Preparation method of substrate material with surface enhanced Raman scattering effect
A surface-enhanced Raman and scattering effect technology, applied in the field of chemical analysis, can solve the problems of particle aggregation, complex process, and low efficiency of self-assembly methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
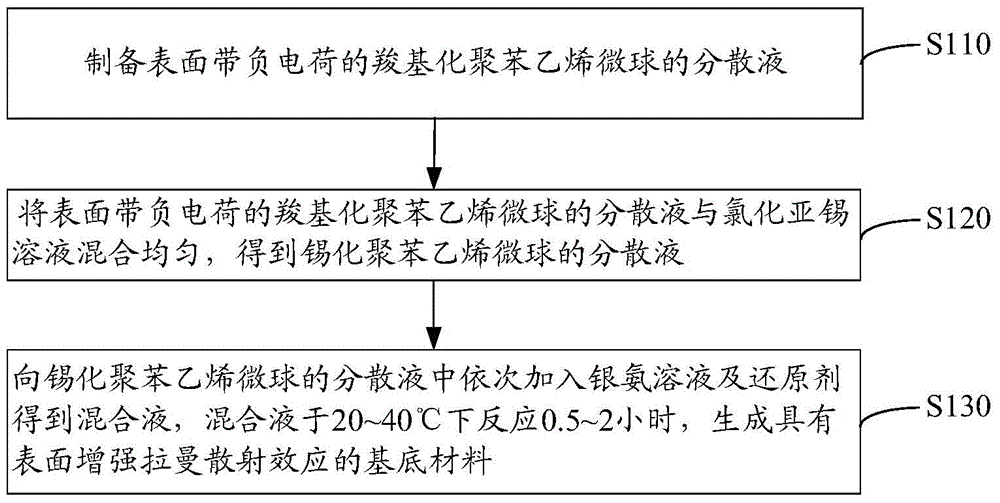
[0031] see figure 1 , a method for preparing a base material having a surface-enhanced Raman scattering effect according to an embodiment includes the following steps S110 to S130.
[0032] Step S110: preparing a dispersion of carboxylated polystyrene microspheres with negative charges on the surface.
[0033] The preparation of the dispersion liquid of the carboxylated polystyrene microspheres with negative charges on the surface comprises the following steps:
[0034] Add styrene and negatively charged functional monomers into the solvent at a mass ratio of 5.0-10.0:0.5-3.0, mix well, then raise the temperature to 60-80°C in a protective gas atmosphere, add the initiator, and React at 80° C. for 12 to 24 hours, and obtain a dispersion of carboxylated polystyrene microspheres with negative charges on the surface after cooling.
[0035] Negatively charged functional monomers are copolymerized with styrene to increase the negative charge of polymer microspheres, enhance the a...
Embodiment 1
[0061] (1) Preparation of a dispersion of carboxylated polystyrene microspheres with negative charges on the surface
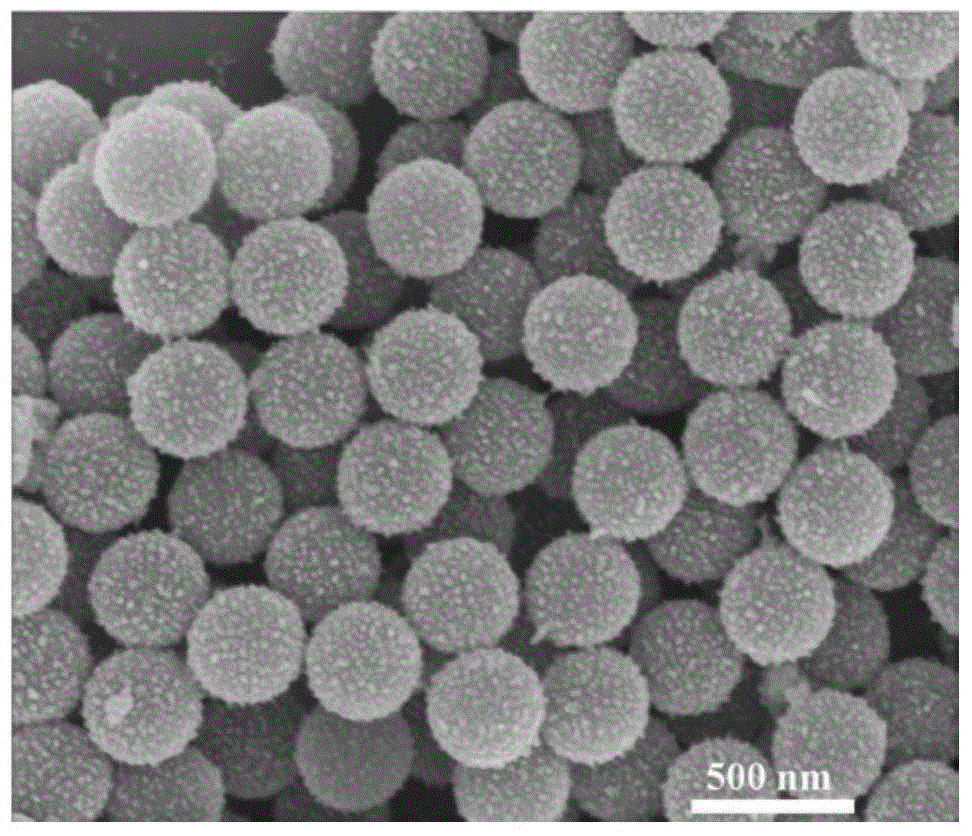
[0062] Weigh 5g of styrene, 0.5g of acrylic acid, 95mL of deionized water and 0.05g of initiator potassium persulfate into a 250mL flask, fill with nitrogen to remove oxygen for 30min, heat up to 65°C, and react at a constant temperature of 65°C under 200rpm magnetic stirring At the end of 24 hours, a dispersion of negatively charged carboxylated polystyrene microspheres on the surface with a particle size of 350 nm was prepared.
[0063] (2) Preparation of carboxylated polystyrene and silver composite nanoparticles
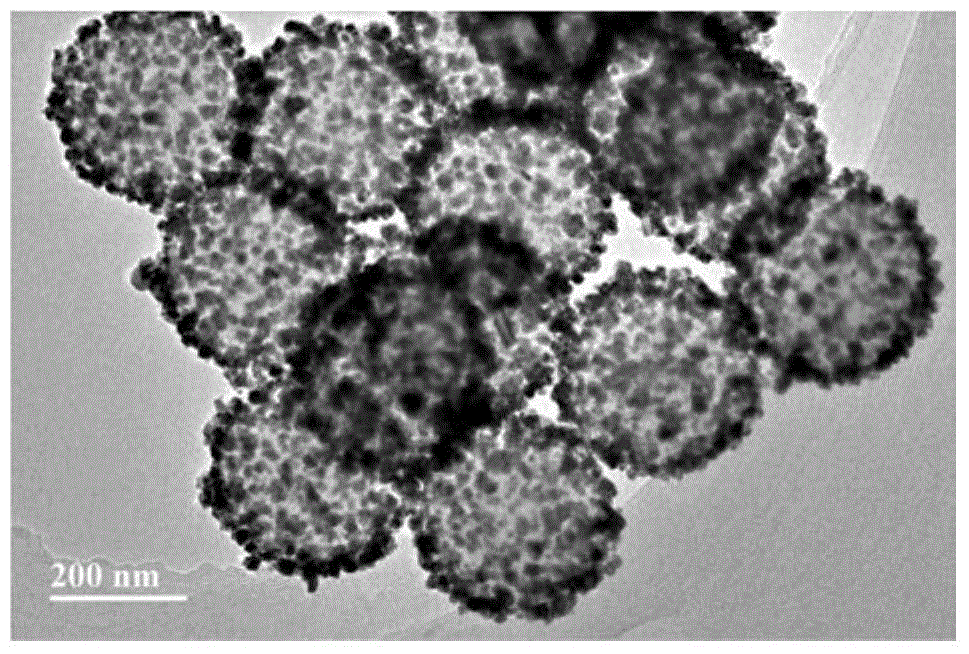
[0064] Take 50mL of a 10mg / mL dispersion of carboxylated polystyrene microspheres with a negative charge on the surface, and add 100mL of a 10mg / mL aqueous solution of stannous chloride under stirring conditions to make stannous ions adsorb on the surface by electrostatic action Negatively charged carboxylated polystyrene microsphere surface to ...
Embodiment 2
[0068] (1) Preparation of a dispersion of carboxylated polystyrene microspheres with negative charges on the surface
[0069] Weigh 10g of styrene, 3g of acrylic acid, 90mL of deionized water and 0.5g of ammonium persulfate as an initiator, add them to a 250mL flask, fill with nitrogen to remove oxygen for 30min, heat up to 75°C, and react at a constant temperature of 75°C for 24h under 200rpm magnetic stirring At the end, a dispersion of negatively charged carboxylated polystyrene microspheres on the surface with a particle size of 1.2 μm was prepared.
[0070] (2) Preparation of carboxylated polystyrene and silver composite nanoparticles
[0071] Take 50mL of the 100mg / mL surface negatively charged carboxylated polystyrene microsphere dispersion, under stirring conditions, add 5mL of 100mg / mL stannous chloride aqueous solution, the stannous ions are adsorbed on the surface by electrostatic action Negatively charged carboxylated polystyrene microsphere surface to prepare tin...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com