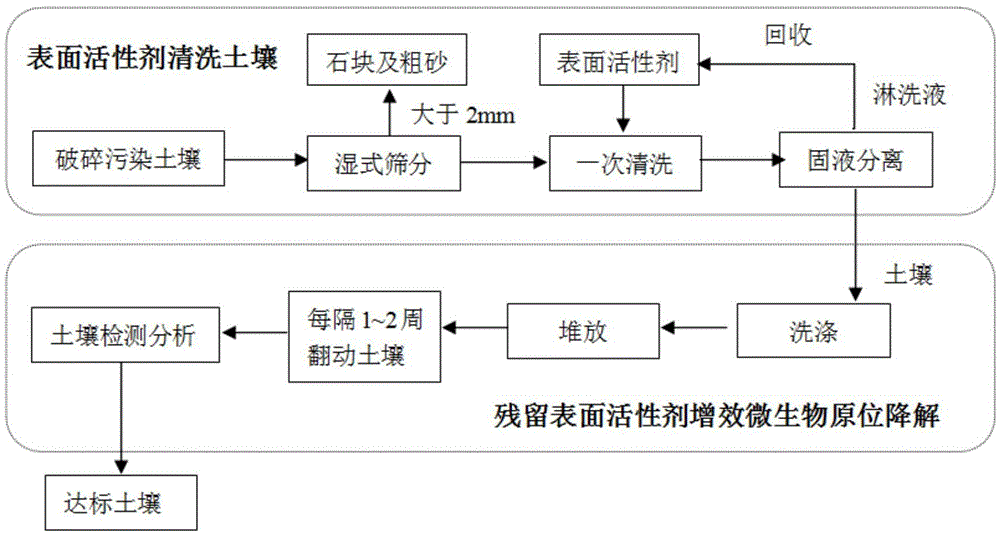
Method for remedying soil polluted by organo-chlorine pesticides (OCPs) on basis of solubilization, elution and microorganism strengthening effects of surface active agent
A surfactant and microbial remediation technology, applied in the field of organic contaminated soil remediation, can solve problems such as increasing the amount of surfactants, and achieve the effects of improving community structure, increasing quantity and activity, and promoting microbial degradation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Prepare 400 mg / L rhamnolipid-inorganic salt solution, adjust its ionic strength to 5.0 mg / L, pH to 7.0, sterilize at 121°C for 30 minutes, and after cooling, measure 5L of rhamnolipid solution and put it in In the beaker containing the soil to be eluted, place it under a six-joint stirrer to stir; among them, the amount of rhamnolipid required for 1000 g of soil sample is 2 g.
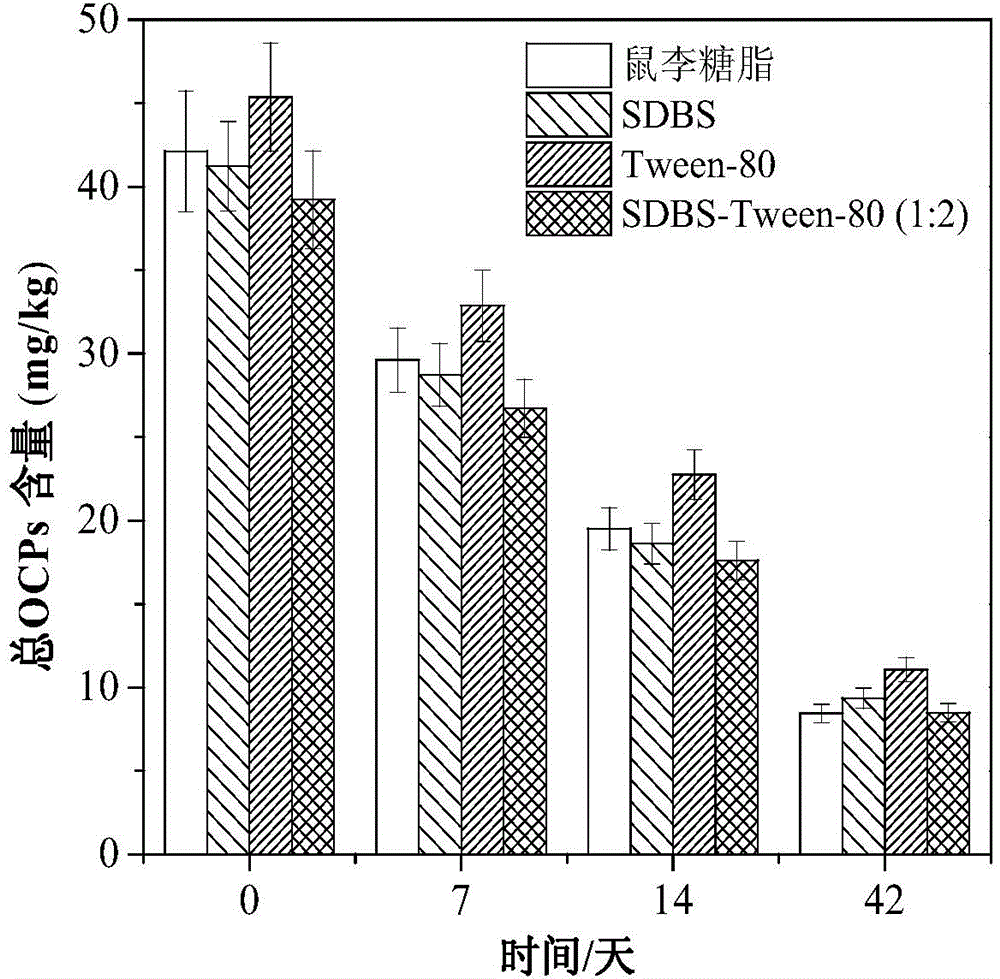
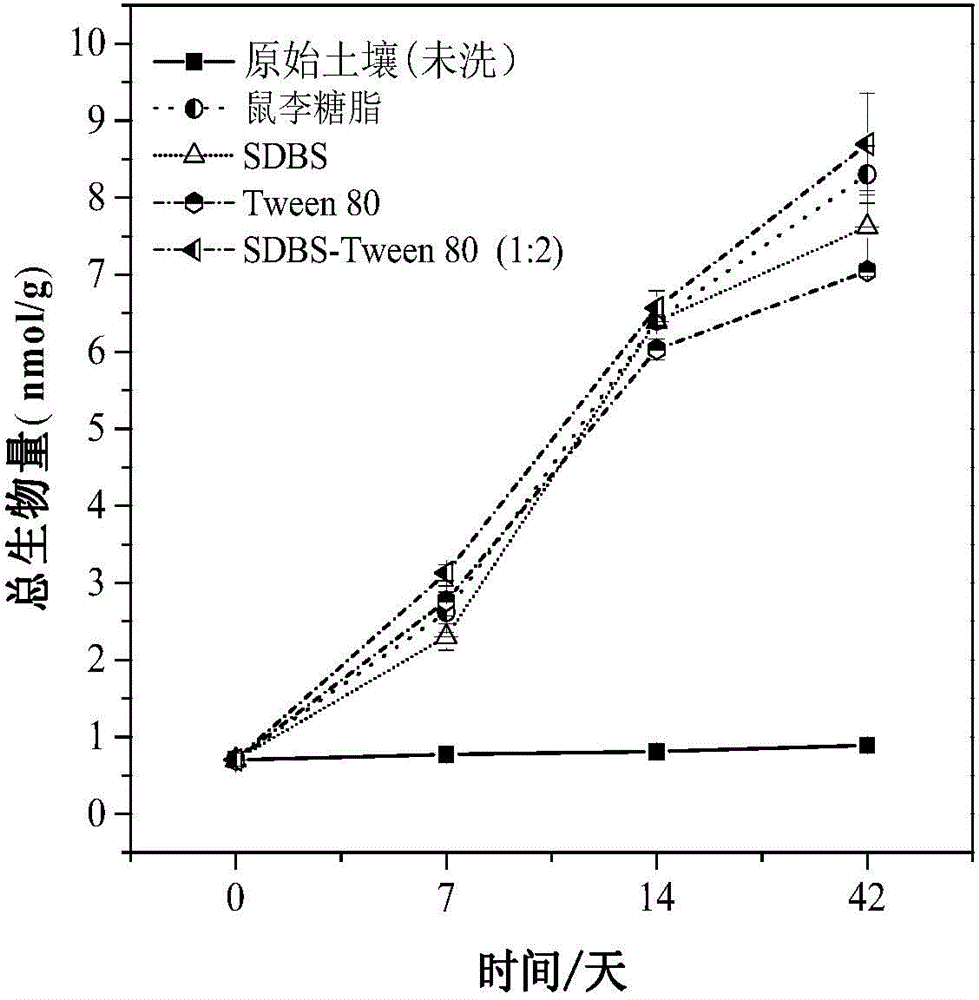
[0023] Stir for 30 min, centrifuge the eluted soil, evenly select 5 g of the eluted soil sample, and after freeze-drying, the measured OCPs elution efficiency is 89.0% (eg Figure 4 shown), in which DDE and DDT in OCPs did not meet soil environmental quality standards (such as Figure 5 shown).
[0024]The content of rhamnolipid in the supernatant was determined, and the concentration of rhamnolipid in the soil was washed with water to a concentration range of 10-50 mg / kg.
[0025] The soil after the first wash was piled up on the open space with ventilation in the overlying shed, and water wa...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Prepare 1000 mg / L SDBS-inorganic salt solution, adjust its ionic strength to 5.0 mg / L, pH to 7.0, sterilize at 121 °C for 30 minutes, and after cooling, measure 5 L SDBS solution into the soil to be eluted In the beaker of 1000 g soil sample, the required amount of SDBS is 5 g.
[0028] Stir for 30 min, centrifuge the eluted soil, evenly select 5 g of the eluted soil sample, freeze-dry it, and determine the total OCPs elution efficiency to be 89.3% (eg Figure 4 shown), in which neither DDE nor DDT in OCPs met soil environmental quality standards (e.g. Figure 5 shown).
[0029] The SDBS content in the supernatant was determined, and the SDBS concentration in the soil was washed with water to a concentration range of 10-50 mg / kg.
[0030] The soil after the first wash was piled up on the open space with ventilation in the overlying shed, and water was sprayed as needed to keep the soil moisture content at 30%, and the soil was turned every 2 weeks. At the end of each...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Prepare 800 mg / L Tween 80-inorganic salt solution, adjust its ionic strength to 5.0 mg / L, pH to 7.0, sterilize at 121°C for 30 minutes, and after cooling, measure 5 L of Tween 80 solution and put it into a container to be washed In the de-soiled beaker, place it under a six-joint stirrer to stir; among them, the amount of Tween 80 required for 1000 g of soil sample is 4 g.
[0033] Stir for 30 min, centrifuge the eluted soil, evenly select 5 g of the eluted soil sample, and freeze-dry it to determine the total OCPs elution efficiency of 88.2% (eg Figure 4 shown), in which neither DDE nor DDT in OCPs meet the requirements of environmental quality standards (such as Figure 5 shown).
[0034] The content of Tween 80 in the supernatant was determined, and the concentration of Tween 80 in the soil was washed with water to a concentration range of 10-50 mg / kg.
[0035] The soil after the first wash was piled up on the open space with ventilation in the overlying shed, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com