Method for detecting antibiotic residues in milk, and application thereof
A detection method and antibiotic technology, applied in the field of food safety and food safety detection, to achieve the effects of avoiding loss of analytes, strong selectivity, and improving detection efficiency and throughput
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1. Detection of multiple antibiotic residues in pasteurized milk
[0024] ⑴Sample preparation
[0025] Accurately weigh 1.00g (±0.01g) of milk sample into a centrifuge tube, add 0.5ml of zinc acetate solution with a concentration of 1mol / L, vortex and mix well, then add 1ml of 1mol / L phosphate buffer solution to control the pH of the solution The value is 4.5. After centrifugal filtration, pass through a 0.45 μm filter membrane into a sampling bottle for determination by an online solid phase extraction-high resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometer.
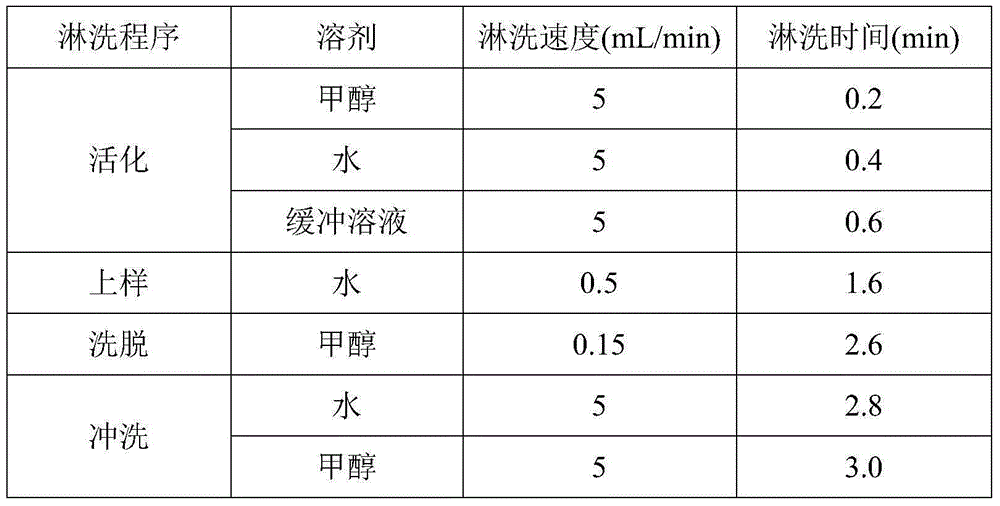
[0026] (2) The gradient elution conditions of the online solid phase extraction column are shown in Table 1, and the required solid phase extraction column is a C18 or HLB column.
[0027] Table 1 Gradient conditions of online solid phase extraction
[0028]
[0029] (3) The chromatographic separation conditions of the high-performance liquid chromatography-high resolution mass spectrometer are shown...
Embodiment 2
[0037] On the basis of Example 1, further in this example, prepare standard working solutions with mass concentrations of 10, 50, 75, 100.0, and 200.0 ng / mL, and take the ratio of the peak area of the standard solution to the area of the internal standard as the ordinate , the solution concentration (ng / ml) is the abscissa, and the standard working curve is drawn. All compounds had a good linear relationship in the range of 10-200ng / mL, and the correlation coefficient (r) was greater than 0.99. Samples were quantified using a standard working curve. The response value of the drug in the sample solution should be within the linear range of the instrument.
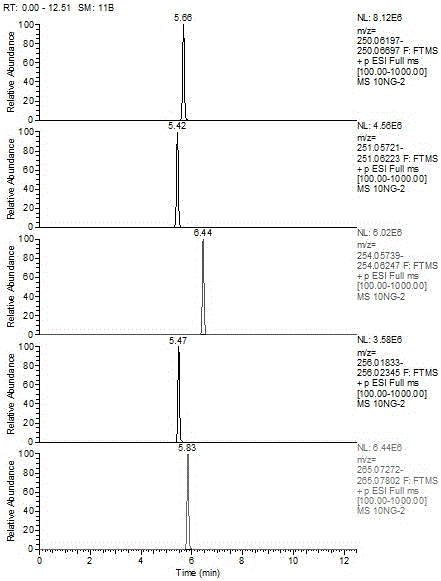
[0038]To determine whether there is a certain antibiotic in the sample, the following conditions must be met: the retention time of the chromatographic peak that appears in the sample is no more than ±2.5% from the retention time of the standard; the deviation of the accurate mass number between the sample and the stand...
Embodiment 3
[0041] Example 3. Detection of multiple antibiotic residues in organic milk
[0042] Using pasteurized milk as a negative control, the antibiotic residues in pasteurized milk and organic milk were detected respectively.
[0043] Treat pasteurized milk and organic milk separately as follows.
[0044] Accurately weigh 1.00g (±0.01g) of milk sample into a centrifuge tube, add 0.5mL zinc acetate solution with a concentration of 1mol / L, vortex and mix well, then add 1mL of 1mol / L phosphate buffer solution to control the pH of the solution The value is 4.5. After centrifugal filtration, pass through a 0.45 μm filter membrane into a sampling bottle for determination by an online solid phase extraction-high resolution liquid chromatography-mass spectrometer. The online solid phase extraction and analysis chromatographic conditions are shown in Table 2 and Table 3. The recoveries for pasteurized milk and organic milk for negative samples analyzed are shown in Table 4.
[0045] Table...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com