Evaluation Method for Surface Defects of Spherical Optical Components
A technology for spherical optics and defect evaluation, which is applied in the direction of optical devices, material analysis through optical means, scientific instruments, etc., can solve problems such as human eye fatigue and the inability to give quantitative descriptions of defect information, and achieve reliable numerical basis, Improvement of detection efficiency and detection accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Below, embodiment 1 of the present invention will use Figure 1-9 to describe in detail.
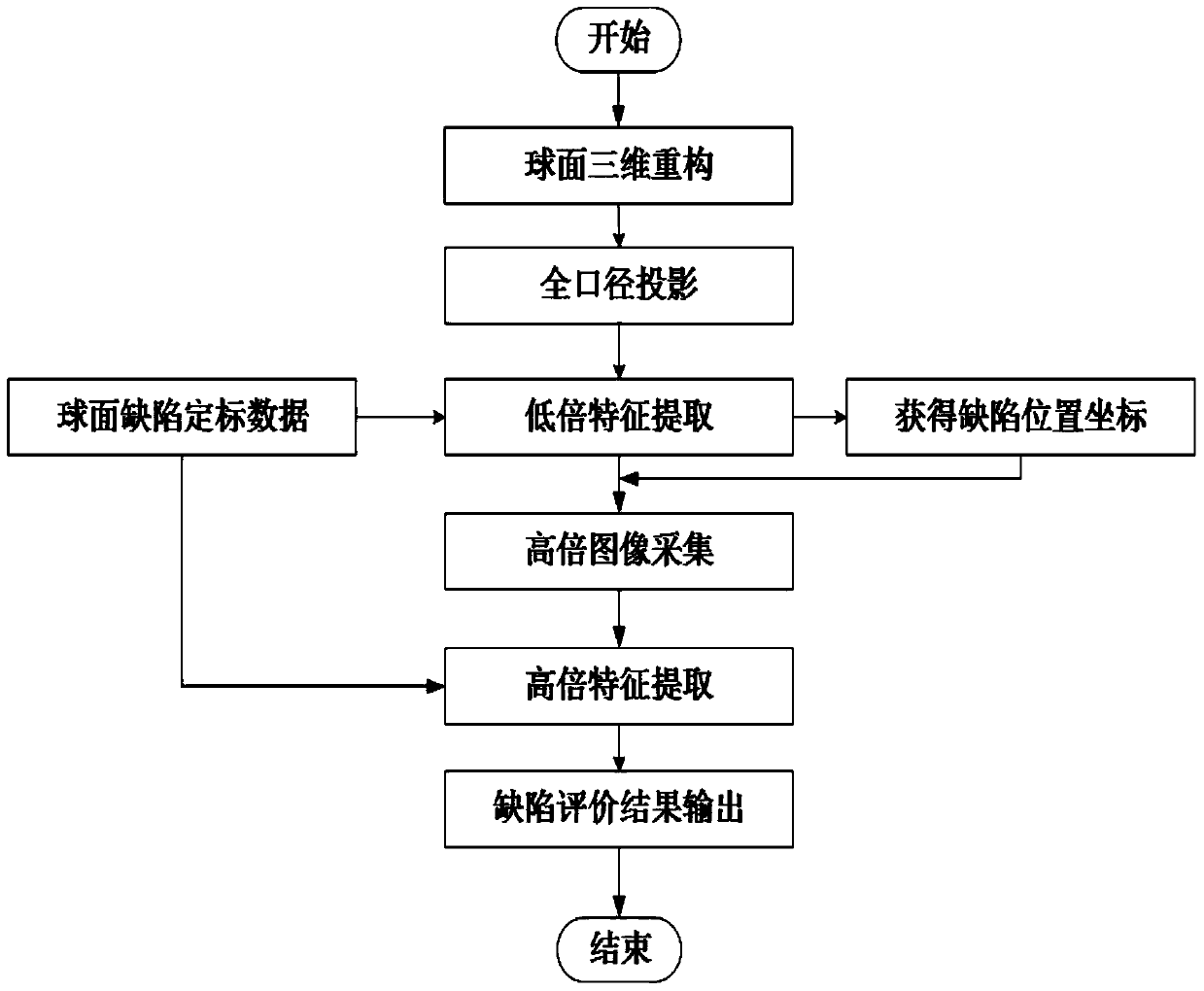
[0055] The method for evaluating the surface defect of a spherical optical element specifically includes the following steps:
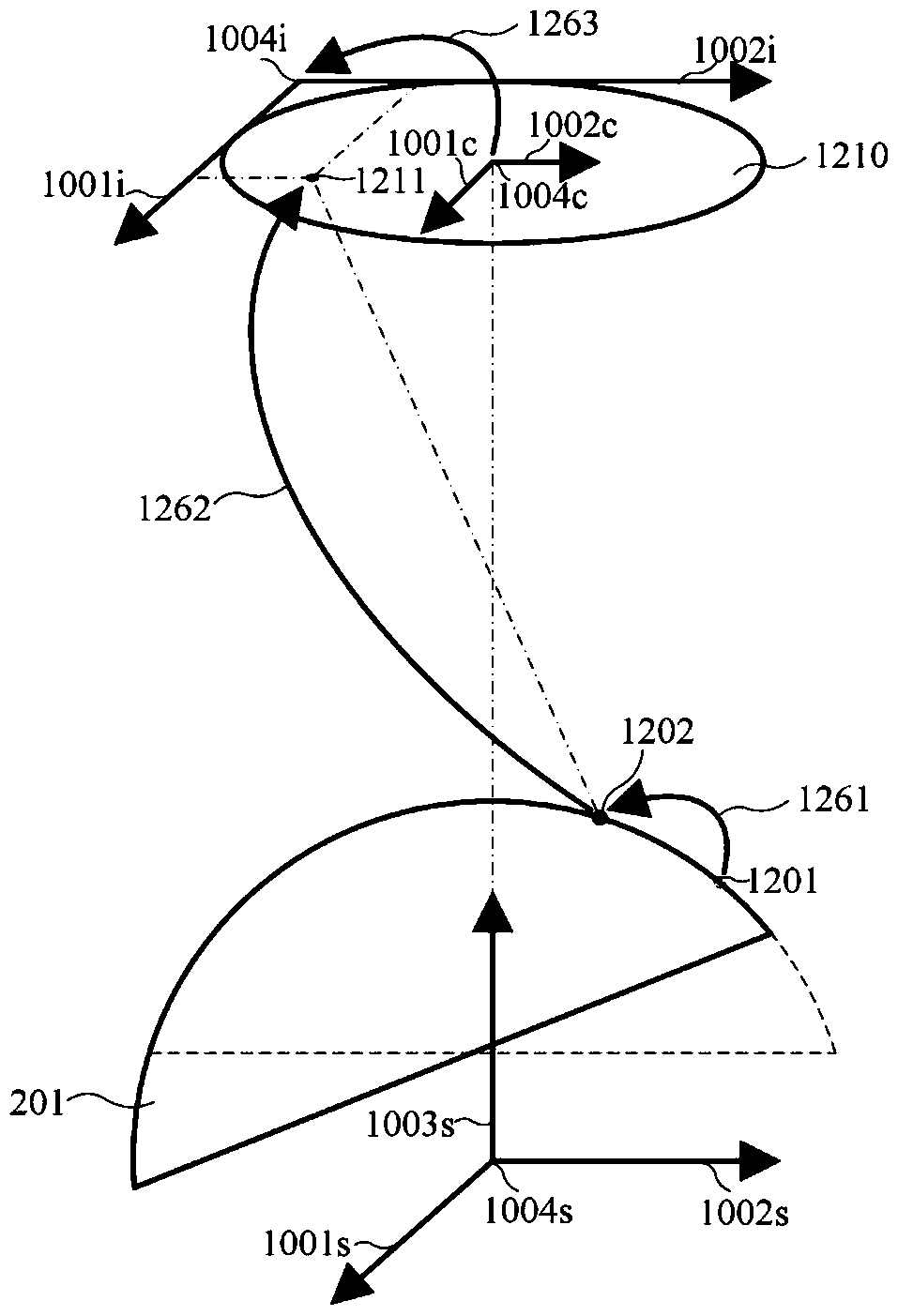
[0056] Step 1. When the spherical optical element 201 is imaged on the image plane through micro-scattering dark field imaging, the obtained imaging sub-aperture image is a two-dimensional image. Since information compression along the optical axis of imaging occurs during the optical imaging process, three-dimensional reconstruction of the spherical surface must first be performed to correct the information compression along the optical axis of imaging caused by surface defects of the spherical optical element 201 through optical imaging.
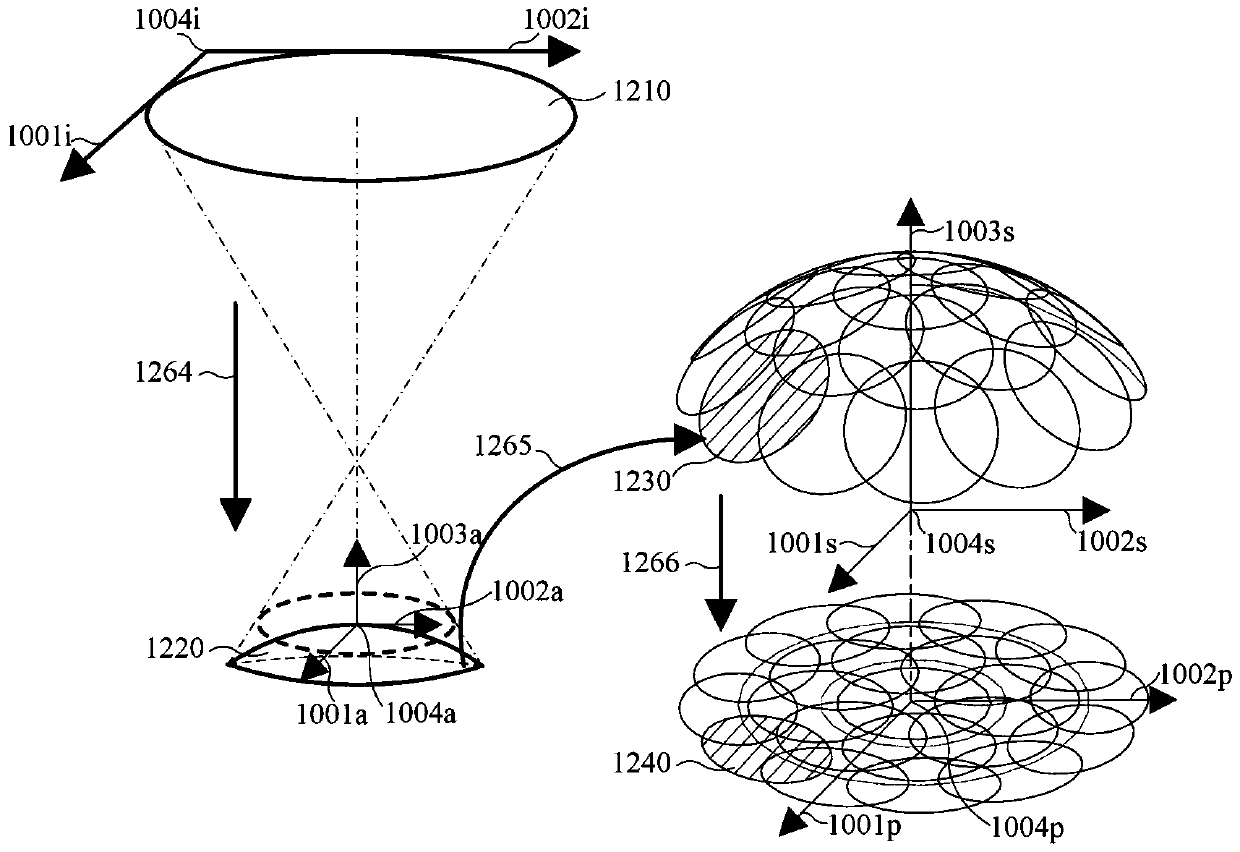
[0057] Step 2. The three-dimensional sub-aperture image is obtained after three-dimensional reconstruction of the spherical surface. In order to facilitate feature extraction, the information of the three-dimensional...
Embodiment 2
[0095] Below, embodiment 2 of the present invention will combine Figure 10 to describe in detail. In Example 2, a method of evaluating a surface defect of a spherical optical element when evaluating a small-diameter spherical optical element will be described.
[0096] The characteristic of the small-aperture spherical optical element discussed in this embodiment is that the full-aperture imaging of the entire surface of the small-aperture spherical optical element can be obtained only by performing microscopic scattering dark-field imaging on a sub-aperture at the apex of the spherical surface. Therefore, the corresponding defect evaluation method is also simpler than that in Embodiment 1, and the spherical defect information can be obtained by processing the sub-aperture image through image processing and defect calibration.
[0097] The sub-aperture image is processed through image processing and defect calibration to obtain spherical defect information, see Figure 10 ,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com