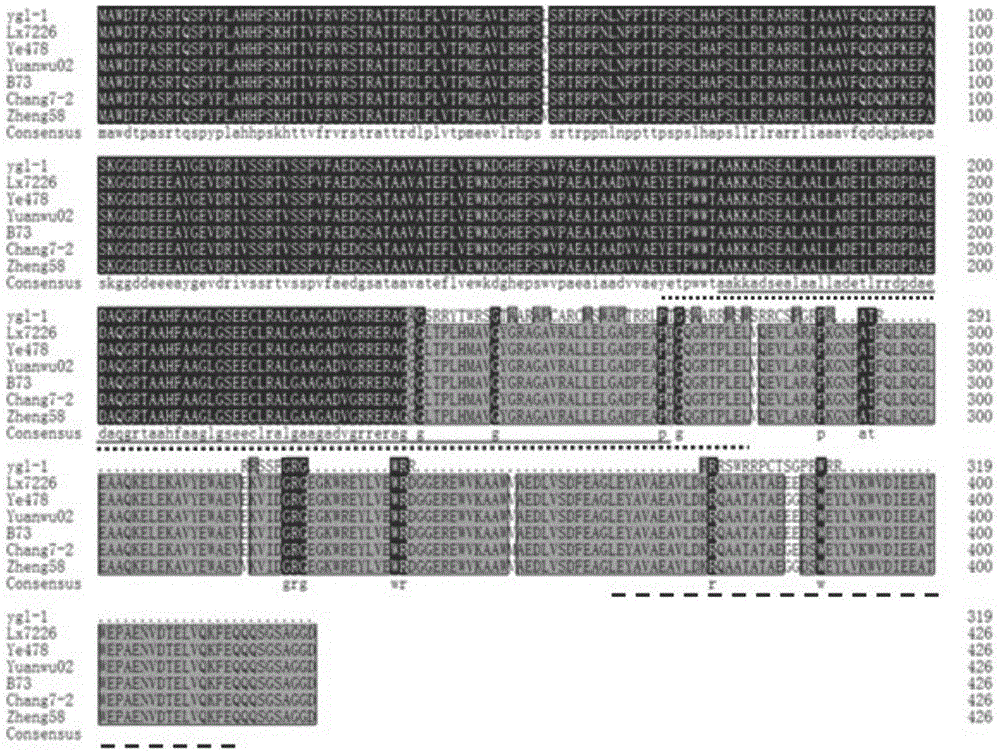
Maize yellow-green leaf gene ygl-1, and coded protein and application thereof
A technology of corn yellow-green leaves and mutation genes, applied in the field of genetics, can solve the problem of preliminary positioning of limited genes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1 Phenotype and Genetic Analysis
[0030] (1) Analysis of blade characteristics
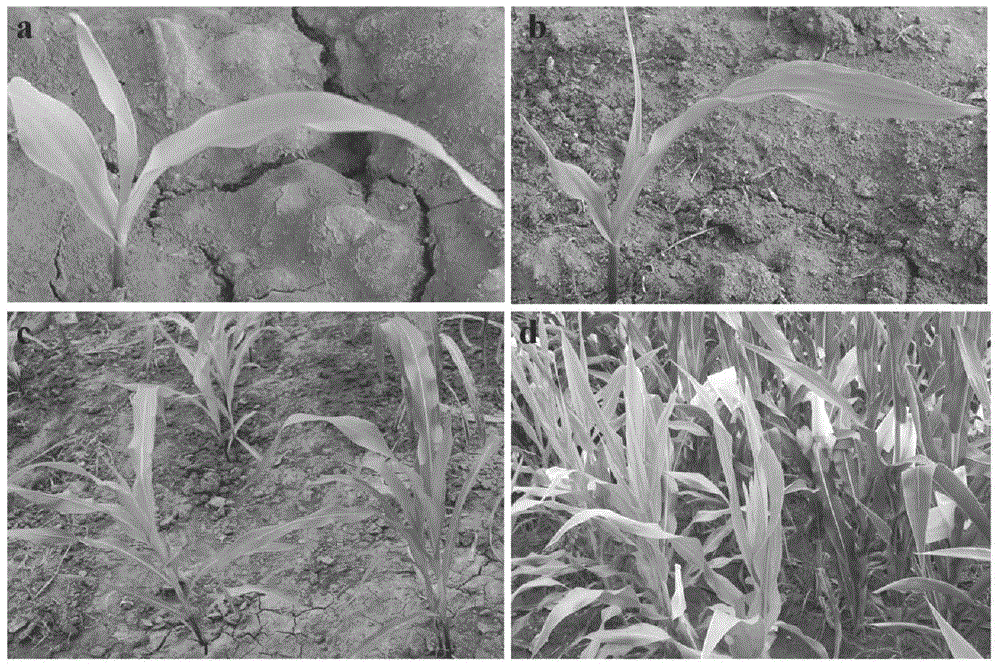
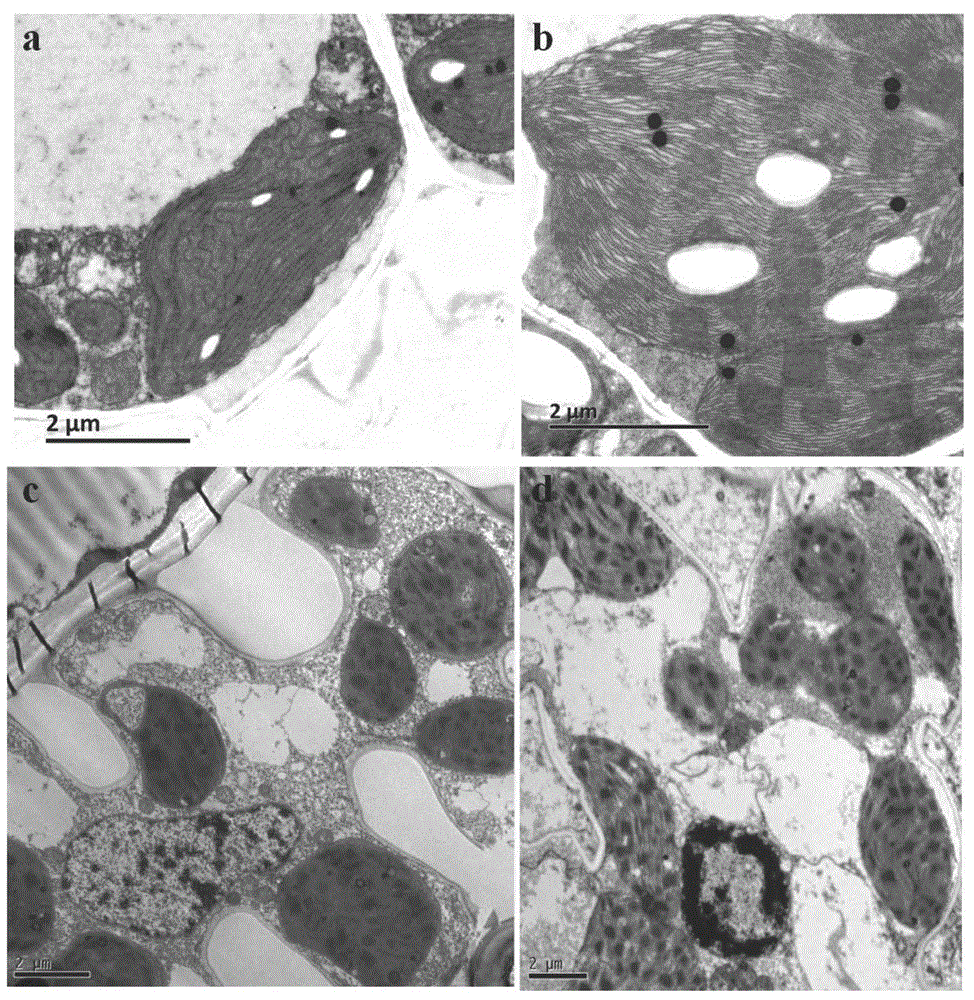
[0031] The maize ygl-1 mutant was bred inbred lines (two maize inbred lines are Yuanwu 02 and Ye 478, the materials are common breeding materials in this unit, Dr. found in the progeny materials found in the test base), the leaves of the whole growth period are light green ( figure 2 ).
[0032] (2) Determination of chlorophyll-related components
[0033] At the seedling stage and the adult plant stage, samples were taken from the corresponding positions of the leaves of the normal plant Lx7226 and the yellow leaf mutant ygl-1, and the contents of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoids were measured. Compared with normal plants, the contents of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoids in yellow-leaf mutants in the early stage decreased significantly, and the content of chlorophyll b decreased the most. It is speculated that the phenotype of yellow-green leaf mutant yg...
Embodiment 2
[0044] Example 2 Location of mutant gene ygl-1 site
[0045]Using 224 pairs of core SSR primers synthesized in the laboratory, a polymorphic molecular marker P3 linked to the target gene was found by means of BSA segregation analysis method, located in the Bin1.01 region, and the known functional gene of the yellow-green leaf mutant in maize elm1(8.06), elm2(9.03) and vyl(Chr.9) are not on the same chromosome. It is preliminarily concluded that the gene controlling this trait is a new gene whose function is still unclear. Using the 23 pairs of SSR primers in the Bin1.01 area published on the maizegdb website to mine polymorphic molecular markers linked to the target gene, 5 polymorphic markers were found, namely P1, P2, P4, P5, and P6 (as shown in Table 3). Show). These six polymorphic molecular markers were used to detect the genotypes of 231 yellow-green leaf mutants in the F2 segregation population, and combined with their phenotypes, a genetic linkage map of the yellow-gr...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Example 3 Cloning of mutant gene ygl-1
[0052] The sequence of the gene coding region was amplified from wild-type and mutant leaf genomes using PCR primers (as shown in SEQ ID NO.3 and 4), directly connected to the cloning vector, sequenced, and then compared with the sequence analysis software DNAStar. PCR amplification program: 95°C for 5min, 95°C for 45s, 65°C for 45s, 72°C for 90s, a total of 30 cycles, finally 72°C for 10min, 4°C forever.
[0053] Sequence analysis found that the mutant gene ygl-1 lacked a G at ORF713, which caused a frameshift mutation in the coding region and caused premature termination ( Image 6 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com