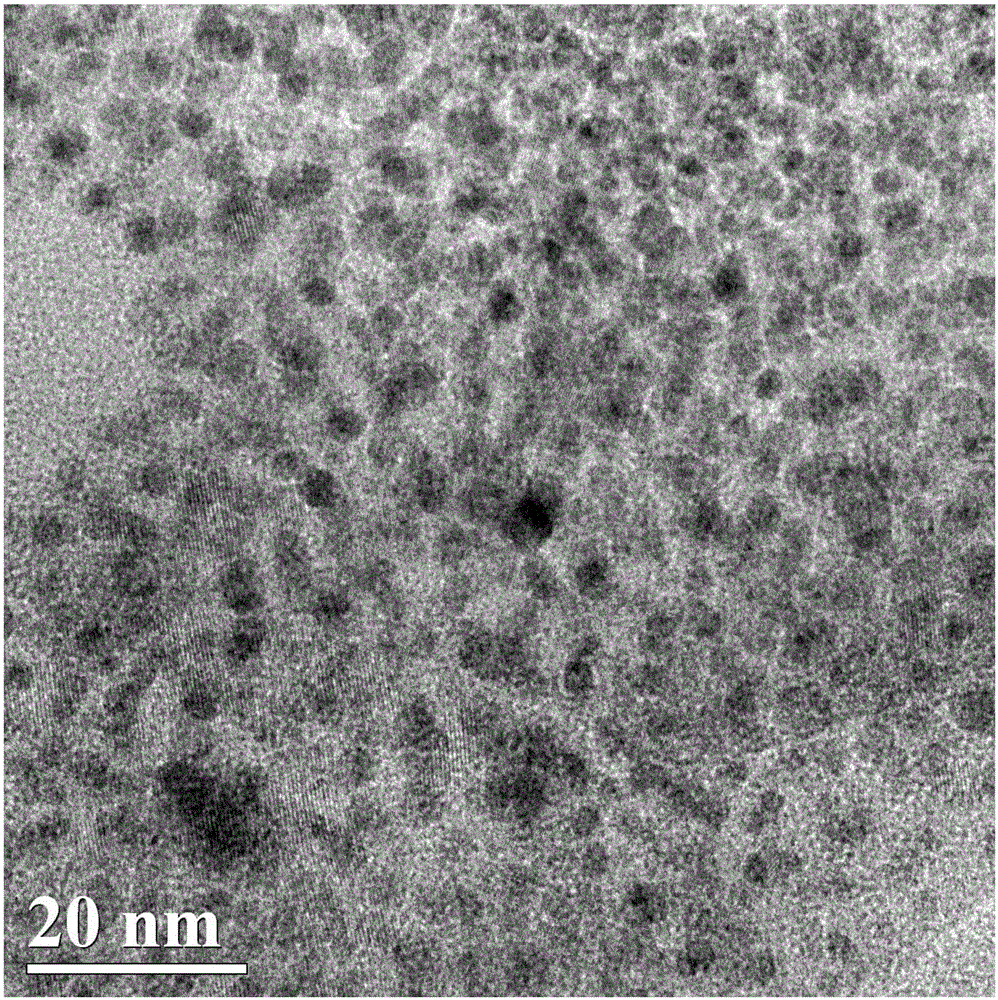
[0060] see figure 1 , which is the transmission electron microscope image of the copper-doped fluorescent carbon dots prepared in this example, from figure 1 The carbon dots were tested to be uniform circular particles with a size between 2.5nm and 5nm and an average particle diameter of 3.76nm.
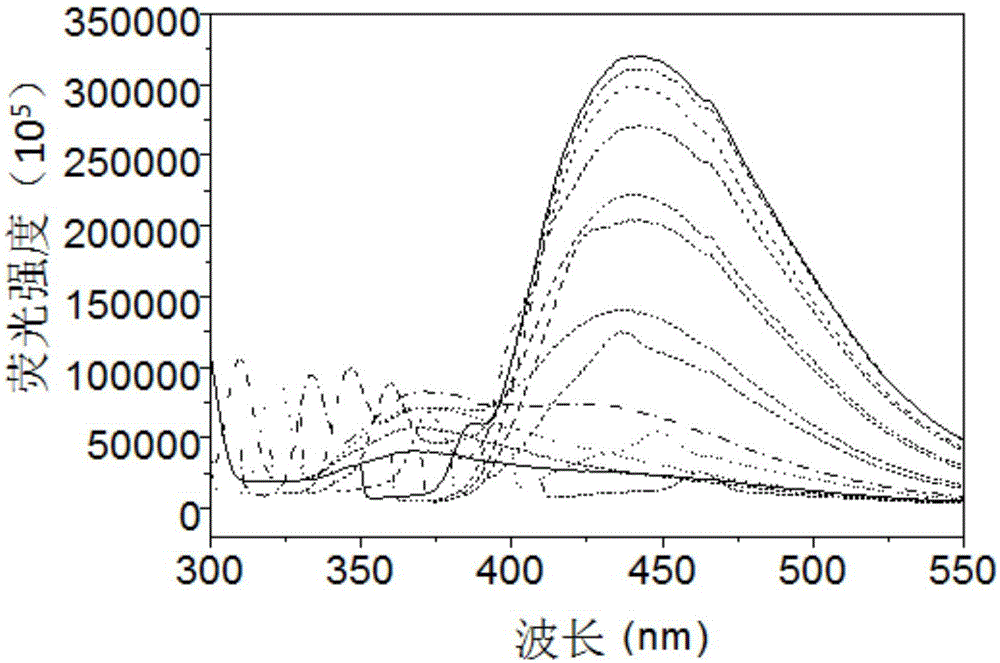
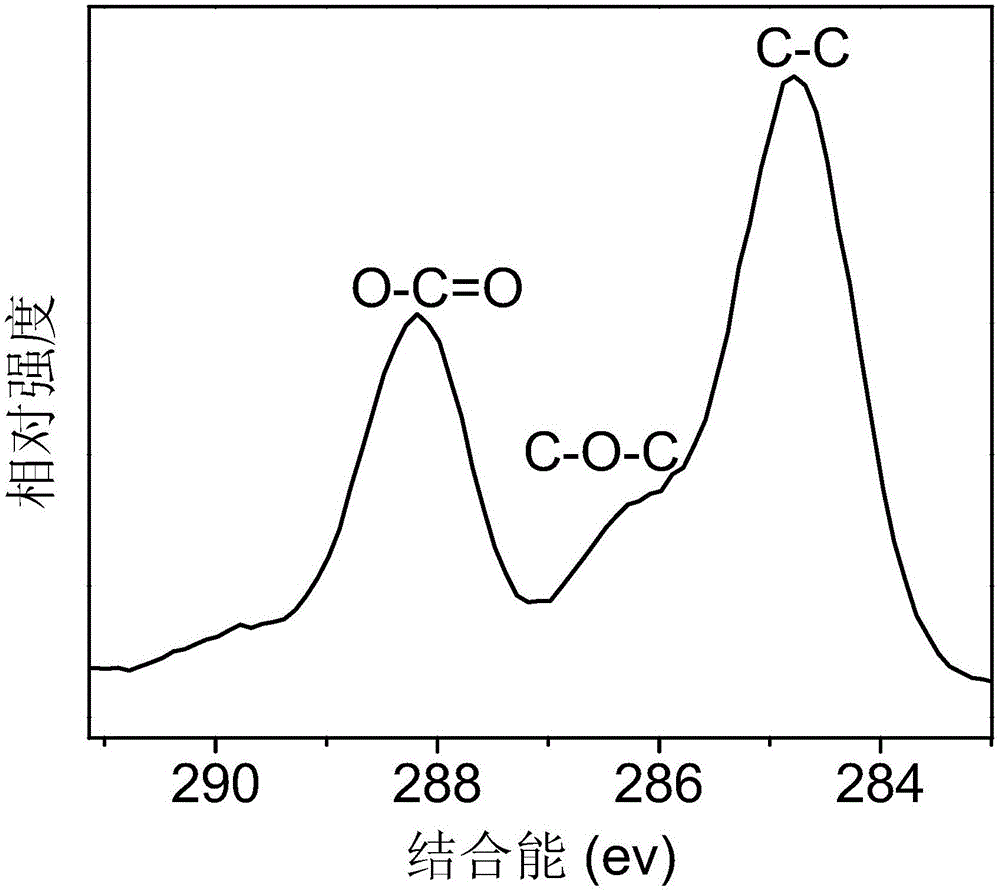
[0061] see figure 2 , it is the copper-doped fluorescent carbon dot pr...
Embodiment 2
[0064] (a) Take 0.735g of sodium citrate and 0.0617g of cuprous chloride, dissolve in 25mL of deionized water and stir for 5min to obtain a precursor solution;
[0065] (b) Place the obtained precursor solution in a 50mL polytetrafluoroethylene-lined stainless steel autoclave, seal and react at 200°C for 6h, and cool naturally to room temperature to obtain a suspension;
[0066] (c) Filtrating the suspension with a cylindrical membrane separation filter with a molecular weight cut-off of 3 kDa, collecting the filtrate, and drying to obtain copper-doped carbon dots with a high fluorescence yield. The carbon dots obtained in this example have a luminous intensity of 350,000 under the irradiation of 340nm light.
Embodiment 3
[0068] (a) Take 0.735g of sodium citrate and 0.0617g of cuprous chloride, dissolve in 25mL of deionized water and stir for 5min to obtain a precursor solution;
[0069] (b) Place the obtained precursor solution in a 50mL polytetrafluoroethylene-lined stainless steel autoclave, react for 6h under sealed conditions at 180°C, and cool naturally to room temperature to obtain a suspension;
[0070] (c) Filtrating the suspension with a cylindrical membrane separation filter with a molecular weight cut-off of 5 kDa, collecting the filtrate, and drying to obtain a copper-doped carbon dot with a high fluorescence yield. The carbon dots obtained in this example had a luminous intensity of 140,000 under the irradiation of 450nm light.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com