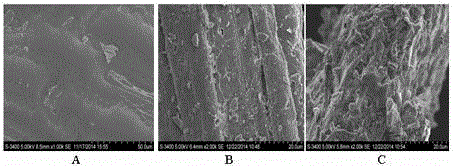
Novel process for jointly degrading and saccharifying crop straw by means of thermo-chemical treatment, microbial fermentation and enzymatic hydrolysis
A technology of crop straw and thermochemical treatment, applied in the direction of fermentation, can solve the problems of unsuitable feed production, damage to animal health, environmental pollution and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0022] 1. Materials and methods
[0023] 1.1 Materials
[0024] Naturally air-dried corn stalks were pulverized by a hammer mill, sieved with 1 mm, and stored at room temperature. Cellulase and xylanase were purchased from Shandong Zesheng Biotechnology Co., Ltd. According to the American Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) cellulase assay method, the cellulase activity and xylanase activity were 323FPU / g and 5500U / g, respectively. Trichoderma kangning was purchased from China General Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Center, strain number CGMCC3.4262.
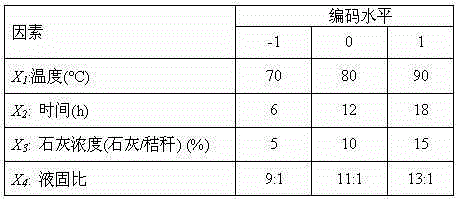
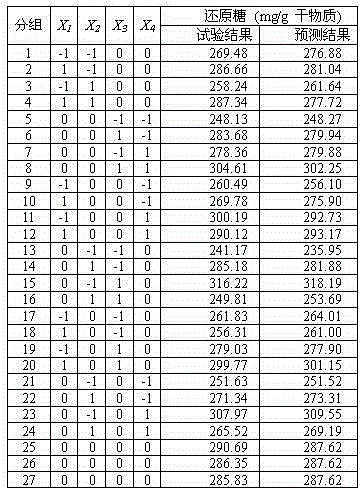
[0025] 1.2 Response surface design for optimal chemical treatment conditions
[0026] Using Design-Expert8.0.5 software, Box-Behnken design was used for experimental design, model fitting and data analysis. In the test, 15g of corn stalks were put into a 500ml beaker, sealed with tinfoil paper, and kept in a water bath for heat preservation. Response surface optimization is based on the previous single-factor...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com